| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="box3 left biosafety" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Safety"> | <div class="box3 left biosafety" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Safety"> | ||
| − | <h1> | + | <h1>Safety</h1> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="box3 left about" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Team"> | <div class="box3 left about" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Team"> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">At the beginning of our project, we visited local and foreign wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and learned that there are currently very few | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">At the beginning of our project, we visited local and foreign wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and learned that there are currently very few wastewater treatment methods that specifically target nanoparticle (NP) waste. We designed our constructs, prototype and modeling based directly from information given by these treatment plants. Our biofilm parts collection was designed to be able to control biofilm production in sedimentation tanks. Our proteorhodopsin construct is designed to be used in aeration tanks where other microbes are already breaking down organic substances. We also use the pre-existing biosafety aspect of the wastewater plants. Additionally, we reached out to several NP manufacturers, researchers, disposal services and wastewater experts who provided us with information on the advantages and potential consequences of NP usage, as well as where to target NP waste removal. The feedback we received guided the direction of our project and confirmed the importance of our project to our community. |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | We hosted a Bioethics Panel, where we invited students and teachers to discuss the moral, social and environmental concerns of our project. To encourage participants to consider the problems from multiple perspectives, we created a role-playing game and assigned different roles to participants. We then asked for their opinions on NP usage and disposal from the perspective of their assigned role. (Whole team activity) | + | We hosted a Bioethics Panel, where we invited students and teachers to discuss the moral, social and environmental concerns of our project. To encourage participants to consider the problems from multiple perspectives, we created a role-playing game and assigned different roles to the participants. We then asked for their opinions on NP usage and disposal from the perspective of their assigned role. (Whole team activity) |
<br><br> For instance, one of our questions was: | <br><br> For instance, one of our questions was: | ||
<br><br> “Dihua WWTP has no nanoparticle removal plan. Should this be the job of the wastewater plant? Or the nanoparticle manufacturer?” | <br><br> “Dihua WWTP has no nanoparticle removal plan. Should this be the job of the wastewater plant? Or the nanoparticle manufacturer?” | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<div class="para col-lg-12"> | <div class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | This activity gave us great insight on how the public perceives NP usage and regulation, and provided us a chance to inform people about both the benefits and the dangers of using NPs. We first had the idea that we should create a filter that the consumers can purchase to clean NPs out of their household waste. However, after the bioethics panel, the results showed that most people think WWTPs functioning under the government should be responsible for cleaning NP waste, because all wastewater would eventually accumulate in the WWTPs. Aside from analyzing the responses from the bioethics panel, we also tested products from NP manufactures (discussed below) that proved targeting wastewater would be the most ideal approach to clean NP waste. This is why we decided to focus our project on trapping NPs in WWTPs. | |
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| Line 197: | Line 198: | ||
<div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1e/T--TAS_Taipei--SEM_comparison_Tap_vs._Showerhead.png" alt="test" id="group2"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1e/T--TAS_Taipei--SEM_comparison_Tap_vs._Showerhead.png" alt="test" id="group2"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Tap water under SEM.</b>The image on the left shows a tap water sample under the SEM, in which we observed some bacteria (round objects that are approximately 1 μm in diameter). The SEM image on the | + | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Tap water under SEM.</b>The image on the left shows a tap water sample under the SEM, in which we observed some bacteria (round objects that are approximately 1 μm in diameter). The SEM image on the right shows that water filtered by the showerhead contains less bacteria, as the showerhead uses embedded nanosilver antibacterial filters. (SEM images: Christine C. and Florence L.) |
<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 206: | Line 207: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-8"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> | ||
| − | + | In order to learn firsthand about the effect of NPs in WWTPs, we visited the Dihua WWTP (迪化污水處理廠). Here, we were given a tour around the plant, and were able to ask questions to the managers and people who work there. They confirmed that the current facilities are unable to remove NPs from wastewater mainly due to their small size. In addition to this information, they kindly provided us with samples of sludge, effluent water, and the polymers they add during the wastewater treatment process. | |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
<div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | ||
| Line 215: | Line 216: | ||
<div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e1/T--TAS_Taipei--DihuaDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e1/T--TAS_Taipei--DihuaDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either | + | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria to either the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will then kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
