| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<title>About Us</title> | <title>About Us</title> | ||
<link href='http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lato' rel='stylesheet' type='text/css'> | <link href='http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lato' rel='stylesheet' type='text/css'> | ||
| − | <!-- | + | <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://2017.igem.org/Template:TAS_Taipei/Bootstrap"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://2017.igem.org/Template:TAS_Taipei/JqueryJS"> <script src="https://2017.igem.org/Template:TAS_Taipei/BootstrapJS"></script> --> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | --> | + | |
<style type='text/css'> | <style type='text/css'> | ||
#top_title, | #top_title, | ||
| Line 16: | Line 12: | ||
display: none !important; | display: none !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | ||
#content { | #content { | ||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
| Line 23: | Line 19: | ||
background: #f3f4f4; | background: #f3f4f4; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | ||
.cv { | .cv { | ||
box-shadow: 100px 0px 0 0px #FBB5A4; | box-shadow: 100px 0px 0 0px #FBB5A4; | ||
| Line 41: | Line 37: | ||
<div class="yellow"> | <div class="yellow"> | ||
<div class="box right"> | <div class="box right"> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right project" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Background"> | + | <div class="box2 right project" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Background"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/00/T--TAS_Taipei--Project_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Project</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Project</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right experiment" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Experimental_Summary"> | + | <div class="box2 right experiment" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Experimental_Summary"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b0/T--TAS_Taipei--Exp_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Experiments</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Experiments</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right modeling" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Model"> | + | <div class="box2 right modeling" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Model"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/be/T--TAS_Taipei--Modeling_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Modeling</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Modeling</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right prototype" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Applied_Design"> | + | <div class="box2 right prototype" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Applied_Design"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2e/T--TAS_Taipei--Prototype_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Prototype</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Prototype</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right policy" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Human_Practices"> | + | <div class="box2 right policy" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Human_Practices"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/42/T--TAS_Taipei--HP2_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Human Practices</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Human Practices</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right biosafety" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Safety"> | + | <div class="box2 right biosafety" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Safety"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b8/T--TAS_Taipei--Biosafety_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Safety</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Safety</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right about" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Team"> | + | <div class="box2 right about" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Team"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1a/T--TAS_Taipei--About_Us_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">About Us</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">About Us</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="box2 right acknowledgments" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Attributions"> | + | <div class="box2 right acknowledgments" href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei/Attributions"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/52/T--TAS_Taipei--Attributions_C.png" id="dna"> |
| − | + | ||
<h6 class="navCap">Attributions</h6> | <h6 class="navCap">Attributions</h6> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 101: | Line 89: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <box class="home"> | + | <box class="home"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/6c/T--TAS_Taipei--4home.svg" alt="Home" id="home" onclick="location.href='https://2017.igem.org/Team:TAS_Taipei';" style="cursor: pointer;"> </box> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<!--全版面大型看板開始--> | <!--全版面大型看板開始--> | ||
<div class="jumbotron" id="prototype-jumbo"> | <div class="jumbotron" id="prototype-jumbo"> | ||
| Line 109: | Line 95: | ||
<h1>Prototype</h1> | <h1>Prototype</h1> | ||
<h4>More than just lego building</h4> | <h4>More than just lego building</h4> | ||
| − | </div> | + | </div> <a href="#cv"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4a/T--TAS_Taipei--Chevron_500px_200ppi.png" alt="test" id="chevron"></a> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<!--全版面大型看板結尾--> | <!--全版面大型看板結尾--> | ||
<div class="cv" id="cv"> | <div class="cv" id="cv"> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 101: | ||
<nav class="pageNav col-lg-1"> | <nav class="pageNav col-lg-1"> | ||
<ul class="nav"> | <ul class="nav"> | ||
| − | <li> | + | <li> <a href="#WWT" class="pageNavBig">WASTEWATER TREATMNET</a> </li> |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#what" class="pageNavSm">What is in the process?</a> </li> | |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#biosafety" class="pageNavSm">Biosafety</a> </li> | |
| − | <li> | + | <li> <a href="#PR" class="pageNavBig">APPLYING PR IN WWTPs</a> </li> |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#biofilm" class="pageNavBig">APPLYING BIOFILM IN WWTPs</a> </li> | |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#volume" class="pageNavSm">Volume Does Not Affect NP Trapping</a> </li> | |
