Motivation: Biosensors, synthetic systems designed to detect and respond to a target analyte, are a common application of synthetic biology. However, the production and screening of multiple biosensor system variants is hindered by the inefficiency and specificity of the gene assembly techniques used. The production of circuit variants is important in biosensor production, as sensitivity to target molecules must be tuned. Aim: To develop a multicellular biosensor development platform which utilises cell-mixing, as opposed to genetic re-engineering, to construct biosensor variants.
Background Information
Human Practices Quotes:
Biosensor Development. When developing biosensors, it would be useful to test multiple variants of a circuit. This is especially important in the fine-tuning of biosensor behaviour as this requires the screening of many variants to find appropriate activation thresholds for a system. Apart from the initial detection unit, many constructs used in synthetic biology based biosensors are reusable between different biosensor systems, such as fluorescent protein coding sequences or devices which amplify signals. However, these parts rarely get reused. For example, the Cambridge iGEM team (2009) developed a library of sensitivity tuners which were able to convert polymerase per second inputs to a desired polymerase per second output, allowing a biosensor developer control over the sensitivity of their systems to various target analyte concentrations. This project was impressive enough to win the competition. However, despite the parts' clear usefulness, there is no documentation that the parts have ever been successfully reused within the iGEM competition. We suggest that this is due to the difficulties in assembling biosensors systems – the screening of a library of sensitivity tuners would require the ability to easily generate multiple sensor circuits. Although only one part would be changing in each circuit variant, current genetic engineering techniques mean that parts are tightly coupled together, preventing the simple swapping of parts.
Therefore, we propose a modular, multicellular system for biosensor development, using a cell-to-cell communication system to eradicate the requirement for further genetic engineering of reusable biosensor devices (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Multicellular Sensynova system.
Cell-to-Cell communication
Bacteria have native quorum sensing systems which enable cell-to-cell communication through the production and detection of hormone-like auto-inducers. These molecules allow the synchronisation of behaviour in large populations of bacterial cells (Waters & Bassler, 2005). One such system involves the autoinducer AHL (Acylated Homoserine Lactone). AHLs compose of a lactone ring with an acyl side chain containing between 4 and 18 carbons (Churchill & Chen, 2011). Various AHL synthases exist, which produce AHL with different modifications and side change lengths. AHL receptors are sensitive to AHLs of specific length. For example, it has been found that the Rhl system, producing and detecting AHL of acyl carbon length 4 and the Las system, producing and detecting AHL of acyl carbon length 12, exhibit little crosstalk – the receptor component of the system is sensitive only to carbon chains of the correct length (Brenner et al., 2007). The orthogonal nature of the AHL family of autoinducers has enabled their use in a variety of synthetic systems. They are often used as biological “wires”, linking either inter- or intracellular processes. These “wires” have been previously used in a number of synthetic biology systems, e.g. Gupta et al. (2013) and Tasmir et al. (2011).
In this project, it is proposed that modularity, and therefore the ability to use parts “off-the-shelf” without further genetic engineering, could be improved by splitting components of biosensors into different cells which communicate to coordinate responses. The orthogonal quorum sensing systems Rhl and Las will be used as biological “wires”, linking different biosensor components together. This separation of components will enable the decoupling of non-specific components from specific detection systems. Using this approach, production of biosensor variants will not require subsequent engineering steps: cells containing desired components will simply be mixed together (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Modular and multicellular Sensynova framework design.
