| (56 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
.result_picture td p { | .result_picture td p { | ||
text-align: center; | text-align: center; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .keyres_hide { | ||
| + | display: none; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | #key_res:hover { | ||
| + | cursor:pointer; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 118: | Line 126: | ||
<div class="container-fluid text-center" style="max-width: 80%; font-size: 1em"> | <div class="container-fluid text-center" style="max-width: 80%; font-size: 1em"> | ||
| − | <h1 style=" | + | <h1 class="display 4" style="font-family: Rubik; margin: 0">Our Experimental Results</h1> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <div class="jumbotron rounded" style="background-color: #e8e8e8; border: 1px solid #222222; padding: 10px !important;"> | ||
| + | <h2 id="key_res" class="display-5 keyres_show" style="color: #222222">Key Achievements - click to show</h2> | ||
| + | <hr class="keyres_hide" style="color: #222222"> | ||
| + | <ul class="keyres_hide" style="color: #222222"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <li class="keyres_hide" style="font-family: Rubik">Demonstrated that biosensors can be successfully split into three modules</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li class="keyres_hide" style="font-family: Rubik">Produced biosensor variants by co-culturing different module variants together</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li class="keyres_hide" style="font-family: Rubik">Used 3D spatial modelling to begin optimisation of a multicellular biosensor</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li class="keyres_hide" style="font-family: Rubik">Characterised a 'standby switch' based on an improved part <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1632007">(BBa_K1632007)</a></li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li class="keyres_hide" style="font-family: Rubik">Demonstrated that a Design of Experiments approach can be used to optimise cell-free systems</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<p> | <p> | ||
Below is a diagram of our Sensynova Framework. Clicking on each part of the framework (e.g. detector modules) links to the relevant results.<br /> | Below is a diagram of our Sensynova Framework. Clicking on each part of the framework (e.g. detector modules) links to the relevant results.<br /> | ||
| Line 385: | Line 415: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Glyphosate is a herbicide that works by blocking the activity of the enzyme enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), which converts carbohydrates derived from glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway to plant metabolites and aromatic amino acids. | + | <p>Glyphosate is a herbicide that works by blocking the activity of the enzyme enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), which converts carbohydrates derived from glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway to plant metabolites and aromatic amino acids. It was identified as a biosensor target through our <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">human practices</a> when we attended the N8 conference. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | We attempted to design a system capable of glyphosate detection. With little information regarding mechanisms of glyphosate interactions within the cell, we could not identify a simple system in which a responsive transcription factor was able to affect the production of a reporter gene. This is a common issue in many biosensor projects. | + | We attempted to design a system capable of glyphosate detection. With little information regarding mechanisms of glyphosate interactions within the cell, we could not identify a simple system in which a responsive transcription factor was able to affect the production of a reporter gene. This is a common issue in many biosensor projects. |
| + | To show the adaptor in action we chose to develop a part that would measure the level of glyphosate through the production of formaldehyde. There are known sensors for formaldehyde such as <a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:TMU-Tokyo">Tokyo’s 2012 biosensor</a>. Our design relies on the natural biochemical systems, the c-p lyase pathways, in <i>E. coli</i> to convert glyphosate to sarcosine. We then designed a part, SOX, based on the production of the enzyme sarcosine oxidase, encoded by <i>soxA</i> to convert sarcosine to formaldehyde ready for detection by a formaldehyde producing input module. | ||
| + | |||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
The mining of transcriptome data has previously been used to find responsive DNA elements to a molecule of interest (Groningen 2012). Therefore, we analysed differences in transcriptome data between glyphosate sensitive and insensitive plants. A number of genes were found which were differently expressed. However, it was determined that it is more likely that this differential expression was not due to glyphosate directly, but rather the aromatic amino acid starvation caused by EPSPS inhibition by glyphosate, making these systems unsuitable for direct glyphosate detection. Various other systems we designed were also far from ideal, with high levels of complexity and reliance on native plant machinery. | The mining of transcriptome data has previously been used to find responsive DNA elements to a molecule of interest (Groningen 2012). Therefore, we analysed differences in transcriptome data between glyphosate sensitive and insensitive plants. A number of genes were found which were differently expressed. However, it was determined that it is more likely that this differential expression was not due to glyphosate directly, but rather the aromatic amino acid starvation caused by EPSPS inhibition by glyphosate, making these systems unsuitable for direct glyphosate detection. Various other systems we designed were also far from ideal, with high levels of complexity and reliance on native plant machinery. | ||
| Line 421: | Line 453: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <p>This | + | <p>This construct was designed to have 30 bp overhangs with the pSB1C3 plasmid, so that it could be Gibson assembled into a pSB1C3 plasmid digested with XbaI and SpeI. Extra bases were added between the overhangs and the construct so that once the part was assembled into the plasmid, the XbaI and SpeI sites could be regenerated and the biobrick prefix and suffix restored. A T7 promoter was added to enable expression to be under the control of IPTG. This construct was then submitted to IDT for synthesis as a gBlock. |
| − | <br /> | + | <br /><br /> |
To ensure the codon usage of our SOX protein was not differing significantly from the average codon usage of <i> E. coli</i>, rare codons were removed from the sequence using the <a href="https://www.idtdna.com/CodonOpt">IDT codon optimisation tool</a>to produce high protein expression.</p> | To ensure the codon usage of our SOX protein was not differing significantly from the average codon usage of <i> E. coli</i>, rare codons were removed from the sequence using the <a href="https://www.idtdna.com/CodonOpt">IDT codon optimisation tool</a>to produce high protein expression.</p> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 467: | Line 499: | ||