| − | <li> | + | <li> <a href="#SA" class="pageNavSm">Surface Area Affects NP Trapping Rate</a> </li> |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#prototype" class="pageNavBig">BIOFILM PROTOTYPE</a> </li> | |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#max" class="pageNavSm">Maximize NP-Biofilm Contact Area</a> </li> | |
| − | <li> | + | <li> <a href="#infra" class="pageNavSm">Maximize Adaptability to Existing Infrastructure</a> </li> |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#WWTPModel" class="pageNavSm">Biofilm Prototype in a WWTP Model</a> </li> | |
| − | + | <li> <a href="#ref" class="pageNavBig">Reference</a> </li> | |
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <li> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</nav> | </nav> | ||
| − | <div class="white col-lg-2"> | + | <div class="white col-lg-2"> hi </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<div class="col-lg-10"> | <div class="col-lg-10"> | ||
<!-- header --> | <!-- header --> | ||
<header> | <header> | ||
<div class="row" id="HPSummary"> | <div class="row" id="HPSummary"> | ||
| − | <h1 class="name col-lg-12"> | + | <h1 class="name col-lg-12">PROTOTYPE</h1> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">It is estimated that about 95% of nanoparticles used in consumer products end up in wastewater (<i>Kiser et al.</i> 2009). <b>Our goal is to apply our biofilm and Proteorhodopsin (PR) bacteria in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) to remove most nanoparticles</b> (NPs) before the effluent is released into the environment. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row this_border"></div> | <div class="row this_border"></div> | ||
| Line 184: | Line 129: | ||
<section class="main"> | <section class="main"> | ||
<div class="row" id="Research"> | <div class="row" id="Research"> | ||
| − | <h1 class="title2 col-lg-12"> | + | <h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">WASTEWATER TREATMENT</h1> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | < | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/ce/T--TAS_Taipei--Dihua_Tank-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg- | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">When wastewater enters a plant, the first step is to remove coarse solids and large materials using a grit screen (figure___). The water can then be processed in three main stages: Primary, Secondary, and sometimes Tertiary Treatment (Pescod 1992). In <b>Primary Treatment</b>, heavy solids are removed by sedimentation, and floating materials (such as oils) can be taken out by skimming. However, dissolved materials and colloids—small, evenly dispersed solids such as nanoparticles—are not removed here (Pescod 1992). <b>Secondary Treatment</b> generally involves the use of aeration tanks, where aerobic microbes help to break down organic materials. This is also known as the activated sludge process (Davis 2005). In a subsequent sedimentation step, the microbes are removed and the effluent is disinfected (often by chlorine or UV) before it is released into the environment. In certain WWTPs, wastewater may go through <b>Tertiary Treatment</b>, an advanced process typically aimed to remove nitrogen and phosphorous, and assumed to produce an effluent free of viruses. However, Tertiary Treatment requires additional infrastructure that is expensive and complex, limiting its global usage (Pescod 1992; Malik 2014). </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e1/T--TAS_Taipei--DihuaDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either in the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either in the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 213: | Line 145: | ||
<video controls="" class="col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | <video controls="" class="col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
<source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/97/T--TAS_Taipei--Dihua_WWTP_%281%29.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. | <source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/97/T--TAS_Taipei--Dihua_WWTP_%281%29.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. | ||
| + | </video> | ||
| + | </div><br> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2f/T--TAS_Taipei--BoswellDiagram-new.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | ||
| + | <h4 class="subtitle">We plan to add our bacteria either in the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div><br> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <video controls="" class="col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | ||
| + | <source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4b/T--TAS_Taipei--Final_Video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. | ||
</video> | </video> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="Boswell"> | <div class="row" id="Boswell"> | ||
| − | <h1 class="section-title col-lg-12"> | + | <h1 class="section-title col-lg-12">Biosafety</h1> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We have chosen to use a safe and common lab strain of <i>E. coli</i>, K-12, as our chassis (Environmental Protection Agency 1977). In both approaches, our constructs do not express proteins associated with virulence: PR is a membrane protein that commonly exists in marine bacteria, and for biofilm production we were careful to avoid known virulence factors such as alpha hemolysins (<i>Fattahi et al.</i> 2015). Most importantly, <b>biosafety is built into WWTPs</b>. Before treated effluent is released back into the environment, it must go through a final disinfection step, where chlorine, ozone, or UV radiation are used to kill microbes still present in the wastewater (Pescod 1992). |
| − | + | </h4> | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="row"> | + | <div class="row" id="Research"> |
| − | < | + | <h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">APPLYING PR IN WWTPs</h1> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="tap"> | <div class="row" id="tap"> | ||