| Line 225: | Line 226: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | Throughout the year we visited | + | Throughout the year, we visited Dihua WWTP several times to discuss how our project could be implemented in their current system. We planned to add our proteorhodopsin (PR) bacteria in the aeration tanks, where other microbes already exist to break down organic solids. Our biofilm, attached to biocarriers, will then be placed in the sedimentation tanks (shown above). We gathered information about flow rates, tank dimensions, and water retention time in each tank to provide realistic conditions for our experimental, prototype, and modeling work. For example, during our conversation with WWTP engineers, we learned that wastewater is retained in aeration tanks and sedimentation tanks for up to 4.8 and 3.8 hours, respectively. This means PR and biofilm will only have up to ~5 hours and ~4 hours respectively, to interact and trap NPs in wastewater. Taking realistic timing into consideration, we added PR to citrate-capped silver NP (CC-AgNP) solution and mixed the solution for only up to ~5 hours (figure 2-6). We also added a flocculant powder (supplied by Dihua WWTP) to aggregate suspended solids, which mimics the next step in the treatment process. |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 231: | Line 232: | ||
<div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bd/T--TAS_Taipei--2-6_new-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bd/T--TAS_Taipei--2-6_new-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Figure 2-6 Proteorhodopsin traps CC-AgNPs. </b> A) Absorbance decreased markedly when PR bacteria was added to CC-AgNPs; the absorbance did not change significantly when GFP-Gen (negative control) bacteria was added. B) Over the 5 hour period, we observed | + | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Figure 2-6 Proteorhodopsin traps CC-AgNPs. </b> A) Absorbance decreased markedly when PR bacteria was added to CC-AgNPs; the absorbance did not change significantly when GFP-Gen (negative control) bacteria was added. B) Over the 5 hour period, we observed a larger orange region (aggregated CC-AgNPs) in the PR group. <span class="subCred"> Experiment & Figure: Justin Y.</span></h4> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | Furthermore, we created | + | Furthermore, we created calculators based on our mathematical models, which took variables--such as wastewater flow rate, bacteria concentration, and biofilm surface area--into consideration, to calculate the amount of PR bacteria or biofilm necessary to trap NPs. Lastly, we tested our PR bacteria and biofilm in realistic conditions by constructing a simulated WWTP (for example, see our biofilm trapping gold NPs in a simulated tank below!). |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 242: | Line 243: | ||
<div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/da/T--TAS_Taipei--prototype_gold-min.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/da/T--TAS_Taipei--prototype_gold-min.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="subtitle"> | + | |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="image_container col-lg-8"> | ||
| + | <video controls="" class="col-lg-12"> | ||
| + | <source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/7/75/T--TAS_Taipei--Biofilm_Video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. | ||
| + | </video> | ||
| + | <h4 class="subtitle"><b> Video 5-2 Testing biofilm in simulated sedimentation tanks.</b> Based on Boswell’s circular tank design, we built our own “sedimentation tanks” using clear plastic tubes, and attached biocarriers to a central spinning rotor. Three tanks were set up: biofilm + distilled water (left), biofilm + AuNP (middle), and AuNP solution alone (right). After about 30 hours of mixing, the color of the AuNP solution started to change from purple to clear in the cylinder containing biofilm. In contrast, the cylinder containing only AuNP solution did not change at all. Timelapse video shows the tanks 36 hours after the start. <span class="subCred">Experiment & Video: Yvonne W.</span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row" id="Boswell"> | <div class="row" id="Boswell"> | ||
| Line 253: | Line 257: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | + | Not all WWTPs are as large as the one in Taipei. One of our advisors (Jude Clapper) went to visit the Boswell WWTP in rural southwestern Pennsylvania. We learned that the same processes that occur in the Taipei Dihua WWTP also occur in the Boswell WWTP, but with different water flow rates and waste quantities. Since both facilities use a similar water purification process, we were inspired to create our current prototype design--a rotating polymeric bioreactor coated in biofilm--which is applicable to both WWTPs. This prototype will be placed in the secondary sedimentation tank, where the majority of organic solids have been removed and only smaller particles exist. The plant manager, Robert J. Blough, also confirmed that since our project is bacteria-based, it will be killed by UV light and chlorine in the disinfection tank, similar to the Dihua WWTP, before the water turns into effluent and goes to the rivers and oceans. | |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 259: | Line 263: | ||
<div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2f/T--TAS_Taipei--BoswellDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2f/T--TAS_Taipei--BoswellDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either | + | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either to the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will then kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | </div><br> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <video controls="" class="col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
| + | <source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/3a/T--TAS_Taipei--BoswellVid.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. | ||
| + | </video> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="EPA"> | <div class="row" id="EPA"> | ||
| Line 267: | Line 276: | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | ||
| − | Thomas J. Brown, the Water Program Specialist of the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) occasionally helps with the Boswell | + | Thomas J. Brown, the Water Program Specialist of the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) occasionally helps with the Boswell Wastewater Treatment Plant. He also has experience working with the EPA in Taiwan on wastewater treatments. We interviewed Mr. Brown about our methods to clean NPs in WWTPs and how to achieve our goal of implementation. With his expertise in the field of wastewater treatment, he provided us some suggestions as to how we could turn our project into reality. |
</h4> | </h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:21, 1 November 2017
X

