| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
<div class="fig" align="center"> | <div class="fig" align="center"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img width=" | + | <img width="650px" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bc/Peptide_Production_table.png"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<strong>Table: Antimicrobial activity (MIC in μM) of GF-17, GE-18 and their variants (Wang et al., 2011)</figcaption> | <strong>Table: Antimicrobial activity (MIC in μM) of GF-17, GE-18 and their variants (Wang et al., 2011)</figcaption> | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img width=" | + | <img width="650px" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/d5/Peptide_Production_3c.png"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<strong>Figure 3c: anti-Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm assay. Two different Staphylococcus aureus strain: USA200 | <strong>Figure 3c: anti-Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm assay. Two different Staphylococcus aureus strain: USA200 | ||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
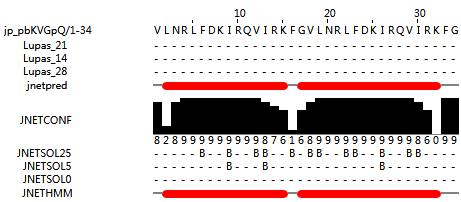
(predicted by http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/index.html ) | (predicted by http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/index.html ) | ||
</figcaption> | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="para"> | ||
| + | <h1>Grammistin-Pp1</h1> | ||
| + | <p style="font-size:20px">Grammistin-Pp1 is an AMP found in skin secretions from the clown grouper fish and is made up of thirteen amino | ||
| + | acid residues. This AMP is used primarily to fend off predators. Although initially thought to have little | ||
| + | antimicrobial properties, studies proved that grammistin-Pp1 target cell membranes by interacting with phospholipids. | ||
| + | Grammistin-Pp1 has been shown to be lethal against many gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria including | ||
| + | S. aureus. A primary reason for our selection of Grammistin-Pp1 was the high concentration needed to inhibit | ||
| + | the growth of E. coli. (Yokota et al., 2001)</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="fig" align="center"> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <img width="650px" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/d8/Peptide_Production_5.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption><strong>Figure 5: Grammistin-Pp1 2D structure (PubChem)</strong></figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 30 October 2017
Peptide Production
Anti-Microbial Peptide
Anti-microbial peptide (AMP) is a part of the innate immune system of most multi-cellular organisms to counter microbial infections (Margitta and Torsten, 1999). The cationic and amphipathic α-helix structure is the most wildly conformation in those peptides but some hydrophobic α-helical peptides which possess antimicrobial activity. This year we choose three different cationic antimicrobial peptides which encompass α-helical conformation in our project.
Figure 1 shows the molecular mechanism of cationic AMPs α-helical structure. Most of cationic AMPs associate with lipid group of bacteria membrane. The α-helical structure disrupt the packing of lipid molecules such that the membrane becomes leaky (Rocca et al., 1999).

LL-37
LL-37 is the only cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide found in humans (Dürr, Sudheendra and Ramamoorthy, 2006). Mature LL-37 has 37 amino acid residues starting with two leucines (NH2-LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES-COOH). The peptide is cleaved from a larger protein, hCAP-18 by extracellular proteolysis of proteinase 3 from the C-terminal end of hCAP18 (Patricia, 2010; Ramos, Domingues, and Gama, 2011). The peptide composed of two mainly parts: from residue Leu2 to Leu31 is α-helical structure (Fig 2b) and 6 residues form loop structure (Fig 2a).
Ramos, Domingues, and Gama (2011) also reported that LL-37 has additional roles such as regulating the inflammatory response to wound or infection sites, binding and neutralizing LPS, and wound closure apart from anti-microbial property (Figure 2c).



GF-17
GF-17 is a high efficiency anti-microbial peptide which modified from LL-37 residue Phe-17 to Val-32 (Fig 3a).


Table shows the Minimal Inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Anti-microbial peptides GF-17, GF-18 and their variants. GF-17 was capable of eliminating both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, such as S. aureus USA300 and E. coli K-12 in vitro (Wang et al., 2011). Additionally, to compare with LL-37, GF-17 has highly efficiency on anti-Staphylococcus aureus biofilm and killing efficiency (Fig 3c, table) ( Mishra et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2011 ).


GF-17 Reverse
GF-17 reverse sequence is reverse from GF-17, the structure of GF-17 reverse sequence dimer is semi-α helix.
Grammistin-Pp1
Grammistin-Pp1 is an AMP found in skin secretions from the clown grouper fish and is made up of thirteen amino acid residues. This AMP is used primarily to fend off predators. Although initially thought to have little antimicrobial properties, studies proved that grammistin-Pp1 target cell membranes by interacting with phospholipids. Grammistin-Pp1 has been shown to be lethal against many gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria including S. aureus. A primary reason for our selection of Grammistin-Pp1 was the high concentration needed to inhibit the growth of E. coli. (Yokota et al., 2001)