| Line 233: | Line 171: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We visited the tap water museum hoping to find out more about how tap water is treated. We learned that water filtration methods vary in different areas of Taiwan, with Taipei’s filtration method being the simplest since the water is relatively clean compared to other regions, such as Kaohsiung, where the city is heavily industrialized. In Taipei, the source of tap water comes from a protected zone upstream of Xindian river. We also learned that they use sedimentation tanks and flocculation to help clump up and remove impurities. Due to the lack of a disinfection step, however, we realized that our project would not be applicable here, since our project depends on the use of <i>E. coli</i> bacteria. (Whole team activity) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ec/T--TAS_Taipei--Tap_Water_Musuem_Group-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/fd/T--TAS_Taipei--Tap_Water_Musuem-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="researchers"> | <div class="row" id="researchers"> | ||
| Line 252: | Line 184: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-9"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-9"> Before we started to conduct experiments, we emailed Dr. Eric P. Lee, senior member of technical staff at Maxim Integrated, and TAS alumnus, to ask him some general questions about our approach of our project. We told him about our two approaches, one with <i>E. coli</i> receptors that bind to the capping agents of nanoparticles, the other with biofilm that traps nanoparticles. Dr. Lee suggested that our membrane receptor must be specific to a particular capping agent. He also commented that the biofilm approach was a good idea since we could trap multiple types of nanoparticles regardless of their capping agent. (Interviewed by Emily C.) </h4> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/48/T--TAS_Taipei--Doctors6.png" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="roam"> | <div class="row" id="roam"> | ||
| Line 263: | Line 191: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We interviewed Professor Roam of National Central University and former general director of the Environmental Analysis Labs (EAL) of the Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency to learn more about the background and potential threat of nanoparticles. Dr. Roam informed us that the most common nanoparticles used in Taiwan include: TiO2, ZnO, Ag, Au, Fe, Carbon Nanotubes, Fullerenes, Clay, and Graphene. He also told us that the toxicity of a nanoparticle is directly related to its size, but there are currently no regulations or guidelines that specify the toxicity of different types and sizes of nanoparticle. With the increased use of nanoparticles in society, Dr. Roam believes that more attention should be placed on waste management, risk assessment and regulations. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> After our first visit to the Dihua WWTP, we learned that the sludge removed from wastewater is either 1) sent to landfills, 2) used as fertilizer, or 3) incinerated. We asked Dr. Roam if sludge containing aggregated nanoparticles would still be harmful to the environment if disposed of using current methods. He said that all of these sludge disposal solutions are still harmful to the environment, but they are still better than letting nanoparticles flow into bodies of water. He advised us to target removal of nanoparticles in the wastewater treatment process before it is discharged. (Interviewed by Candice L. and Justin Y.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-5 col-md-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-5 col-md-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/0d/T--TAS_Taipei--Roam-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">Professor Gwo-Dong Roam (left) of National Central University and former general director of the Environmental Analysis Labs (EAL) of Taiwan EPA.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">Professor Gwo-Dong Roam (left) of National Central University and former general director of the Environmental Analysis Labs (EAL) of Taiwan EPA.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-5"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-5"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/46/T--TAS_Taipei--Roam_Info-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">Materials that Dr. Roam provided the team with.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">Materials that Dr. Roam provided the team with.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="EPA"> | <div class="row" id="EPA"> | ||
| Line 288: | Line 208: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Thomas J. Brown, the Water Program Specialist of the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) occasionally helps with the Boswell Wastewater Treatment Plant. He has also worked with the EPA in Taiwan on wastewater treatments. We interviewed Mr. Brown about our methods to clean nanoparticles in wastewater treatment plants and how to achieve our goal of implementation. With his expertise in the field of wastewater treatment, he provided us some suggestions as to how we could turn our project into reality. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | < | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> For example, we asked him if there were differences between rural and urban plants that we should take into consideration when thinking about implementing our project. He responded that the biological processes used for treatment remains the same regardless of facility size. This helped us think about and design our final prototype, which can potentially be used in both rural and urban treatment plants. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/15/T--TAS_Taipei--TomBrownResponse.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-4 col-lg-offset-4"> Click here to see Tom Brown’s full response </a> </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="NPManu"> | <div class="row" id="NPManu"> | ||
<h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">Nanoparticle Manufacturers and Disposal Services</h1> | <h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">Nanoparticle Manufacturers and Disposal Services</h1> | ||