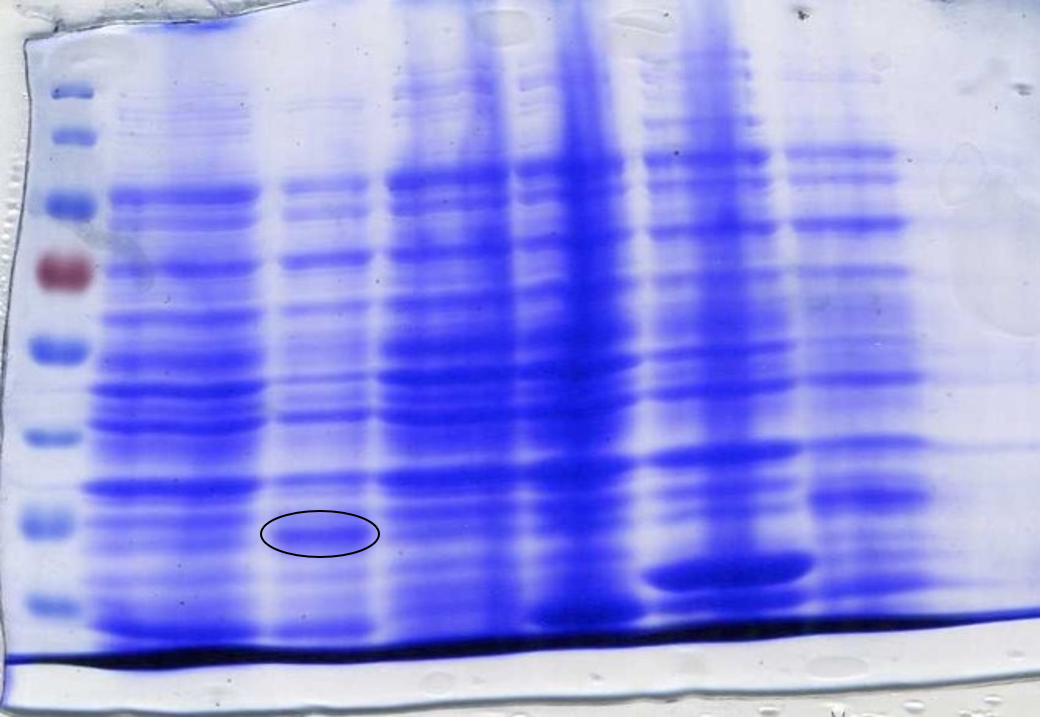
<p>To determine whether the now correct SOX had been successfully expressed another SDS-Page gel was performed. After inducing, harvesting and washing the cells 1 ml was taken from each culture to be loaded into the gel. The cells were lysed using lysozyme and boiled for 3 minutes at 100°C loading 10 µl into the gel (Figure 7). | <p>To determine whether the now correct SOX had been successfully expressed another SDS-Page gel was performed. After inducing, harvesting and washing the cells 1 ml was taken from each culture to be loaded into the gel. The cells were lysed using lysozyme and boiled for 3 minutes at 100°C loading 10 µl into the gel (Figure 7). | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | <div class="SOX"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/89/T--Newcastle--Correct_sox_protein_gel_2.png" width="30%" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt="" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block"/> | + | <div class="SOX"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/89/T--Newcastle--Correct_sox_protein_gel_2.png" width="30%" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt="" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block"/> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 7:</strong> Sarcosine Oxidase expression was induced by adding 40 µl of 100 mM IPTG. Lane 1: 6 µl ladder, Lane 2: 10 µl sfGFP, Lane 3: BL21-DE3, Lane 4: 10µl SOX 1, Lane 5: 10 µl SOX 2, Lane 6: 10 µl SOX 3, Lane 7: 10 µl SOX 4, Lane 8: 10 µl SOX 5, Lane 9: 10 µl SOX 6, Lane 10: 6 µl ladder. Circled bands show sarcosine oxidase at ~42 kDa, the expected weight.</p></center> | + | <p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 7:</strong> Sarcosine Oxidase expression was induced by adding 40 µl of 100 mM IPTG. Lane 1: 6 µl ladder, Lane 2: 10 µl sfGFP, Lane 3: BL21-DE3, Lane 4: 10µl SOX 1, Lane 5: 10 µl SOX 2, Lane 6: 10 µl SOX 3, Lane 7: 10 µl SOX 4, Lane 8: 10 µl SOX 5, Lane 9: 10 µl SOX 6, Lane 10: 6 µl ladder. Circled bands show sarcosine oxidase at ~42 kDa, the expected molecular weight.</p></center> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | <p>To test for the presence of formaldehyde, and to demonstrate this part works, larger cultures were grown following the aforementioned protocols, and the cells harvested, washed and lysed by sonication. 0 µl, | + | <p>To test for the presence of formaldehyde, and to demonstrate this part works, larger cultures were grown following the aforementioned protocols, and the cells harvested, washed and lysed by sonication. 0 µl, 50 µl and 200 µl of Sarcosine at 0.9 g/50 ml concentration was added to the cell lysate and incubated at 37°C. Every 2.5 hours the lysate was tested for the presence of formaldehyde with commercial <a href="http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/37072?lang=en®ion=GB">formaldehyde testing strips</a> (Figure 8).</p> |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="SOX"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4b/T--Newcastle--SOX_testing.JPG" width="30%" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt="" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block"/> | <div class="SOX"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4b/T--Newcastle--SOX_testing.JPG" width="30%" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt="" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block"/> | ||
<br /><br /> | <br /><br /> | ||
| Line 483: | Line 511: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | <p> | + | <p>Formaldehyde was detected, showing that SOX works as expected, however there is slight leaky expression as formaldehyde is produced when no IPTG is added.</p> |
| − | </p> | + | </p> |
| − | </br></br> | + | </br> |
| + | <p> We also decided to add Glyphosate to determine the efficiency of the native C-P Lyase pathway. Everything was repeated the same but instead we added 0 µl, 20 µl, 200 µl and 2 ml of glyphosate at 10mg/L. After 8 hours of testing and left overnight, none of the samples had produced formaldehyde according to the testing strips. The testing strips detect a minimum formaldehyde concentration of 10 mg/L, so it was possible that formaldehyde had been produced but that there was too little of it to detect with the strips.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </br> | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p><i>E. coli</i> cells naturally have the C-P lyase pathway which degrades glyphosate into sarcosine. The fact that | + | <p><i>E. coli</i> cells naturally have the C-P lyase pathway which degrades glyphosate into sarcosine. The fact that formaldehyde was produced when sarcosine was added, but not when glyphosate was added, indicates that we have not overexpressed the C-P lyase pathway enough to produce enough sarcosine for SOX to convert into formaldehyde to be detected. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
<p>Due to time constraints, we were unable to produce an <i>in vivo</i> formaldehyde detector variant of the Sensynova framework. Future characterisation of this part would include using the platform customised as a formaldehyde biosensor in order to sense compound produce and therefore creating a biosensor of glyphosate. | <p>Due to time constraints, we were unable to produce an <i>in vivo</i> formaldehyde detector variant of the Sensynova framework. Future characterisation of this part would include using the platform customised as a formaldehyde biosensor in order to sense compound produce and therefore creating a biosensor of glyphosate. | ||
| Line 536: | Line 567: | ||
<center><b>Figure 2:</b> Graph Indicating the Most Frequent Spacer Between -35 and -10 Regions Found in <i>E. coli</i> Promoters. This image was taken from Harley and Reynolds (1987).</center> | <center><b>Figure 2:</b> Graph Indicating the Most Frequent Spacer Between -35 and -10 Regions Found in <i>E. coli</i> Promoters. This image was taken from Harley and Reynolds (1987).</center> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | </br> | + | </br> |
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| Line 582: | Line 613: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Though we have generated a sizable library of promoters of varying strengths and functions, we lacked the time to complete its characterization by the screening against targeted molecules. | + | <p>Though we have generated a sizable library of promoters of varying strengths and functions, we lacked the time to complete its characterization by the screening against targeted molecules. |
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Due to time constraints, we also lacked the time to characterise these parts into the Sensynova platform within the lab. | Due to time constraints, we also lacked the time to characterise these parts into the Sensynova platform within the lab. | ||
| Line 589: | Line 620: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Becker, N., Peters, J., Lionberger, T. and Maher, L. (2012). Mechanism of promoter repression by Lac repressor–DNA loops. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(1), pp.156-166. <br/> | + | <p>Becker, N., Peters, J., Lionberger, T. and Maher, L. (2012). Mechanism of promoter repression by Lac repressor–DNA loops. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(1), pp.156-166. <br/><br/> |