Project

Experiments
Modeling

Prototype

Human Practices

Safety

About Us

Attributions
Project
Experiment
Modeling
Prototype
Human Practice
Safety
About Us
Attributions

hi
HP GOLD INTEGRATED
At the beginning of our project, we visited local and foreign wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and learned that there are currently very few wastewater treatment methods that specifically target nanoparticle (NP) waste. We designed our constructs, prototype and modeling based directly from information given by these treatment plants. Our biofilm parts collection was designed to be able to control biofilm production in sedimentation tanks. Our proteorhodopsin construct is designed to be used in aeration tanks where other microbes are already breaking down organic substances. We also use the pre-existing biosafety aspect of the wastewater plants. Additionally, we reached out to several NP manufacturers, researchers, disposal services and wastewater experts who provided us with information on the advantages and potential consequences of NP usage, as well as where to target NP waste removal. The feedback we received guided the direction of our project and confirmed the importance of our project to our community.
Bioethics Panel
We hosted a Bioethics Panel, where we invited students and teachers to discuss the moral, social and environmental concerns of our project. To encourage participants to consider the problems from multiple perspectives, we created a role-playing game and assigned different roles to the participants. We then asked for their opinions on NP usage and disposal from the perspective of their assigned role. (Whole team activity)
For instance, one of our questions was:
“Dihua WWTP has no nanoparticle removal plan. Should this be the job of the wastewater plant? Or the nanoparticle manufacturer?”
The following roles were assigned:
- Wastewater plant manager
- Nanoparticle manufacturer
- Citizen
- Fisherman
- Fish
Most of the wastewater plant managers thought that NP manufacturers should be responsible for removing NP, because they have more information (e.g., solubility, toxicity, etc.) about their own products. However, many other participants were skeptical that manufacturers could be trusted to remove their own contamination and agreed that WWTPs should ultimately be responsible for cleaning water contaminated with NPs.
This activity gave us great insight on how the public perceives NP usage and regulation, and provided us a chance to inform people about both the benefits and the dangers of using NPs. We first had the idea that we should create a filter that the consumers can purchase to clean NPs out of their household waste. However, after the bioethics panel, the results showed that most people think WWTPs functioning under the government should be responsible for cleaning NP waste, because all wastewater would eventually accumulate in the WWTPs. Aside from analyzing the responses from the bioethics panel, we also tested products from NP manufactures (discussed below) that proved targeting wastewater would be the most ideal approach to clean NP waste. This is why we decided to focus our project on trapping NPs in WWTPs.

Apex Nanotek
To learn more about the applications of NPs, we visited a nanotech company that uses silver NPs to make various antimicrobial products. The researcher and manager of Apex Nanotek, Chery Yang, introduced us to their main product, which is antimicrobial nanosilver activated carbon. Pure activated carbon, commonly used to treat sewage and industrial exhaust, is prone to bacterial growth. To overcome this problem, they integrate crystallized nanosilver into the activated carbon for their antimicrobial effects. One of their products is a showerhead, with nanosilver activated carbon filters to kill bacteria when water flows through the showerhead.
We tested the product by comparing SEM images between tap water and filtered water from the showerhead. The showerhead decreased the number of bacteria and larger particles from tap water! However, we also observed the release of NPs from the filter, which will flow into wastewater. (Interviewed by Christine C., Kelly C., Yvonne W., Chansie Y., and Justin Y.)

Chery Yang (third person from the left), the main researcher of Apex Nanotek Corporation

Product of Apex Nanotek: Silver Spring Shower Head.

Tap water under SEM.The image on the left shows a tap water sample under the SEM, in which we observed some bacteria (round objects that are approximately 1 μm in diameter). The SEM image on the right shows that water filtered by the showerhead contains less bacteria, as the showerhead uses embedded nanosilver antibacterial filters. (SEM images: Christine C. and Florence L.)
WWTP -- Dihua Wastewater Treatment Plant
In order to learn firsthand about the effect of NPs in WWTPs, we visited the Dihua WWTP (迪化污水處理廠). Here, we were given a tour around the plant, and were able to ask questions to the managers and people who work there. They confirmed that the current facilities are unable to remove NPs from wastewater mainly due to their small size. In addition to this information, they kindly provided us with samples of sludge, effluent water, and the polymers they add during the wastewater treatment process.