| Line 309: | Line 221: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> To learn more about the applications of nanoparticles, we visited a nanotech company that uses silver nanoparticles to make various antimicrobial products. The researcher and manager of Apex Nanotek, Chery Yang, introduced us to their main product, which is antimicrobial nanosilver activated carbon. Pure activated carbon, commonly used to treat sewage and industrial exhaust, is prone to bacterial growth. To overcome this problem, they integrate crystallized nanosilver into the activated carbon for their antimicrobial effects. One of their products is a showerhead, with nanosilver activated carbon filters to kill bacteria when water flows through the showerhead. <br><br> We tested the product by comparing SEM images between tap water and filtered water from the showerhead. The showerhead decreased the number of bacteria and larger particles from tap water! However, we also observed the release of nanoparticles from the filter, which will flow into wastewater. (Interviewed by Christine C., Kelly C., Yvonne W., Chansie Y., and Justin Y.) </h4> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/07/T--TAS_Taipei--Group_Pic_Apex-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">Chery Yang (third person from the left), the main researcher of Apex Nanotek Corporation<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">Chery Yang (third person from the left), the main researcher of Apex Nanotek Corporation<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b3/T--TAS_Taipei--Shower_Head-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">Product of Apex Nanotek: Silver Spring Shower Head.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">Product of Apex Nanotek: Silver Spring Shower Head.<span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> | + | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1e/T--TAS_Taipei--SEM_comparison_Tap_vs._Showerhead.png" alt="test" id="group2"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle"><b>Figure 1-3 Tap water under SEM.</b><span class="subCred"></span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Figure 1-3 Tap water under SEM.</b><span class="subCred"></span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> The image on the left shows a tap water sample under the SEM, in which we observed some bacteria (round objects that are approximately 1 μm in diameter). The SEM image on the left shows water that was filtered by the showerhead from Apex nanotek. There is less bacteria as the showerhead uses embedded nanosilver antibacterial filters. (SEM images: Christine C. and Florence L.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="theps"> | <div class="row" id="theps"> | ||
| Line 337: | Line 241: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We contacted the company that removes our nanoparticle waste because we wanted to know what happens when it leaves our lab. They directed us to National Cheng Kung university who actually treats the waste for them. The university uses chemicals and burning to aggregate nanoparticles. Through literature research, we discovered that burning nanoparticles is the most prevalent way for removal, however it is not 100% effective at removing all types of nanomaterials (Marr et. al. 2013). (Interviewed by Katherine H, Audrey T. and Christine C.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="public"> | <div class="row" id="public"> | ||
| Line 348: | Line 250: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We created a survey that helped us identify public knowledge and misconceptions about synthetic biology and nanoparticle usage. Over 240 people completed the survey. (Survey created by Abby H., Christine C. and Emily C.) <br><br> Here are some results from our survey: <br><br> <u>General Questions</u> <br><br> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>The majority of people think that gene modification is acceptable if the goal is to save or improve quality of life; however, it is not acceptable for non-medical related reasons, such as changing hair or eye color. In addition, most people do not have a preference between chemical or biological drug synthesis. <i>These results suggest that people are accepting of genetic engineering when it is related to health and medicine.</i></li> | <li>The majority of people think that gene modification is acceptable if the goal is to save or improve quality of life; however, it is not acceptable for non-medical related reasons, such as changing hair or eye color. In addition, most people do not have a preference between chemical or biological drug synthesis. <i>These results suggest that people are accepting of genetic engineering when it is related to health and medicine.</i></li> | ||
| Line 360: | Line 258: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/97/T--TAS_Taipei--general_questionsPic.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle"><b>Two examples of general questions from our survey.</b> (<b>Left</b>) 87% (201 out of 243 total responses) think that genes should be modified if the goal is to save or improve quality of life. (<b>Right</b>) 96.7% of the people surveyed care about the quality of wastewater (236 out of 244 total responses).<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Two examples of general questions from our survey.</b> (<b>Left</b>) 87% (201 out of 243 total responses) think that genes should be modified if the goal is to save or improve quality of life. (<b>Right</b>) 96.7% of the people surveyed care about the quality of wastewater (236 out of 244 total responses).<span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> <u>Project-Specific Questions</u> |
| − | + | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>The majority of people have heard of nanoparticles and know that nanoparticles are used in consumer products; however, they do not know <i>why</i> nanoparticles are used.</li> | <li>The majority of people have heard of nanoparticles and know that nanoparticles are used in consumer products; however, they do not know <i>why</i> nanoparticles are used.</li> | ||
| Line 375: | Line 271: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/9e/T--TAS_Taipei--project_specific-new.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Two examples of project-specific questions from our survey.</b> (<b>Left</b>) A majority of the people we asked (58.6%) do not know why nanoparticles are used in consumer products (143 out of 244 total responses). (<b>Right</b>) People believe that nanoparticle manufacturers and the government (including WWTPs) are most responsible for the regulation of nanoparticle usage and disposal. <span class="subCred">Figure: Christine C.</span></h4> | |
| − | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>Two examples of project-specific questions from our survey.</b> (<b>Left</b>) A majority of the people we asked (58.6%) do not know why nanoparticles are used in consumer products (143 out of 244 total responses). (<b>Right</b>) People believe that nanoparticle manufacturers and the government (including WWTPs) are most responsible for the regulation of nanoparticle usage and disposal. | + | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-4"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-4"> Click to see all survey results: </h4> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b9/T--TAS_Taipei--general_questions.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-3"> General Questions </a> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/32/T--TAS_Taipei--project_specific.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-3 col-lg-offset-1"> Project Specific </a> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<div class="row" id="bioethics"> | <div class="row" id="bioethics"> | ||