DeBoer, H. (1985). Microbial hybrid promoters. US4551433 A. | DeBoer, H. (1985). Microbial hybrid promoters. US4551433 A. | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Harley, C. and Reynolds, R. (1987). Analysis of <i>E.Coli</i> Promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 15(5), pp.2343-2361. | Harley, C. and Reynolds, R. (1987). Analysis of <i>E.Coli</i> Promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 15(5), pp.2343-2361. | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| − | Hawley, D. and McClure, W. (1983). Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 11(8), pp.2237-2255. | + | Hawley, D. and McClure, W. (1983). Compilation and analysis of <i>Escherichia coli</i> promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 11(8), pp.2237-2255. |
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Lisser, S. and Margalit, H. (1993). Compilation of <i>E.coli</i> mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 21(7), pp.1507-1516. | Lisser, S. and Margalit, H. (1993). Compilation of <i>E.coli</i> mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 21(7), pp.1507-1516. | ||
| Line 614: | Line 645: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> | + | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> that hamper the success in biosensor development. One of these limits regards the lack of modularity and reusability of the various components. Our platform design, based on the expression of three main modules (Detector, Processor and Reporter) by three <i> E. coli</i> strains in co-culture, allows the switch of possible variances for each module and the production of multiple customised biosensors. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by replacing the IPTG detector part of the Sensynova design with different detecting parts. In particular, an Arsenic sensing part will be used.</p> | This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by replacing the IPTG detector part of the Sensynova design with different detecting parts. In particular, an Arsenic sensing part will be used.</p> | ||
| Line 667: | Line 698: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Characterisation </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Characterisation </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p><b>Qualitative assay.</b> Due to time constraints only a preliminary qualitative assay was carried out. Co-cultures of Arsenic detector, processor unit and 3 different reporter modules carrying | + | <p><b>Qualitative assay.</b> Due to time constraints only a preliminary qualitative assay was carried out. Co-cultures of Arsenic detector, processor unit and 3 different reporter modules carrying two chromoproteins (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205016">BBa_K2205016</a>, <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205018">BBa_K2205018</a>) and sfGFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205015">BBa_K2205015</a>) were inoculated and grown overnight in LB+chloramphenicol (12.5ng/ul). The day after the cultures were diluted at OD600 0.1 and mixed together to obtain co-cultures with ratio 1:1:13 (detector:processor:reporter). The samples were supplemented with different concentration of Arsenic (0ppb, 10ppb, 50ppb, 100ppb) to induce the expression of quorum sensing molecules and eventually achieve the chromoproteins visualisation (Figures 6, 7, 8). </p> |
<table class="image_table" style="background:none"> | <table class="image_table" style="background:none"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 713: | Line 744: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Brenner K, Karing D, Weiss R, Arnold F (2007) Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(44): 17300 - 17304 </br> de Mora K, Joshi N, Balint BL, Ward FB, Elfick A, French CE (2011) A pH-based biosensor for detection of arsenic in drinking water. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(4):1031-9 (Epub 2011 Mar 27).</p> | + | <p>Brenner K, Karing D, Weiss R, Arnold F (2007) Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(44): 17300 - 17304 <br/><br/> de Mora K, Joshi N, Balint BL, Ward FB, Elfick A, French CE (2011) A pH-based biosensor for detection of arsenic in drinking water. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(4):1031-9 (Epub 2011 Mar 27).</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 726: | Line 757: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/ | + | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> that hamper the success in biosensor development. One of these limits regards the lack of modularity and reusability of the various components. Our platform design, based on the expression of three main modules (Detector, Processor and Output) by three <i>E.coli </i> strains in co-culture, allows the switch of possible variances for each module and the production of multiple customised biosensors. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by implementing the biosensor created by the 2017 Evry Paris-Saclay iGEM team into the Sensynova platform as part of our <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/Collaborations#eps_collab">collaboration</a> requirement.</p> | This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by implementing the biosensor created by the 2017 Evry Paris-Saclay iGEM team into the Sensynova platform as part of our <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/Collaborations#eps_collab">collaboration</a> requirement.</p> | ||
| Line 788: | Line 819: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Characterisation</h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Characterisation</h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p> A preliminary qualitative assay was carried out as an initial test for this construct. Co-cultures of Psicose detector, processor unit and sfGFP reporter (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2205015">BBa_K2205015</a>) were inoculated and grown overnight in LB+chloramphenicol (12.5 ng/ul). | + | <p> A preliminary qualitative assay was carried out as an initial test for this construct. Co-cultures of Psicose detector, processor unit and sfGFP reporter (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2205015">BBa_K2205015</a>) were inoculated and grown overnight in LB+chloramphenicol (12.5 ng/ul). |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
The day after the cultures were diluted at OD600 0.1 and mixed together to obtain co-cultures with ratio 1:1:13 (detector:processor:reporter). The samples were supplemented with 33.22 mM Psicose to induce the expression of quorum sensing molecules and eventually achieve the reporter visualisation (Figures 8). </p> | The day after the cultures were diluted at OD600 0.1 and mixed together to obtain co-cultures with ratio 1:1:13 (detector:processor:reporter). The samples were supplemented with 33.22 mM Psicose to induce the expression of quorum sensing molecules and eventually achieve the reporter visualisation (Figures 8). </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </br> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/f2/T--Newcastle--BB_framework_framework_green.jpg" width="360px"/> </br> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/f2/T--Newcastle--BB_framework_framework_green.jpg" width="360px"/> </br> | ||