The splitting of biosensor components into separate cells may have additional advantages besides ease of variant production. Goni-Moreno et al. (2011) have previously suggested that the use of synthetic quorum sensing circuits enables each cell to be considered an independent logic gate, which may rectify the “fuzzy logic” seen in some biosensors, where stochastic cellular processes may produce false positive results. Quorum sensing has also been previously used to synchronise gene expressions, leading to reduced variability within a population (Danino et al., 2010).
Preliminary Experiment
In order to support our theory that genetic assembly is the rate limiting step in biosensor development, we attempted to assemble a simple GFP producing system using three engineering techniques: BioBrick, Gibson and Golden Gate. Further information about this experiment can be found on our interlab page . Gibson was the only successful technique we trailed, however, Gibson assembly is not an ideal method for circuit variant production due the the specificity of the overlapping regions: For example, to assemble ten genetic parts into all possible orders would require the use of 90 different overlapping sequences (Ellis et al., 2011). Therefore, the ability to generate circuit variants without the need for further genetic engineering would be useful.
Design Stage
To modularise biosensor components, it was necessary to first confirm which devices types are commonly found in biosensors. An in depth systematic review was conducted to determine these components. Team seeker, a tool for keyword searches of iGEM team titles and abstracts for the years 2008 to 2016, was used to identify biosensor based projects (Aalto-Helsinki iGEM team, 2014). The search terms used to identify potentially relevant projects were “sense” and “biosensor”. 121 projects were identified by these search terms. In projects including multiple sensors, the most well characterised sensors were used for this review. Sensor designs, rather than constructed biosensors, were used for analysis, as time constraints in iGEM often prevents project completion.
Ten projects were unable to be reviewed because their wiki was broken. Of the remaining 111 projects, 18 projects were deemed not eligible for further analysis. This was either due to a lack of information regarding biosensor mechanism provided by the team or their project was irrelevant. 3 projects were excluded as the sensing component of their project was unchanged from a previous project, to prevent the overrepresentation of biosensors in our database. Therefore, a total of 93 biosensors were used for analysis in our systematic review (Figure 3 and table 1). The systematic review revealed that all biosensors could be split into four components:
1)Detector: The part responsible for detection of the target molecules. For example, riboswitches and transcription factors.
2)Processing: Adds downstream processing to a signal, which enables response turning. For example, logic gates, signal amplification and sensitivity tuning.
3)Reporter or output: Produces a response to the target. For example, fluorescent proteins and beta-galactosidase. Additionally, some biosensors may produce outputs which interact with the target molecule once it has been sensed, such as the production of degradation enzymes in bioremediation projects. We have termed these outputs as “effectors”.
4)Adaptors: If the molecule is hard to detect, adaptor components can be placed before the detector unit, to convert the target molecules to something able to be sensed by the detector component. For example, for target that degrades into an easily detectable molecule, a biochemical conversion adaptor could be placed before the detector component which enzymatically degrades the target molecule into the molecule detected by the detector module.