<h1 class="section-title col-lg-12">Bioethics Panel</h1> | <h1 class="section-title col-lg-12">Bioethics Panel</h1> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We hosted a Bioethics Panel, where we invited students and teachers to discuss the moral, social and environmental concerns of our project. To encourage participants to consider the problems from multiple perspectives, we created a role-playing game and assigned different roles to participants. We then asked for their opinions on nanoparticle usage and disposal from the perspective of their assigned role. (Whole team activity) <br><br> For instance, one of our questions was: <br><br> “Dihua WWTP has no nanoparticle removal plan. Should this be the job of the wastewater plant? Or the nanoparticle manufacturer?” <br><br> The following roles were assigned: |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>Wastewater plant manager </li> | <li>Wastewater plant manager </li> | ||
| Line 411: | Line 292: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <div class="para col-lg-12"> Most of the wastewater plant managers thought that nanoparticle manufacturers should be responsible for removing nanoparticles, because they have more information (e.g., solubility, toxicity, etc.) about their own products. <b>However, many other participants were skeptical that manufacturers could be trusted to remove their own contamination and agreed that WWTPs should ultimately be responsible for cleaning water contaminated with nanoparticles.</b> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <div class="para col-lg-12"> This activity gave us great insight on how the public perceives nanoparticle usage and regulation in society. This also gave us a chance to talk to people about both the benefits and the dangers of using nanoparticles. </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/7/76/T--TAS_Taipei--bioethics_panel_results_pdf.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-6 col-lg-offset-3"> Click here to see the compiled results from all participants </a> </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/97/T--TAS_Taipei--general_questionsPic.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="Impact"> | <div class="row" id="Impact"> | ||
| Line 434: | Line 305: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Even though we can’t implement our project in an actual wastewater treatment system, we still wanted to make a difference! We decided on two areas where we could make an immediate impact: 1) Creating an policy brief to highlight current obstacles in effective nanoparticle regulation and propose new policy solutions, and 2) Raising funds for two organizations that promote environmental protection. </h4> |
| − | Even though we can’t implement our project in an actual wastewater treatment system, we still wanted to make a difference! We decided on two areas where we could make an immediate impact: 1) Creating an policy brief to highlight current obstacles in effective nanoparticle regulation and propose new policy solutions, and 2) Raising funds for two organizations that promote environmental protection. | + | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="policy"> | <div class="row" id="policy"> | ||
| Line 442: | Line 311: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Our team has conducted extensive research on existing regulatory laws and policies regarding nanoparticles and nanomaterials. We have investigated chemical regulations, including the Restriction, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), A Toxic Substances Control Act (TCSA), CLP, and the Clean Air Act (CAA). There are significant obstacles to successfully regulating nanoparticles, such as conflicting definitions on nanoparticles that lead to an inability to successfully regulate manufacturers. Research has also been conducted on the hazardous effects of nanoparticles on the human body and environment. We decided to compose a policy brief highlighting the existing challenges in nanoparticle regulation and the lessons learned from previous failure to regulate new chemical substances. The brief was sent out to regulatory agencies, government agencies, and news outlets to raise awareness about the issue. We feel responsible to let others know about the damage nanoparticle waste can do to the environment. (Policy Brief created by Ashley L.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/0c/T--TAS_Taipei--policy_brief_pdf.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-4 col-lg-offset-4"> Click here to read our policy brief! </a> </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | < | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-9"> We sent this policy brief to the <b>Environmental Protection Administration (EPA) minister in Taiwan</b>, and they responded! They read our policy brief and said that they will take it into consideration when they make policy regulations on the use of nanoparticles in the future. They understand that nanotechnology is still developing and definitely needs more attention and regulation. (Correspondence: Christine C.) </h4> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/95/T--TAS_Taipei--%E6%9D%8E%E6%87%89%E5%85%83.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/6f/T--TAS_Taipei--EPAResponse.pdf" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-4 col-lg-offset-4"> Click to see his reply! </a> </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We were interviewed by <b>News Lens International</b> about nanoparticle regulation. Many of the questions focused on why we chose to target nanoparticles and how nanoparticles are dealt with in Taiwan. We emphasized that the lack of regulatory legislation prevents agencies from acquiring regulatory power. We also talked about the lack of nanoparticle filtration in wastewater treatment plants. (Interviewed by Ashley L.) </h4> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> <a href="https://international.thenewslens.com/article/80829" type="button" class="btn btn-info col-lg-4 col-lg-offset-4"> View the article here </a> </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="fund"> | <div class="row" id="fund"> | ||