| Line 806: | Line 839: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>iGEM Community. (2017). Team Evry Paris-Saclay 2017. [online] Available | + | <p>iGEM Community. (2017). Team Evry Paris-Saclay 2017. [online] Available <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Evry_Paris-Saclay">here</a>.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| − | + | ||
<h1 style="font-family: Rubik"> Formaldehyde <button class="btn btn-primary collapsed" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#formaldehyde" aria-expanded="false" aria-controls="formaldehyde" style="margin-left: 1%"></button></h1> | <h1 style="font-family: Rubik"> Formaldehyde <button class="btn btn-primary collapsed" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#formaldehyde" aria-expanded="false" aria-controls="formaldehyde" style="margin-left: 1%"></button></h1> | ||
<div id="formaldehyde" class="collapse"> | <div id="formaldehyde" class="collapse"> | ||
| Line 816: | Line 849: | ||
<h2 style="font-size: 1em"> BioBricks used: <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205029">BBa_K2205029 (New)</a>, <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205030">BBa_K2205030 (New)</a>, <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K749021">BBa_K749021(TMU-Tokyo 2012 )</a> </h2> | <h2 style="font-size: 1em"> BioBricks used: <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205029">BBa_K2205029 (New)</a>, <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205030">BBa_K2205030 (New)</a>, <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K749021">BBa_K749021(TMU-Tokyo 2012 )</a> </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | + | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/ | + | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> that hamper the success in biosensor development. One of these limits regards the lack of modularity and reusability of the various components. Our platform design, based on the expression of three main modules (Detector, Processor and Output) by three <i>E.coli </i> strains in co-culture, allows the switch of possible variances for each module and the production of multiple customised biosensors. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by implementing the formaldehyde biosensor as a variant to the detector module of the Sensynova platform.</p> | This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by implementing the formaldehyde biosensor as a variant to the detector module of the Sensynova platform.</p> | ||
| Line 827: | Line 860: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Background Information </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Background Information </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The formaldehyde biosensor, part BBa_K749021, was selected was originally made and submitted to the iGEM registry by the TMU-Tokyo 2012 team. | + | <p>The formaldehyde biosensor, part BBa_K749021, was selected was originally made and submitted to the iGEM registry by the TMU-Tokyo 2012 team. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | This part was chosen as a variant to the detector module present in the Sensynova platform due to the fact that our adaptor module present in the framework, Sarcosine Oxidase, was made in order to convert glyphosate into formaldehyde, in order to overcome the limitation in the detection of glyphosate due to its little-known knowledge. | + | This part was chosen as a variant to the detector module present in the Sensynova platform due to the fact that our adaptor module present in the framework, Sarcosine Oxidase, was made in order to convert glyphosate into formaldehyde, in order to overcome the limitation in the detection of glyphosate due to its little-known knowledge. |
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1f/T--Newcastle--Lais--FO--Ruler.png" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded" style="margin: 2%"> | + | <center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1f/T--Newcastle--Lais--FO--Ruler.png" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded" style="margin: 2%"></center> |
<p><center> | <p><center> | ||
<b>Figure 1:</b> <!--- Insert image name between tags. ----> | <b>Figure 1:</b> <!--- Insert image name between tags. ----> | ||
| Line 848: | Line 881: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Design Stage </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>In order to implement the Formaldehyde biosensor variant to the Sensynova platform, a design was created by replacing the IPTG sensing system in the original detector module with the construct detailed above, creating part <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205030">BBa_K2205030 </a>. | + | <p>In order to implement the Formaldehyde biosensor variant to the Sensynova platform, a design was created by replacing the IPTG sensing system in the original detector module with the construct detailed above, creating part <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205030">BBa_K2205030 </a>. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
We chose to redesign the Formaldehyde biosensor detailed above to mirror the design used when producing the Psicose detector variant. The system detailed in the image below is made up of the constitutive promoter present within the platform triggering transcription of the FrmR repressing the PfrmR and subsequently the connector 1 of the Sensynova platform. We have also replaced the colour output present in the TMU-Tokyo design, we have added our part <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205008">BBa_K2205008</a>, which produces our first connector in order to trigger a response from following modules of the Sensynova platform in the presence of Formaldehyde.</p> | We chose to redesign the Formaldehyde biosensor detailed above to mirror the design used when producing the Psicose detector variant. The system detailed in the image below is made up of the constitutive promoter present within the platform triggering transcription of the FrmR repressing the PfrmR and subsequently the connector 1 of the Sensynova platform. We have also replaced the colour output present in the TMU-Tokyo design, we have added our part <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205008">BBa_K2205008</a>, which produces our first connector in order to trigger a response from following modules of the Sensynova platform in the presence of Formaldehyde.</p> | ||
| Line 878: | Line 911: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%">Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%">Conclusions and Future Work </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Due to time constraints, we lacked the time to synthesise, implement and characterise this part into the Sensynova platform within the lab. Future work on this part would include characterisation <i>in vivo</i> guided by the modelling of the framework when customised as a formaldehyde biosensor and testing against the Sarcosine Oxidase adaptor module currently present in the framework. | + | <p>Due to time constraints, we lacked the time to synthesise, implement and characterise this part into the Sensynova platform within the lab. Future work on this part would include characterisation <i>in vivo</i> guided by the modelling of the framework when customised as a formaldehyde biosensor and testing against the Sarcosine Oxidase adaptor module currently present in the framework. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| Line 889: | Line 922: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | ||
