(→Motivation) |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Aix-Marseille|title=KILL XYL|toc=__TOC__}} | {{Aix-Marseille|title=KILL XYL|toc=__TOC__}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | Our project | + | [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--KX.png|500px|right|thumb|KILL XYL project.]] |
| + | |||
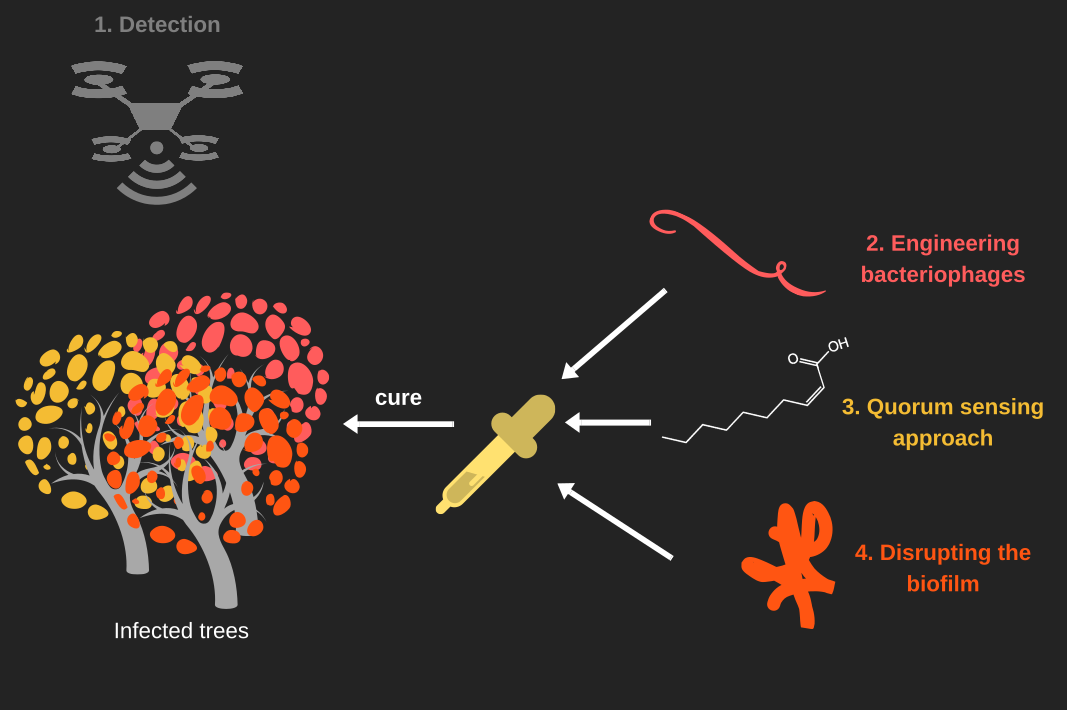
| + | Our project '''KILL XYL''' is to find a cure for the disease caused by the plant pathogen [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Xylella_fastidiosa|''Xylella fastidiosa'']]. This disease currently causes the loss of thousands of acres of European crops and currently there is no cure for it. | ||
| − | + | At Aix-Marseille University, we thought about developing a solution that focuses on multiple aspects. First, we wanted to improve [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Hardware|detection]] of the disease. To do this we used an NDVI camera that would help us to see if the plant is stressed or not. If the plant is infected by [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Xylella_fastidiosa|''Xylella fastidiosa'']], it suffers from a hydric stress that stops the photosynthesis. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Secondly, we wanted to get rid of the bacteria. | |
| + | Phages are natural predators of bacteria. | ||
| + | They can also be used to transfer DNA into bacteria. | ||
| + | Phages have the additional advantages of being strain specific and in some cases customizable. | ||
| + | As we wanted an eco-friendly treatment | ||
| + | to facilitate obtaining [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Legislation|marketing authorizations]], | ||
| + | we decided to create [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Bacteriophages|phage-like particles]] (PLPs), that aren't able to spread. | ||
| + | So we set out the construction of a phage specific to [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Xylella_fastidiosa|''X. fastidiosa'']], | ||
| + | capable of injecting genes coding for toxic proteins into the bacteria. | ||
| − | + | The main cause of the plant mortality in the case of an infection by [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Xylella_fastidiosa|''X. fastidiosa'']] is hydric stress induced by the accumulation of biofilm in xylem vessels. | |
| + | To disrupt the biofilm we thought about two different approaches. | ||
| + | The first is to keep the bacteria from producing extra-cellular polysaccharides. | ||
| + | We achieve this by [[Team:Aix-Marseille/QS|quenching bacterial quorum sensing]] using a short chain fatty acid called: 2-cis-decenoic acid. | ||
| + | The second approach is to destroy the biofilm's exo-polysaccharides using an [[Team:Aix-Marseille/DEPS|enzyme]] obtained from a bacteriophage to hydrolyse the polysaccharides. | ||
| − | + | Hence, '''KILL XYL''' simply detects the disease, disrupts biofilm and kills [[Team:Aix-Marseille/Xylella_fastidiosa|''Xylella fastidiosa'']]. | |
| − | [[Team:Aix-Marseille/ | + | <div class="row-icons"> |
| + | * [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--drone.png|link=Team:Aix-Marseille/Hardware]]<span class="legend">Detection</span> | ||
| + | * [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--icon-phage.png|link=Team:Aix-Marseille/Bacteriophages]]<span class="legend">Engineering PLPs</span> | ||
| + | * [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--icon-QS.png|link=Team:Aix-Marseille/QS]]<span class="legend">Quorum sensing</span> | ||
| + | * [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--icon-deps.png|link=Team:Aix-Marseille/DEPS]]<span class="legend">Disrupting biofilm</span> | ||
| + | * [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--icon-model.png|link=Team:Aix-Marseille/Model]]<span class="legend">Modelling</span> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:37, 1 November 2017
KILL XYL
Our project KILL XYL is to find a cure for the disease caused by the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. This disease currently causes the loss of thousands of acres of European crops and currently there is no cure for it.
At Aix-Marseille University, we thought about developing a solution that focuses on multiple aspects. First, we wanted to improve detection of the disease. To do this we used an NDVI camera that would help us to see if the plant is stressed or not. If the plant is infected by Xylella fastidiosa, it suffers from a hydric stress that stops the photosynthesis.
Secondly, we wanted to get rid of the bacteria. Phages are natural predators of bacteria. They can also be used to transfer DNA into bacteria. Phages have the additional advantages of being strain specific and in some cases customizable. As we wanted an eco-friendly treatment to facilitate obtaining marketing authorizations, we decided to create phage-like particles (PLPs), that aren't able to spread. So we set out the construction of a phage specific to X. fastidiosa, capable of injecting genes coding for toxic proteins into the bacteria.
The main cause of the plant mortality in the case of an infection by X. fastidiosa is hydric stress induced by the accumulation of biofilm in xylem vessels. To disrupt the biofilm we thought about two different approaches. The first is to keep the bacteria from producing extra-cellular polysaccharides. We achieve this by quenching bacterial quorum sensing using a short chain fatty acid called: 2-cis-decenoic acid. The second approach is to destroy the biofilm's exo-polysaccharides using an enzyme obtained from a bacteriophage to hydrolyse the polysaccharides.
Hence, KILL XYL simply detects the disease, disrupts biofilm and kills Xylella fastidiosa.