<h1 class="section-title col-lg-12">Fundraising and Donation</h1> | <h1 class="section-title col-lg-12">Fundraising and Donation</h1> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We held multiple fundraising sales, selling small ice cream dots (resembling nanoparticles!) and Oreo fudge during our lunch periods in school, and making “glitter slime” at our school’s annual spring fair (see Spring Fair in the Outreach section above). (Team activity) <br><br>In total, we raised around 500 USD, and donated the money to two organizations: </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/6a/T--TAS_Taipei--WaterIsLife.png" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> WaterisLife is an organization that provides clean drinking water, as well as sanitation and hygiene education programs to schools and communities in need. We donated to this organization in hopes that more people will have access to clean water. Visit WaterisLife <a href="http://waterislife.com/">here</a>. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-3"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/96/T--TAS_Taipei--TEPU.gif" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Taiwan Environmental Protection Union (TEPU) is a local organization founded in 1987 to promote public awareness and participation to prevent pollution and damage to public resources. Visit TEPU <a href="http://www.tepu.org.tw/?page_id=4975">here</a>. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="Outreach"> | <div class="row" id="Outreach"> | ||
| Line 507: | Line 345: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">In Outreach, we raised awareness of the beneficial qualities and harmful consequences associated with nanoparticles. We also educated the general public about nanoparticle usage, synthetic biology, and science in general. Lastly, we communicated with other iGEM teams to share ideas and collaborate on experiments. | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12">In Outreach, we raised awareness of the beneficial qualities and harmful consequences associated with nanoparticles. We also educated the general public about nanoparticle usage, synthetic biology, and science in general. Lastly, we communicated with other iGEM teams to share ideas and collaborate on experiments. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="education"> | <div class="row" id="education"> | ||
| Line 517: | Line 354: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Our iGEM team hosted over 120 kindergarten students to teach them the power of observation and the basics of science. For example, we taught them how to use microscopes to look at anti-counterfeiting measures on paper money and how to use refraction lenses to see that white light is made up of various colors. (Whole Team activity) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-5 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-5 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/7/73/T--TAS_Taipei--Kindergarten-Group.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-5"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/59/T--TAS_Taipei--Kindergarten-AS.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-5"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="seventhGrade"> | <div class="row" id="seventhGrade"> | ||
| Line 533: | Line 364: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> We introduced iGEM and the basics of synthetic biology to all 200+ students in the seventh grade. They learned how to use micropipettes, as well as how to load and run dyes through an agarose gel. We also gave students different real world problems. Using paper biobrick parts, students put together constructs that would solve the given problems. (Whole Team activity) </h4> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e1/T-TAS_Taipei--HP-7-1.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/dc/T-TAS_Taipei--HP-7-2.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/38/T--TAS_Taipei--HP_Jumbo.jpg" alt="test" id="group2"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="Fair"> | <div class="row" id="Fair"> | ||
| Line 552: | Line 375: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> At our school’s annual spring fair, we manned a booth where people could create their own glitter slime by mixing polyvinyl alcohol and sodium borate solutions. The slime was meant to simulate the biofilm we use to trap nanoparticles (in this demo, glitter) in wastewater treatment plants. We also showed a few SEM images of bacteria, as well as everyday products that contain nanoparticles such as toothpaste and sunscreen. Everyone who came by our booth was encouraged to take our survey so we could record opinions on bioethics and concerns about nanoparticles. (Whole team activity) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/53/T--TAS_Taipei--Spring_Fair-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">iGEM Slime booth at Spring Fair along with the iPad surveys set up next to the tables.</h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">iGEM Slime booth at Spring Fair along with the iPad surveys set up next to the tables.</h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/61/T--TAS_Taipei--Spring_Fair_Sage-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/a4/T--TAS_Taipei--Spring_Fair_NP-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle">SEM images that show nanoparticles in daily products (ex: toothpaste and sunscreen)</h4> | <h4 class="subtitle">SEM images that show nanoparticles in daily products (ex: toothpaste and sunscreen)</h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 573: | Line 390: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> At TAS we conduct research symposiums twice a year to showcase the research of students who take a variety of research courses. Before we decided our project topic, we developed 4 different project ideas to present at our first research symposium (poster session). We received feedback from both students and teachers, then decided on our current project. At our second research symposium, we presented on our current project, Nanotrap! (Presenters: Candice L., William C., Chansie Y., Christine C., Yvonne, W., Justin Y., Dylan L., and Catherine Y.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8 col-lg-offset-2"> | + | <div class="image_container_big col-lg-8 col-lg-offset-2"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/c3/T--TAS_Taipei--Symposium-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="NCTU"> | <div class="row" id="NCTU"> | ||