<div class="tab-pane fade" id="nav-processor" role="tabpanel" aria-labelledby="nav-processor-tab"> | <div class="tab-pane fade" id="nav-processor" role="tabpanel" aria-labelledby="nav-processor-tab"> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| Line 930: | Line 963: | ||
<img class="FIM" style="width:100%" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/d8/--T--Newcastle_amplify_G_Fim.png"/> | <img class="FIM" style="width:100%" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/d8/--T--Newcastle_amplify_G_Fim.png"/> | ||
<center><b>Figure 2:</b> <!--- Insert image name between tags. ----> | <center><b>Figure 2:</b> <!--- Insert image name between tags. ----> | ||
| − | High fidelity amplification of the 3 gBlock fragments for assembly of the Fim Switch. The gBlock-1 amplification is shown in lanes 1+2 (819 bp), gBlock-2 amplification is shown in lanes 3+4 (1148 bp) and the gBlock-3 amplification is shown in lanes 5+6 (939bp).</center></p> | + | High fidelity PCR amplification of the 3 gBlock fragments for assembly of the Fim Switch. The gBlock-1 amplification is shown in lanes 1+2 (819 bp), gBlock-2 amplification is shown in lanes 3+4 (1148 bp) and the gBlock-3 amplification is shown in lanes 5+6 (939bp).</center></p> |
<p> | <p> | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| Line 973: | Line 1,006: | ||
<h2 style="text-align: left; clear: both"> Conclusions</h2> | <h2 style="text-align: left; clear: both"> Conclusions</h2> | ||
| − | < | + | <br/> |
<p> | <p> | ||
The aim of the Fim switch part was to make a processor module which can be visually inspected for functionality. The Fim switch has been shown to expresses the eforRed chromoprotein under normal (uninduced) conditions which allows the user to both determine that the strain is alive and has maintained the Fim switch plasmid. Following induction, the Fim promoter flips direction and begins expressing RhlI which synthesises the C4-AHL quorum sensing molecule. This has been shown to successfully induce expression of sfGFP in the reporter strain (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205015">BBa_K2205015</a>).<br/><br/> | The aim of the Fim switch part was to make a processor module which can be visually inspected for functionality. The Fim switch has been shown to expresses the eforRed chromoprotein under normal (uninduced) conditions which allows the user to both determine that the strain is alive and has maintained the Fim switch plasmid. Following induction, the Fim promoter flips direction and begins expressing RhlI which synthesises the C4-AHL quorum sensing molecule. This has been shown to successfully induce expression of sfGFP in the reporter strain (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205015">BBa_K2205015</a>).<br/><br/> | ||
| Line 979: | Line 1,012: | ||
Despite several attempts we were unable to produce a Fim switch testing construct where <i>fimE</i> expression could be controlled using the <i>E. coli</i> arabinose inducible promoter. Though transformations did yield some colonies when trying to make this part, none were red in colour. This possibly indicates that the arabinose inducible promoter (even when grown on 0.5% w/v glucose) is still too active. The design for this construct has been submitted (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205006">BBa_K2205006</a>).<br/><br/> | Despite several attempts we were unable to produce a Fim switch testing construct where <i>fimE</i> expression could be controlled using the <i>E. coli</i> arabinose inducible promoter. Though transformations did yield some colonies when trying to make this part, none were red in colour. This possibly indicates that the arabinose inducible promoter (even when grown on 0.5% w/v glucose) is still too active. The design for this construct has been submitted (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2205006">BBa_K2205006</a>).<br/><br/> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | <h2 style="text-align: left; | + | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Future Work </h2> |
</br> | </br> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| Line 987: | Line 1,020: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | P. Klemm, Two regulatory fim genes, fimB and fimE, control the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. EMBO J 5, 1389-1393 (1986).<br/><br/> | + | P. Klemm, Two regulatory fim genes, fimB and fimE, control the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in <i>Escherichia coli</i>. EMBO J 5, 1389-1393 (1986).<br/><br/> |
| − | M. S. McClain, I. C. Blomfield, B. I. Eisenstein, Roles of fimB and fimE in site-specific DNA inversion associated with phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173, 5308-5314 (1991).<br/><br/> | + | M. S. McClain, I. C. Blomfield, B. I. Eisenstein, Roles of fimB and fimE in site-specific DNA inversion associated with phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in <i>Escherichia coli</i>. J Bacteriol 173, 5308-5314 (1991).<br/><br/> |
M. R. Parsek, E. P. Greenberg, Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97, 8789-8793 (2000).<br/><br/> | M. R. Parsek, E. P. Greenberg, Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97, 8789-8793 (2000).<br/><br/> | ||
| Line 1,007: | Line 1,040: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/ | + | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> that hamper the success in biosensor development. One of these limits regards the lack of modularity and reusability of the various components. Our platform design, based on the expression of three main modules (Detector, Processor and Reporter) by three <i>E.coli</i> strains in co-culture, allows the switch of possible variances for each module and the production of multiple customised biosensors. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by inserting two different sensitivity tuner constructs between the processing units of the Sensynova platform; <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K274371">BBa_K274371</a> and <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K274381">BBa_K274381</a> . | This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by inserting two different sensitivity tuner constructs between the processing units of the Sensynova platform; <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K274371">BBa_K274371</a> and <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K274381">BBa_K274381</a> . | ||
