(→Modelisation) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Team:Aix-Marseille/KXconcept|Read more…]] | [[Team:Aix-Marseille/KXconcept|Read more…]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Modelling== | ||
==InterLab== | ==InterLab== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
[[Team:Aix-Marseille/InterLab|Read more…]] | [[Team:Aix-Marseille/InterLab|Read more…]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 17:26, 31 August 2017
KILL XYL
Abstract
Our project, KILL XYL will be a cure against the disease caused by the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. This disease currently causes the loss of thousands of hectares of European crops and no extensive cure exists against it.
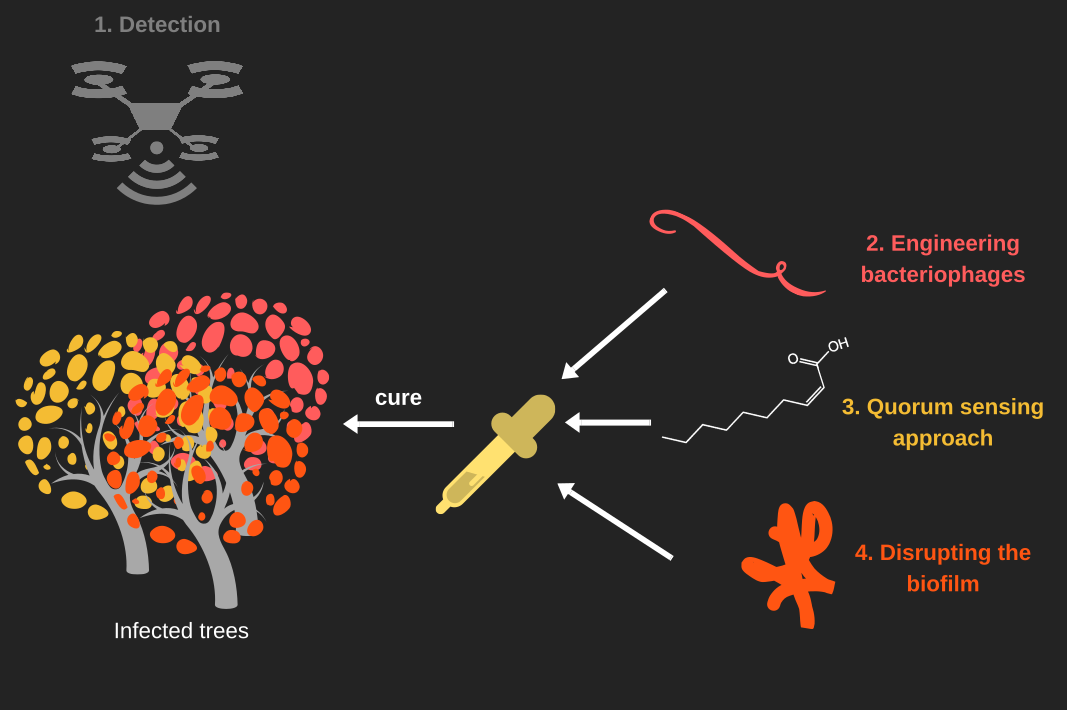
KILL XYL has a two step approach. Since the symptoms of disease are only observed when xylem vessels are highly colonized by the bacterium and photosynthesis is blocked, we first detect the symptoms of the disease using a drone equipped with a camera.
We will then treat the disease with a combination of three strategies. To directly attack the bacterium, we developed specific phage-like particles that inject toxins. To disrupt the biofilm, which is the principal cause of plants death, a particular fatty acid that quenches the quorum sensing activity of the bacterium and an enzyme that degrades the biofilm will be used.