| Line 586: | Line 399: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> In preparation for the Giant Jamboree, we attended the 5th annual Asia-Pacific iGEM conference at NCTU to share and receive valuable feedback from other college and high school teams in Taiwan. This event allowed us to consider different aspects of our project using feedback from other teams. (Presenters: William C., Yvonne W., and Justin Y.) </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/a8/T--TAS_Taipei--NCTU1.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> </div> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ed/T--TAS_Taipei--NCTU2.JPG" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-6"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="pubView"> | <div class="row" id="pubView"> | ||
| Line 602: | Line 409: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-8"> Some members of the iGEM team went to various popular sites in Taipei to pass out fliers and conduct surveys. We visited National Taiwan University, Chiang Kai-Shek Memorial Hall, and Taipei 101. This helped us collect feedback from different age groups and backgrounds. This was a great and fun way to spread awareness of nanoparticle pollution! (Team members: Ashley L., Emily C., Florence L., Candice L., Yvonne W., Justin Y., Avery W., Christine C., Jesse K., and Laurent H.) </h4> |
| − | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/f9/T--TAS_Taipei--Survey_Trip_Gran-min.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-4"> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Here's a video we made for this event. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
| − | <div class="row"> | + | <div class="row"> <video controls="" class="col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <source src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4b/T--TAS_Taipei--Final_Video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. </video> </div> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<div class="row" id="collab"> | <div class="row" id="collab"> | ||
<h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">Collaborations</h1> | <h1 class="title2 col-lg-12">Collaborations</h1> | ||
| Line 626: | Line 423: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Quidem officia sit amet omnis deleniti veritatis ut. Placeat reprehenderit quas in non a quidem vitae aspernatur, nihil vero pariatur rerum nobis est eum, minima aliquid neque quaerat quibusdam quis. Repellendus neque voluptas reiciendis, id dolorum, asperiores dolores debitis libero autem quibusdam. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="CGU"> | <div class="row" id="CGU"> | ||
| Line 634: | Line 429: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> We first met the CGU_Taiwan team at the end of our presentation for the 5th Annual Asia Pacific iGEM Conference hosted in National Chiao Tung University (NCTU). They were excited that our biofilms were able to trap nanoparticles and wanted to know whether they might trap ink particles as well. We offered to test this for CGU_Taiwan. <br><br> CGU_Taiwan also helped us independently test biofilm production using a different dye, crystal violet. Their results verified that overexpression of OmpR234 (BBa_K2229200) produces more biofilm than control (BBa_K342003). </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> | + | <div class="image_container col-lg-10 col-lg-offset-1"> <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/7/70/T--TAS_Taipei--figure_3-18.jpg" alt="test" id="group"> |
| − | + | ||
<h4 class="subtitle"><b>A)</b> Our experimental results showed that <i>E. coli</i> overexpressing OmpR234 (BBa_K2229200) produces more biofilm than a control which does not express OmpR234 (BBa_K342003). <b>B)</b> CGU_Taiwan independently tested our constructs using crystal violet, a dye commonly used to quantify biofilm formation. BBa_K2229200 showed higher absorbance compared to the control BBa_K342003, reflecting the formation of more biofilm, which matches our results.</h4> | <h4 class="subtitle"><b>A)</b> Our experimental results showed that <i>E. coli</i> overexpressing OmpR234 (BBa_K2229200) produces more biofilm than a control which does not express OmpR234 (BBa_K342003). <b>B)</b> CGU_Taiwan independently tested our constructs using crystal violet, a dye commonly used to quantify biofilm formation. BBa_K2229200 showed higher absorbance compared to the control BBa_K342003, reflecting the formation of more biofilm, which matches our results.</h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div><br> | </div><br> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Human Practices Text Written by Christine C., Candice L., Emily C., Justin Y. Edited by advisors Jude Clapper and Teresa Chiang. </h4> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row" id="ref"> | <div class="row" id="ref"> | ||
| Line 654: | Line 443: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
| − | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> | + | <h4 class="para col-lg-12"> Ahamed, M., Alsalhi, M. S., & Siddiqui, M. (2010). Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clinica Chimica Acta,411(23-24), 1841-1848. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.08.016 <br><br> Marr, L. C., & Holder, A. L. (2013). Nanomaterial disposal by incineration. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 15(9), 1652-1664. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00224A </h4> |
| − | Ahamed, M., Alsalhi, M. S., & Siddiqui, M. (2010). Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clinica Chimica Acta,411(23-24), 1841-1848. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.08.016 | + | |
| − | <br><br> | + | |
| − | Marr, L. C., & Holder, A. L. (2013). Nanomaterial disposal by incineration. | + | |
| − | & Impacts, 15(9), 1652-1664. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00224A | + | |
</div> | </div> | ||
</section> | </section> | ||
| Line 853: | Line 638: | ||
}); | }); | ||
}) | }) | ||
| + | |||
</script> | </script> | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Revision as of 08:28, 19 October 2017
X

Project

Experiments
Modeling

Prototype

Human Practices

Safety

About Us

Attributions
Project
Experiment
Modeling
Prototype
Human Practice
Biosafety
About Us
Attributions

hi
PROTOTYPE
It is estimated that about 95% of nanoparticles used in consumer products end up in wastewater (Kiser et al. 2009). Our goal is to apply our biofilm and Proteorhodopsin (PR) bacteria in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) to remove most nanoparticles (NPs) before the effluent is released into the environment.