| Line 1,101: | Line 1,134: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p> iGEM Community. (2009). Team Cambridge 2009. [online] Available | + | <p> iGEM Community. (2009). Team Cambridge 2009. [online] Available <a href="https://2009.igem.org/Team:Cambridge">here</a> [Accessed 30 Oct. 2017]. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 1,227: | Line 1,260: | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | Li X., Zhang G., Ngo N., Zhao X., Kain S.R., Huang C.C., (1997), Deletions of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein define the minimal domain required for fluorescence, <i>J. Biol. Chem.</i>, 272:28545–9, doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.45.28545<br /> | + | Li X., Zhang G., Ngo N., Zhao X., Kain S.R., Huang C.C., (1997), Deletions of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein define the minimal domain required for fluorescence, <i>J. Biol. Chem.</i>, 272:28545–9, doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.45.28545 <br/><br/> |
Shin, J., and Noireaux, V., (2010), Efficient Cell-Free Expression with the Endogenous <i>E. coli</i> RNA Polymerase and Sigma Factor 70, <i>J. Biol. Eng.</i>, 4:8, doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-4-8<br /> | Shin, J., and Noireaux, V., (2010), Efficient Cell-Free Expression with the Endogenous <i>E. coli</i> RNA Polymerase and Sigma Factor 70, <i>J. Biol. Eng.</i>, 4:8, doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-4-8<br /> | ||
| Line 1,248: | Line 1,281: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Rationale and Aim </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/ | + | <p>The Sensynova multicellular biosensor platform has been developed to overcome the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Newcastle/HP/Gold_Integrated">limitations identified by our team</a> that hamper success in biosensor development. One of these limits regards the lack of modularity and reusability of the various components. Our platform design, based on the expression of three main modules (Detector, Processor and Reporter) by three <i>E.coli</i> strains in co-culture, allows the switch of possible variances for each module and the production of multiple customised biosensors. |
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by replacing the sfGFP output part of the Sensynova platform design with three different output chromoprotein variants; BBa_K1033929 (aeBlue), BBa_K1033925 (spisPink) and BBa_K1033915 (amajLime).</p> | This section of the project is based on testing the modularity of the system by replacing the sfGFP output part of the Sensynova platform design with three different output chromoprotein variants; BBa_K1033929 (aeBlue), BBa_K1033925 (spisPink) and BBa_K1033915 (amajLime).</p> | ||
| Line 1,554: | Line 1,587: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| − | |||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/49/Framework_blue.jpg" width="100%"/> </br> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/49/Framework_blue.jpg" width="100%"/> </br> | ||
| Line 1,610: | Line 1,642: | ||
Waters, C. & Bassler, B. (2005) Quorum Sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in Bacteria Annual Review of Cell and Development Biology 21: 319 - 346 | Waters, C. & Bassler, B. (2005) Quorum Sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in Bacteria Annual Review of Cell and Development Biology 21: 319 - 346 | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | Yee Gyung Kwak, George A. Jacoby and David C. Hoopera. (2013) Induction of Plasmid-Carried qnrS1 in Escherichia coli by Naturally Occurring Quinolones and Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules | + | Yee Gyung Kwak, George A. Jacoby and David C. Hoopera. (2013) Induction of Plasmid-Carried qnrS1 in <i>Escherichia coli</i> by Naturally Occurring Quinolones and Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecules |
</br> </p> | </br> </p> | ||
| Line 1,679: | Line 1,711: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Implementation </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> Implementation </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| − | <p>Cell free extract preparation procedures were based on methods reported in literature previously (Kwon & Jewett, 2015). Cell free extracts were prepared from Escherichia coli BL21 and Bacillus subtilis 168. Cells were streak plated out from glycerol stocks on LB agar (15 mg/mL agar, 10 mg/mL tryptone, 5 mg/mL yeast extract, 0.17 M sodium chloride) and incubated overnight at 37oC. A single colony was used to inoculate 10 mL LB broth (10 mg mL-1 tryptone, 5 mg mL-1 yeast extract, 0.17 M sodium chloride) before shake-incubation at 37oC for approximately 16 hours overnight. 2 mL of overnight liquid culture was used to inoculate 200 mL LB broth in a 2 L flask and shake-incubated at 37oC until late exponential phase was reached (OD600 nm of approximately 2.5 for <i>E. coli</i> BL21 cells). The culture was split in half and cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4,500 RPM and 4oC for 20 minutes in pre-weighed falcon tubes. The wet cell pellet weight was determined before storage at -20oC. Cells were defrosted on ice for approximately 1.5 hours and resuspended in approximately 10 mL of ice-cold CFPS wash buffer (60 mM potassium glutamate, 14 mM magnesium glutamate, 10 mM TRIS (pH 8.2 with acetic acid); autoclave sterilised; supplemented with 2 mM DTT immediately before use) per gram of wet cell pellet. Resuspended cells were centrifuged at 4,500 RPM and 4oC for 20 mins. The supernatant was discarded and cell pellets were resuspended and centrifuged in CFPS wash buffer twice more. The washed pellets were then resuspended in 1 mL CFPS wash buffer per gram of wet cell pellet and aliquoted to 1 mL in 2 mL tubes. Cells were lysed by sonication (20% amplitude, cycles of 40 seconds on – 59.9 seconds off, 432.5 Joules) and the lysates were clarified by centrifugation at 12,000 RPM for 10 mins, flash frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80oC. A CFPS supplement solution was prepared based on previously reported protocols (Yang, <i>et al</i>., 2012). Amino acid stock solutions were prepared according to Table 1. Briefly, amino acids were weighed in 2 mL tubes, dissolved in 5 M potassium hydroxide, and stored at -20oC. A 10x amino acid solution was prepared by mixing the stock solutions together in amounts according to Table 1, and the pH was adjusted to 7.9 with acetic acid. The solution was aliquoted to 1.5 mL and stored at -80oC. | + | <p>Cell free extract preparation procedures were based on methods reported in literature previously (Kwon & Jewett, 2015). Cell free extracts were prepared from <i>Escherichia coli</i> BL21 and Bacillus subtilis 168. Cells were streak plated out from glycerol stocks on LB agar (15 mg/mL agar, 10 mg/mL tryptone, 5 mg/mL yeast extract, 0.17 M sodium chloride) and incubated overnight at 37oC. A single colony was used to inoculate 10 mL LB broth (10 mg mL-1 tryptone, 5 mg mL-1 yeast extract, 0.17 M sodium chloride) before shake-incubation at 37oC for approximately 16 hours overnight. 