| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
Mishra et al., 2016)</strong> | Mishra et al., 2016)</strong> | ||
</figcaption> | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="para"> | ||
| + | <h1>GF-17 Reverse</h1> | ||
| + | <p style="font-size:20px">GF-17 reverse sequence is reverse from GF-17, the structure of GF-17 reverse sequence dimer is semi-α helix.</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="fig" align="center"> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <img width="700px" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ed/Peptide_Production_4.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption>Figure 4: protein structure of GF-17 reverse dimer sequence, it seems that the dimer is semi-α helix. We assume the GF-17 reverse sequence is alpha helix structure. | ||
| + | (predicted by http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/index.html ) | ||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 09:24, 30 October 2017
Peptide Production
Anti-Microbial Peptide
Anti-microbial peptide (AMP) is a part of the innate immune system of most multi-cellular organisms to counter microbial infections (Margitta and Torsten, 1999). The cationic and amphipathic α-helix structure is the most wildly conformation in those peptides but some hydrophobic α-helical peptides which possess antimicrobial activity. This year we choose three different cationic antimicrobial peptides which encompass α-helical conformation in our project.
Figure 1 shows the molecular mechanism of cationic AMPs α-helical structure. Most of cationic AMPs associate with lipid group of bacteria membrane. The α-helical structure disrupt the packing of lipid molecules such that the membrane becomes leaky (Rocca et al., 1999).

LL-37
LL-37 is the only cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide found in humans (Dürr, Sudheendra and Ramamoorthy, 2006). Mature LL-37 has 37 amino acid residues starting with two leucines (NH2-LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES-COOH). The peptide is cleaved from a larger protein, hCAP-18 by extracellular proteolysis of proteinase 3 from the C-terminal end of hCAP18 (Patricia, 2010; Ramos, Domingues, and Gama, 2011). The peptide composed of two mainly parts: from residue Leu2 to Leu31 is α-helical structure (Fig 2b) and 6 residues form loop structure (Fig 2a).
Ramos, Domingues, and Gama (2011) also reported that LL-37 has additional roles such as regulating the inflammatory response to wound or infection sites, binding and neutralizing LPS, and wound closure apart from anti-microbial property (Figure 2c).



GF-17
GF-17 is a high efficiency anti-microbial peptide which modified from LL-37 residue Phe-17 to Val-32 (Fig 3a).


Table shows the Minimal Inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Anti-microbial peptides GF-17, GF-18 and their variants. GF-17 was capable of eliminating both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, such as S. aureus USA300 and E. coli K-12 in vitro (Wang et al., 2011). Additionally, to compare with LL-37, GF-17 has highly efficiency on anti-Staphylococcus aureus biofilm and killing efficiency (Fig 3c, table) ( Mishra et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2011 ).


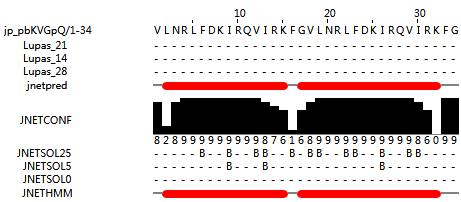
GF-17 Reverse
GF-17 reverse sequence is reverse from GF-17, the structure of GF-17 reverse sequence dimer is semi-α helix.