Figure 3: Frequency of projects based on biosensors development in iGEM.
Table 1: Percentages of biosensors components used in iGEM.

We propose that splitting these modular biosensor components into different cells, as shown below, and co-culturing the cells together, will greatly reduce the complexity of biosensor circuit development.
Implementation
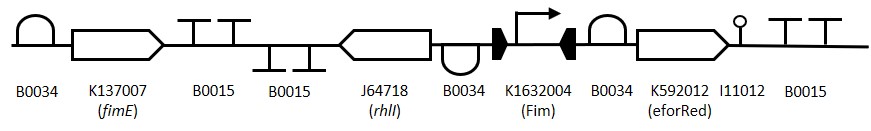
To prove that our concept of splitting biosensors across multiple cells would work, we designed an IPTG sensor. The design of this system can be found in Figure 4. In this system, LacI is constitutively expressed in the detector cell and represses the production of LasI. When IPTG is added, it binds LacI, preventing repression. Therefore, in the presence of IPTG, LasI will produce C12, our first connector molecule. To determine that our system would work, it was first tested in silico. Details on the model of this system can be found on our Modelling page.

Figure 4: Sensynova framework design used for sensing IPTG.
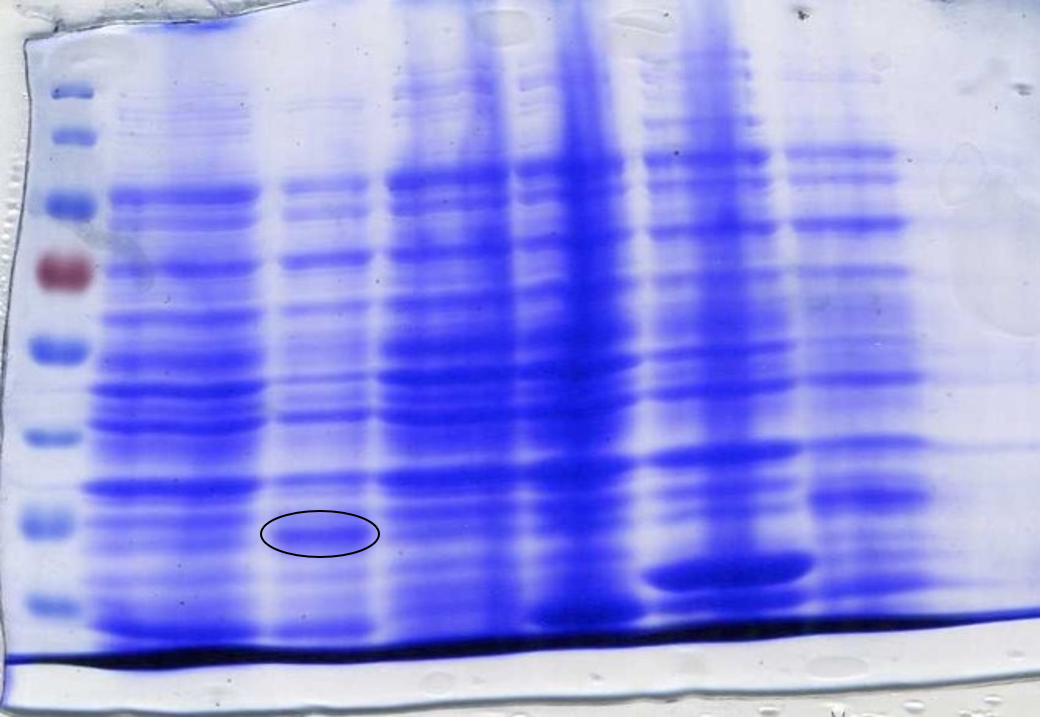
Parts were synthesised by IDT and integration into the pSB1C3 plasmid confirmed by colony PCR and subsequent sequencing. Red boxes show parts later used for biobrick production (Figure 5).

Figure 5: Colony PCR confirming the correct integration of the biosensor fragments into the vector.
Characterisation
The Framework characterisation has been performed using a BMG-Labtech fluostar optima plate reader in order to monitor the absorbance (OD600 nm) and GFP fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 510 nm).
The 3 cultures (IPTG detector, processor and sfGFP reporter) were grown separately in LB+ chloramphenicol on a shaker at 37C. After the overnight incubation the cultures were diluted to OD600 0.1 in order to achieve the syncronised growth to reach the late exponential phase. At OD 600 between 0.5 and 0.7 the cultures were mixed in ratio1:1:1 and IPTG 1mM was added. To test the functionality of the processor and the output, tests with the specific quorum sensing molecules were performed as followed:
Reporter test. The culture carrying the reporter device BBa_K2205015 was also tested individually after induction with the connector C12-RHL 2 ug/ul as shown in the graph (figure6).


Figure 6: The reporter part BBa_K2205015 test shows a significant fluorescence increase after induction with the connecting molecule 2 C12-RHL.
Processor test. The connector 1 (C4-HSL) was added to the co-culture consisting of processor BBa_K2205012 + reporter BBa_K2205015 in ratio 1:1. The plot shows the successful communication via quorum sensing in the Sensynova device. It is clear that the presence of 1mM C4-HSL is detected by the processor cells which produce the connector 2 (C12-RHL) for the reporter cells to detect. This induction in the reporter cells leads to the expression of sfGFP (Figure 7).

 Figure 7: The processor BBa_K2205012 and reporter BBa_K2205015 co-culture test shows increasing fluorescence/time after specific induction with the connecting molecule C12-RHL.
Figure 7: The processor BBa_K2205012 and reporter BBa_K2205015 co-culture test shows increasing fluorescence/time after specific induction with the connecting molecule C12-RHL.
Framework test. The co-culture of the 3 cell types was inoculated at ratio 1:1:1 (detectors:processors:reporters), growth and fluorescence were monitored after induction with IPTG 1mM. The plot shows no significant increasing fluorescence in the induced samples (Figure 8).