2 mL of overnight liquid culture was used to inoculate 200 mL LB broth in a 2 L flask and shake-incubated at 37oC until late exponential phase was reached (OD600 nm of approximately 2.5 for <i>E. coli</i> BL21 cells). The culture was split in half and cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4,500 RPM and 4oC for 20 minutes in pre-weighed falcon tubes. The wet cell pellet weight was determined before storage at -20oC. Cells were defrosted on ice for approximately 1.5 hours and resuspended in approximately 10 mL of ice-cold CFPS wash buffer (60 mM potassium glutamate, 14 mM magnesium glutamate, 10 mM TRIS (pH 8.2 with acetic acid); autoclave sterilised; supplemented with 2 mM DTT immediately before use) per gram of wet cell pellet. Resuspended cells were centrifuged at 4,500 RPM and 4oC for 20 mins. The supernatant was discarded and cell pellets were resuspended and centrifuged in CFPS wash buffer twice more. The washed pellets were then resuspended in 1 mL CFPS wash buffer per gram of wet cell pellet and aliquoted to 1 mL in 2 mL tubes. Cells were lysed by sonication (20% amplitude, cycles of 40 seconds on – 59.9 seconds off, 432.5 Joules) and the lysates were clarified by centrifugation at 12,000 RPM for 10 mins, flash frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80oC. A CFPS supplement solution was prepared based on previously reported protocols (Yang, <i>et al</i>., 2012). Amino acid stock solutions were prepared according to Table 1. Briefly, amino acids were weighed in 2 mL tubes, dissolved in 5 M potassium hydroxide, and stored at -20oC. A 10x amino acid solution was prepared by mixing the stock solutions together in amounts according to Table 1, and the pH was adjusted to 7.9 with acetic acid. The solution was aliquoted to 1.5 mL and stored at -80oC. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 1,701: | Line 1,733: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1d/T--Newcastle--BB_pSB1C3-sfGFP_plasmid_map.png" width="400px" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%; alt=""/> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1d/T--Newcastle--BB_pSB1C3-sfGFP_plasmid_map.png" width="400px" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt=""/> |
<p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 2:</strong> Plasmid map for pSB1C3-sfGFP. Construct is standard biobrick part BBa_ K515105.</center></p> | <p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 2:</strong> Plasmid map for pSB1C3-sfGFP. Construct is standard biobrick part BBa_ K515105.</center></p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 1,756: | Line 1,788: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b0/T--Newcastle--BB_CFPS_figure4.png" width="600px" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%; alt=""/> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b0/T--Newcastle--BB_CFPS_figure4.png" width="600px" class="img-fluid border border-dark rounded mx-auto d-block" style="background-color:white; margin-right: 2%; margin-bottom: 2%;" alt=""/> |
<p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 5:</strong> Screening model constructed using JMP showing which factors were closest to significance. Predictions for interactions are unreliable due to forced orthogonality (*). Of the primary factors, magnesium glutamate is the closest to significant, followed by potassium glutamate, sodium oxalate, and ammonium acetate in that order.</center></p> | <p class="legend"><center><strong>Figure 5:</strong> Screening model constructed using JMP showing which factors were closest to significance. Predictions for interactions are unreliable due to forced orthogonality (*). Of the primary factors, magnesium glutamate is the closest to significant, followed by potassium glutamate, sodium oxalate, and ammonium acetate in that order.</center></p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 1,882: | Line 1,914: | ||
<p>This study has begun multifactorial analysis on the components of the supplemental solution for cell free protein synthesis systems. It has provided evidence that some supplements have a greater effect on a systems protein synthesis activity than others, and that the important factors may differ between cell extract batches. The ability to use a Design of Experiments approach towards the optimisation of CFPS systems has also been demonstrated. While this study has provided evidence towards these claims, further work should be performed to validate the findings. A DoE screening design for the supplements of CFPS systems should be used on the same cell extract batch repeatedly. This will help confirm that the screening models derived from the experimental design data are accurate. The screening design should also be performed on many different batches of at least moderately active cell extracts to confirm that important supplements do differ between batches. | <p>This study has begun multifactorial analysis on the components of the supplemental solution for cell free protein synthesis systems. It has provided evidence that some supplements have a greater effect on a systems protein synthesis activity than others, and that the important factors may differ between cell extract batches. The ability to use a Design of Experiments approach towards the optimisation of CFPS systems has also been demonstrated. While this study has provided evidence towards these claims, further work should be performed to validate the findings. A DoE screening design for the supplements of CFPS systems should be used on the same cell extract batch repeatedly. This will help confirm that the screening models derived from the experimental design data are accurate. The screening design should also be performed on many different batches of at least moderately active cell extracts to confirm that important supplements do differ between batches. | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | Following the above, a surface response design could be used for all commonly important supplements of the CFPS system to determine its effectiveness at optimising CFPS activity. The information could also be used to determine commonly unimportant supplements so they can be eliminated from the supplement solution, hence decreasing the cost per reaction.</p> | + | Following the above, a surface response design could be used for all commonly important supplements of the CFPS system to determine its effectiveness at optimising CFPS activity. The information could also be used to determine commonly unimportant supplements so they can be eliminated from the supplement solution, hence decreasing the cost per reaction. Furthermore, the full Sensynova system can be expressed in cell-free.</p> |
</br> | </br> | ||
<h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | <h2 style="font-family: Rubik; text-align: left; margin-top: 1%"> References </h2> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | Algranati, I. D. & Goldemberg, S. H., 1977. Polyamines and their role in protein synthesis. <i>Trends in Biochem. Sci.</i>, 2(12), pp. 272-274.<br /> | + | Algranati, I. D. & Goldemberg, S. H., 1977. Polyamines and their role in protein synthesis. <i>Trends in Biochem. Sci.</i>, 2(12), pp. 272-274. <br/><br/> |
| − | Anderson, M. J. & Whitcomb, P. J., 2010. Design of Experiments. In: Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. <i>s.l.:John Wiley & Sons, Inc</i>, pp. 1-22. <br /> | + | Anderson, M. J. & Whitcomb, P. J., 2010. Design of Experiments. In: Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. <i>s.l.:John Wiley & Sons, Inc</i>, pp. 1-22. <br/><br/> |
| − | Borg, A. & Ehrenberg, M., 2015. Determinants of the Rate of mRNA Translocation in Bacterial Protein Synthesis. <i>J. Mol. Biol.</i>, 427(9), pp. 1835-1847.<br /> | + | Borg, A. & Ehrenberg, M., 2015. Determinants of the Rate of mRNA Translocation in Bacterial Protein Synthesis. <i>J. Mol. Biol.</i>, 427(9), pp. 1835-1847. <br/><br/> |