Motivation
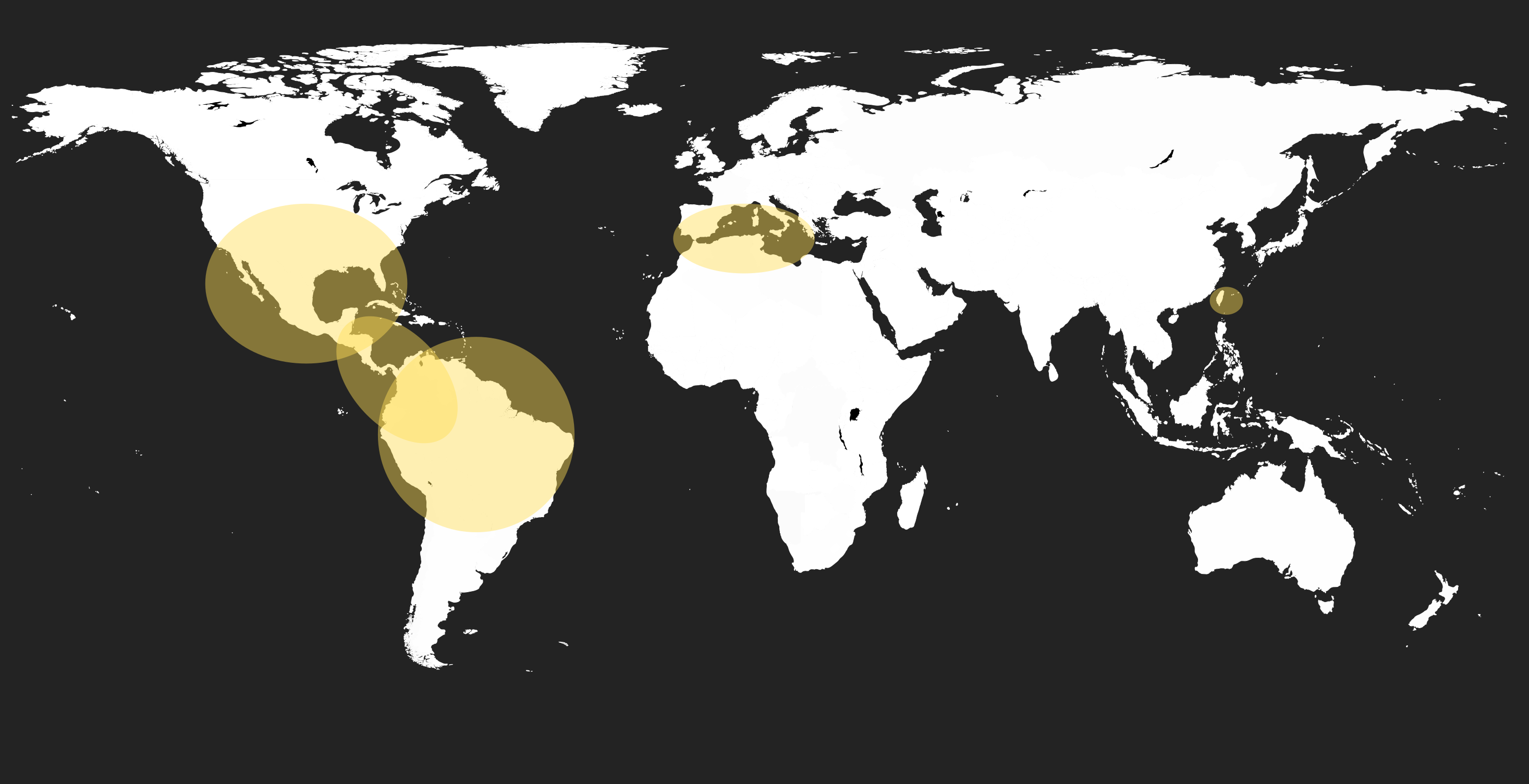
Xylella fastidiosa is a bacterium that infects the xylem tissues of a wide range of plants. This bacterium has been widespread in the Americas for many years and occurs also in Asia. The bacterium is associated with several diseases of crops of economic significance, and has a wide range of host plants comprising 312 species.
X. fastidiosa is transmitted from plant to plant by xylem sucking insects. The bacterium can persist in symptomless uncultivated plants, from which insects may acquire the bacterium and pass it to crops. Symptoms of disease are only observed when xylem vessels are highly colonized by the bacterium. The xylem transports water and soluble mineral, nutrients from the roots throughout the plant, and used to replace water lost during transpiration and photosynthesis. Xylem vessels are interconnected by bordered pits, which allow the passage of xylem sap, but block the passage of larger objects (such as bacterium) by a membrane.
The control of the movement of potential hosts and insect vectors and the eradication of infected material is considered the most effective method of limiting the spread of the disease in the European Union. But there is no method yet to cure the trees.
KILL XYL concept
Modelling
InterLab
We used plasmids containing different promoter from the 2017 distribution kit and transfect into E.coli. Before measuring fluorescence expression, we used LUDOX and fluorescein to calibrate the TECAN. We prepared a dilution series of fluorescein in 4 replicates and measure the fluorescence in a 96 well plate in a plate reader. By measuring these in all standard modes, we generated a standard curve of fluorescence for fluorescein concentration. We used this to correct cell based readings to an equivalent fluorescein concentration and convert this into a concentration of GFP.