Figure 8: Framework (BBa_K2205009 , BBa_K2205012 , BBa_K2205015 ) test with a co-culture in ratio 1:1:1 in response of IPTG induction.
Results from the multicellular modelling predicted that the traditionally used 1:1:1 ratio is not the optimal combination for the Sensynova device to work. It is in fact suggested to adopt a higher concentration of the reporter culture compare with the detector and processor. Thus, the framework test was repeated incorporating our in silico simulation data and combining the 3 cell types in ratio 1:1:13 (detectors:processors:reporters). The experiment results, shown in the picture below, confirm the modelling data. There is a consistent discrepancy between IPTG induced and non-induced samples in the 1:1:13 co-cultures, in comparison with the 1:1:1 co-cultures which don't show any difference in presence or absence of IPTG (figure9).


Figure 9: Framework (BBa_K2205009 , BBa_K2205012 , BBa_K2205015 ) test with a co-culture in ratio 1:1:13 in response of IPTG induction.
The experimental data validate the model prediction showing that the system worked most optimally when the reporter cells were in excess of both the detector and processor cells. One of the reasons that this configuration was the best may be because of signal amplification at each of the quorum sensing communication stages. The quorum sensing mechanism used here is the acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) system in gram negative bacteria. This system works by one cell producing a quorum sensing molecule which can diffuse out through its membrane. Once the extracellular space reaches a certain threshold concentration of AHL molecule, the AHL will begin to diffuse into other cells in the community. If the cell the AHL molecule enters has the appropriate transcription factor present (e.g. LasR for the C12 AHL), then transcription of a gene under the control of the pLas promoter can occur. Therefore, if background expression of the AHL is high enough to reach above the threshold level, then expression of the next quorum sensing molecule in another cell (in this case C4 AHL) will occur. By reducing the amount of detector and processor cells present in the system, the background expression levels of C12 and C4 will be lower, and hence expression of sfGFP by the reporter cell will be lower.
Qualitative test with chromoproteins expression. In order to check the performance of the Sensynova device in terms of modularity, cultures of IPTG detector, processor unit and 3 different reporter modules carrying 2 chromoproteins (Chromoproteins link)(BBa_K2205016, BBa_K2205018)and sfGFP(BBa_K2205015) were inoculated and grown overnight in LB+chloramphenicol(12,5ng/ul). The day after the cultures were diluted at OD600: 0,1 and mixed together to obtain co-cultures with ratio 1:1:1 and 1:1:13. Some samples were supplemented with 1mM IPTG to induce the expression of quorum sensing molecules and eventually achieve the chromoproteins visualisation (Figures 10, 11, 12).
The 3 experiment sets clearly show that the framework is optimised when a higher concentration of cells expressing the reporter device is present (Figures 10, 11, 12, samples labelled 1:1:13). This can be considered as a further validation of our fine-tuning approach using the simbiotics model and the previous plate reader experiments.
Although a background signal is visible in the systems expressing the pink (BBa_K2205018)and the sfGPF(BBa_K2205015) reporters, the blue reporter (BBa_K2205016) due to its lowest background level, constitutes the most suitable reporter module for the Sensynova platform customised as IPTG biosensor. This highlights a crucial advantage of our multicellular, modular framework, which enables each component to be optimised avoiding any extra cloning steps. As each biosensor may be different and require specific designs and optimisation, easily choosing and changing modules and predicting in silico the bacterial community behavior is essential for the development of new biosensors.
Conclusions and Future Work
In conclusion, through a comprehensive systematic review a design pattern of four components was identified for synthetic biology biosensors. The components are detection and output devices, with optional processing and adaptor units. Based on this design pattern, a multicellular biosensor development platform was designed in which biosensor components were split between cells and linked by intercellular connectors. ADD CONCLUSION OF LAB WORK