| − | Carlson, E. D., Gan, R., Hodgman, C. E. & Jewett, M. C., 2012. Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Applications Come of Age. <i>Biotechnol. Adv.</i>, 30(5), pp. 1185-1194.<br /> | + | Carlson, E. D., Gan, R., Hodgman, C. E. & Jewett, M. C., 2012. Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Applications Come of Age. <i>Biotechnol. Adv.</i>, 30(5), pp. 1185-1194. <br/><br/> |
| − | Garamella, J., Marshall, R., Rustad, M. & Noireaux, V., 2016. The All E. coli TX-TL Toolbox 2.0: A Platform for Cell-Free Synthetic Biology. <i>ACS Syn. Biol.</i>, 5(4), pp. 344-355.<br /> | + | Garamella, J., Marshall, R., Rustad, M. & Noireaux, V., 2016. The All E. coli TX-TL Toolbox 2.0: A Platform for Cell-Free Synthetic Biology. <i>ACS Syn. Biol.</i>, 5(4), pp. 344-355. <br/><br/> |
| − | Jelenc, P. C. & Kurland, C. G., 1979. Nucleoside triphosphate regeneration decreases the frequency of translation errors. <i>Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA</i>, 76(7), pp. 3174-3178.<br /> | + | Jelenc, P. C. & Kurland, C. G., 1979. Nucleoside triphosphate regeneration decreases the frequency of translation errors. <i>Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA</i>, 76(7), pp. 3174-3178. <br/><br/> |
| − | Jewett, M. C. & Swartz, J. R., 2004. Mimicking the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic environment activates long-lived and efficient cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Biotechnol. & Bioeng.</i>, 86(1), pp. 19-26.<br /> | + | Jewett, M. C. & Swartz, J. R., 2004. Mimicking the <i>Escherichia coli</i> cytoplasmic environment activates long-lived and efficient cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Biotechnol. & Bioeng.</i>, 86(1), pp. 19-26. <br/><br/> |
| − | Jewett, M. C. et al., 2008. An integrated cell-free metabolic platform for protein production and synthetic biology. <i>Mol. Syst. Biol.</i>, 4(220).<br /> | + | Jewett, M. C. et al., 2008. An integrated cell-free metabolic platform for protein production and synthetic biology. <i>Mol. Syst. Biol.</i>, 4(220). <br/><br/> |
| − | Katsura, K. et al., 2017. A reproducible and scalable procedure for preparing bacterial extracts for cell-free protein synthesis. <i>J. Biochem.</i>, 162(5), pp. 357-369.<br /> | + | Katsura, K. et al., 2017. A reproducible and scalable procedure for preparing bacterial extracts for cell-free protein synthesis. <i>J. Biochem.</i>, 162(5), pp. 357-369. <br/><br/> |
| − | Kelwick, R., Webb, A. J., MacDonald, J. & Freemont, P. S., 2016. Development of a Bacillus subtilis cell-free transcription-translation system for prototyping regulatory elements. <i>Metab. Eng.</i>, Volume 38, pp. 370-381.<br /> | + | Kelwick, R., Webb, A. J., MacDonald, J. & Freemont, P. S., 2016. Development of a Bacillus subtilis cell-free transcription-translation system for prototyping regulatory elements. <i>Metab. Eng.</i>, Volume 38, pp. 370-381. <br/><br/> |
| − | Kwon, Y. & Jewett, M. C., 2015. High-throughput preparation methods of crude extract for robust cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Sci. Rep.</i>, Volume 5.<br /> | + | Kwon, Y. & Jewett, M. C., 2015. High-throughput preparation methods of crude extract for robust cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Sci. Rep.</i>, Volume 5. <br/><br/> |
| − | Lee, K. H. & Kim, D. M., 2013. Applications of cell-free protein synthesis in synthetic biology: Interfacing bio-machinery with synthetic environments. <i>Biotechnol. J.</i>, 8(11), pp. 1292-1300.<br /> | + | Lee, K. H. & Kim, D. M., 2013. Applications of cell-free protein synthesis in synthetic biology: Interfacing bio-machinery with synthetic environments. <i>Biotechnol. J.</i>, 8(11), pp. 1292-1300. <br/><br/> |
| − | Lu, Y., 2017. Cell-free synthetic biology: Engineering in an open world. <i>Syn. and Sys. Biotech.</i>, 2(1), pp. 23-27.<br /> | + | Lu, Y., 2017. Cell-free synthetic biology: Engineering in an open world. <i>Syn. and Sys. Biotech.</i>, 2(1), pp. 23-27. <br/><br/> |
| − | Nierhaus, K. H., 2014. Mg2+, K+, and the Ribosome. <i>J. Bacteriol.</i>, 196(22), pp. 3817-3819.<br /> | + | Nierhaus, K. H., 2014. Mg2+, K+, and the Ribosome. <i>J. Bacteriol.</i>, 196(22), pp. 3817-3819. <br/><br/> |
| − | Nirenberg, M. W. & Matthaei, J. H., 1961. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in <i>E. coli</i> upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. <i>Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA</i>, 47(10), pp. 1588-1602.<br /> | + | Nirenberg, M. W. & Matthaei, J. H., 1961. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in <i>E. coli</i> upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. <i>Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA</i>, 47(10), pp. 1588-1602. <br/><br/> |
| − | Pyle, A. M., 2002. Metal ions in the structure and function of RNA. <i>J. Biol. Inorg.</i>, 7(8), pp. 679-690.<br /> | + | Pyle, A. M., 2002. Metal ions in the structure and function of RNA. <i>J. Biol. Inorg.</i>, 7(8), pp. 679-690. <br/><br/> |
| − | SAS Institute Inc., 2016. JMP® 13 Design of Experiments Guide. Cary, NC, USA: SAS Institute Inc.<br /> | + | SAS Institute Inc., 2016. JMP® 13 Design of Experiments Guide. Cary, NC, USA: SAS Institute Inc. <br/><br/> |
Yang, W. C., Patel, K. & Wong, H. E., 2012. Simplifying and streamlining <i>Escherichia coli</i>-based cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Biotechnol. Prog.</i>, 28(2), pp. 413-420.<br /> | Yang, W. C., Patel, K. & Wong, H. E., 2012. Simplifying and streamlining <i>Escherichia coli</i>-based cell-free protein synthesis. <i>Biotechnol. Prog.</i>, 28(2), pp. 413-420.<br /> | ||
| Line 1,930: | Line 1,962: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 1,936: | Line 1,969: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| Line 1,994: | Line 2,028: | ||
document.getElementById("nav-cellfree").classList.remove("active", "show"); | document.getElementById("nav-cellfree").classList.remove("active", "show"); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | $("#key_res").click(function(){ | ||
| + | $(".keyres_hide").toggle(); | ||
| + | }); | ||
| Line 2,027: | Line 2,066: | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| + | {{Newcastle_footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:39, 1 November 2017
spacefill
spacefill
Our Experimental Results
Key Achievements - click to show
- Demonstrated that biosensors can be successfully split into three modules
- Produced biosensor variants by co-culturing different module variants together
- Used 3D spatial modelling to begin optimisation of a multicellular biosensor
- Characterised a 'standby switch' based on an improved part (BBa_K1632007)
- Demonstrated that a Design of Experiments approach can be used to optimise cell-free systems
Below is a diagram of our Sensynova Framework. Clicking on each part of the framework (e.g. detector modules) links to the relevant results.
Alternatively, at the bottom of this page are tabs which will show you results for every part of the project
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |






























































 The
The