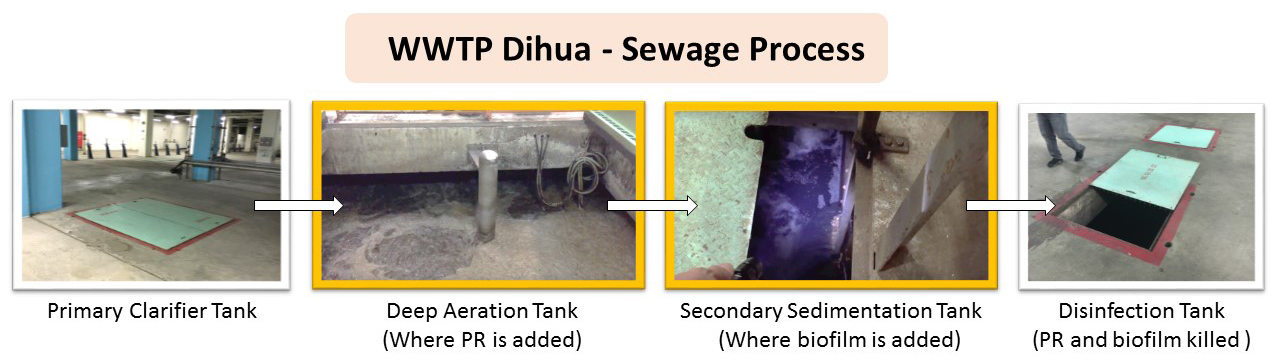
We plan to add our bacteria to either the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will then kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.Figure: Christine C.
Throughout the year, we visited Dihua WWTP several times to discuss how our project could be implemented in their current system. We planned to add our proteorhodopsin (PR) bacteria in the aeration tanks, where other microbes already exist to break down organic solids. Our biofilm, attached to biocarriers, will then be placed in the sedimentation tanks (shown above). We gathered information about flow rates, tank dimensions, and water retention time in each tank to provide realistic conditions for our experimental, prototype, and modeling work. For example, during our conversation with WWTP engineers, we learned that wastewater is retained in aeration tanks and sedimentation tanks for up to 4.8 and 3.8 hours, respectively. This means PR and biofilm will only have up to ~5 hours and ~4 hours respectively, to interact and trap NPs in wastewater. Taking realistic timing into consideration, we added PR to citrate-capped silver NP (CC-AgNP) solution and mixed the solution for only up to ~5 hours (figure 2-6). We also added a flocculant powder (supplied by Dihua WWTP) to aggregate suspended solids, which mimics the next step in the treatment process.

Figure 2-6 Proteorhodopsin traps CC-AgNPs. A) Absorbance decreased markedly when PR bacteria was added to CC-AgNPs; the absorbance did not change significantly when GFP-Gen (negative control) bacteria was added. B) Over the 5 hour period, we observed a larger orange region (aggregated CC-AgNPs) in the PR group. Experiment & Figure: Justin Y.
Furthermore, we created calculators based on our mathematical models, which took variables--such as wastewater flow rate, bacteria concentration, and biofilm surface area--into consideration, to calculate the amount of PR bacteria or biofilm necessary to trap NPs. Lastly, we tested our PR bacteria and biofilm in realistic conditions by constructing a simulated WWTP (for example, see our biofilm trapping gold NPs in a simulated tank below!).

Video 5-2 Testing biofilm in simulated sedimentation tanks. Based on Boswell’s circular tank design, we built our own “sedimentation tanks” using clear plastic tubes, and attached biocarriers to a central spinning rotor. Three tanks were set up: biofilm + distilled water (left), biofilm + AuNP (middle), and AuNP solution alone (right). After about 30 hours of mixing, the color of the AuNP solution started to change from purple to clear in the cylinder containing biofilm. In contrast, the cylinder containing only AuNP solution did not change at all. Timelapse video shows the tanks 36 hours after the start. Experiment & Video: Yvonne W.
Boswell Wastewater Treatment Plant
Not all WWTPs are as large as the one in Taipei. One of our advisors (Jude Clapper) went to visit the Boswell WWTP in rural southwestern Pennsylvania. We learned that the same processes that occur in the Taipei Dihua WWTP also occur in the Boswell WWTP, but with different water flow rates and waste quantities. Since both facilities use a similar water purification process, we were inspired to create our current prototype design--a rotating polymeric bioreactor coated in biofilm--which is applicable to both WWTPs. This prototype will be placed in the secondary sedimentation tank, where the majority of organic solids have been removed and only smaller particles exist. The plant manager, Robert J. Blough, also confirmed that since our project is bacteria-based, it will be killed by UV light and chlorine in the disinfection tank, similar to the Dihua WWTP, before the water turns into effluent and goes to the rivers and oceans.