Modularisation of biosensor components is ensured by the reusability of parts due to these compatible connectors. The production and detection of signalling molecules has been standardised across cells: Detector cells will produce C12 AHL, processing cells will detect C12 AHL and produce C4 AHL, and output cells will detect C4 AHL. Therefore, as long as constructs include the correct connectors, they are compatible will all other devices, without any further engineering of the system. This creates a “plug-and-play” approach to developing biosensors and allows the rapid construction of many biosensor circuit, which can be fine-tuned using only cell-mixing.
The splitting of biosensor components between different cells enables the top-down design of biosensing systems. In the top-down approach, systems are designed at a whole system level without consideration of the smaller subsystems required to generate a behaviour, as opposed to a bottom-up approach, where design begins with the smallest parts required to make a system and behaviour is built-up using the knowledge of these smaller parts. Using our platform with sub-systems of a known function already pieced together within cell, it is possible to simply add a cell to generate desired behaviour instead of having to consider the underlying biological parts. Top-down design will enable a more interdisciplinary approach to biosensor development, as knowledge of underlying biological behaviour is no longer required, and will generate biosensors better suited to their intended functions, as the design process will begin with consideration of end-user specifications, as opposed to discrete biological parts.
The next step
Another advantage to the bypassing of gene assembly enabled by our platform is the increased ability to automate system construction. Microfludic systems are those which control the movement of small volumes of liquids (10–9 to 10–18 litres) using a variety of methods, which may be used to perform biological experiments. These devices have a number of advantages over traditional, manual, lab methods. They only use a small amount of liquid, which means less reagents are consumed and the time taken to perform experiments is reduced. These small amounts of liquids are easier to manipulate than larger volumes, meaning there is greater control over reactions resulting in a high degree of sensitivity (Whitesides, 2006). However, many devices do not have the ability to control temperature, which is important for many methods of gene assembly. Cell mixing, as opposed to gene fragment assembly, is more suited to automation on these platforms, as there is no requirement for precise temperature control. Also, the increased control over small volumes of reagents allows the screening of precise cell ratios. Additionally, programs are in development for the automation of protocols on microfluidic, which will allow the rapid combination of a number of variant biosensor components. To utilise this advantage, we conducted a number of experiments using liquid handling robots (LINK TO ROBOTICS PAGE) and developed software for the simulation of microfludics experiments
References
Aalto-Helsinki iGEM team (2014) Team Seeker [online] Available at: http://igem-qsf.github.io/iGEM-Team-Seeker/dist/ [Accessed 11/07/17]
Brenner, K., Karing, D., Weiss, R. & Arnold, F. (2007) Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(44): 17300 - 17304
Cambridge iGEM team (2009) Sensitivity Tuners [online] Available at: https://2009.igem.org/Team:Cambridge/Project/Amplification [Accessed 28/08/2017]
Churchill, M. & Chen, L. (2011) Structural Basis of Acyl-homoserine Lactone-Dependent Signaling Chemical Reviews 111 (1): 68 - 85
Danino, T., Mondragon-Palomino, O., Tsimring, L. & Hasty, J. (2010) A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks Nature 463: 326 - 330
Ellis, T., Adie, T. & Baldwin, G. (2011) DNA assembly for synthetic biology: from parts to pathways and beyond Integrative Biology 3: 109 – 118
Goni-Moreno, A., Redondo, M., Arroyo, F. & Castellanos, J. (2011) Biocircuit design through engineering bacterial logic gates Natural Computing 10: 119 – 127
Gupta, S., Bram, E. & Weiss, R. (2013) Genetically programmable pathogen sense and destroy ACS Synthetic Biology 2 (12): 715 - 723
Tasmir, A., Tabor, J. & Voigt, C. (2011) Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’ Nature 469 (7329): 212 - 215
Waters, C. & Bassler, B. (2005) Quorum Sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in Bacteria Annual Review of Cell and Development Biology 21: 319 - 346
Yee Gyung Kwak, George A. Jacoby and David C. Hoopera. (2013) Induction of Plasmid-Carried qnrS1 in Escherichia coli by Naturally Occurring Quinolones and Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules





















































 The
The 











