WASTEWATER TREATMENT

When wastewater enters a plant, the first step is to remove coarse solids and large materials using a grit screen (figure___). The water can then be processed in three main stages: Primary, Secondary, and sometimes Tertiary Treatment (Pescod 1992). In Primary Treatment, heavy solids are removed by sedimentation, and floating materials (such as oils) can be taken out by skimming. However, dissolved materials and colloids—small, evenly dispersed solids such as nanoparticles—are not removed here (Pescod 1992). Secondary Treatment generally involves the use of aeration tanks, where aerobic microbes help to break down organic materials. This is also known as the activated sludge process (Davis 2005). In a subsequent sedimentation step, the microbes are removed and the effluent is disinfected (often by chlorine or UV) before it is released into the environment. In certain WWTPs, wastewater may go through Tertiary Treatment, an advanced process typically aimed to remove nitrogen and phosphorous, and assumed to produce an effluent free of viruses. However, Tertiary Treatment requires additional infrastructure that is expensive and complex, limiting its global usage (Pescod 1992; Malik 2014).
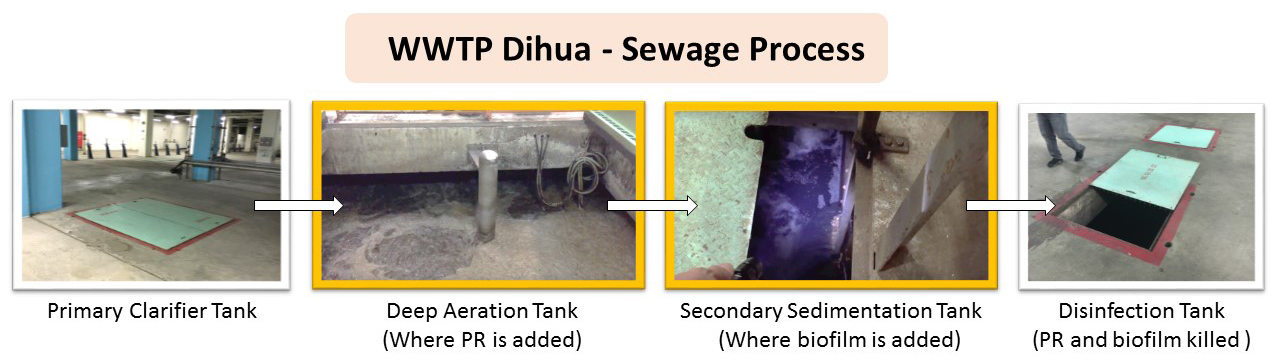
We plan to add our bacteria either in the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.Figure: Christine C.

We plan to add our bacteria either in the deep aeration tanks or the secondary sedimentation tanks. The disinfection tank will kill the bacteria used in previous tanks.Figure: Christine C.
Biosafety
We have chosen to use a safe and common lab strain of E. coli, K-12, as our chassis (Environmental Protection Agency 1977). In both approaches, our constructs do not express proteins associated with virulence: PR is a membrane protein that commonly exists in marine bacteria, and for biofilm production we were careful to avoid known virulence factors such as alpha hemolysins (Fattahi et al. 2015). Most importantly, biosafety is built into WWTPs. Before treated effluent is released back into the environment, it must go through a final disinfection step, where chlorine, ozone, or UV radiation are used to kill microbes still present in the wastewater (Pescod 1992).
APPLYING PR IN WWTPs
Tap Water Museum
We visited the tap water museum hoping to find out more about how tap water is treated. We learned that water filtration methods vary in different areas of Taiwan, with Taipei’s filtration method being the simplest since the water is relatively clean compared to other regions, such as Kaohsiung, where the city is heavily industrialized. In Taipei, the source of tap water comes from a protected zone upstream of Xindian river. We also learned that they use sedimentation tanks and flocculation to help clump up and remove impurities. Due to the lack of a disinfection step, however, we realized that our project would not be applicable here, since our project depends on the use of E. coli bacteria. (Whole team activity)


Nanoparticle and Wastewater experts
Dr. Eric Lee
Before we started to conduct experiments, we emailed Dr. Eric P. Lee, senior member of technical staff at Maxim Integrated, and TAS alumnus, to ask him some general questions about our approach of our project. We told him about our two approaches, one with E. coli receptors that bind to the capping agents of nanoparticles, the other with biofilm that traps nanoparticles. Dr. Lee suggested that our membrane receptor must be specific to a particular capping agent. He also commented that the biofilm approach was a good idea since we could trap multiple types of nanoparticles regardless of their capping agent. (Interviewed by Emily C.)

Dr. Gwo-Dong Roam
We interviewed Professor Roam of National Central University and former general director of the Environmental Analysis Labs (EAL) of the Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency to learn more about the background and potential threat of nanoparticles. Dr. Roam informed us that the most common nanoparticles used in Taiwan include: TiO2, ZnO, Ag, Au, Fe, Carbon Nanotubes, Fullerenes, Clay, and Graphene. He also told us that the toxicity of a nanoparticle is directly related to its size, but there are currently no regulations or guidelines that specify the toxicity of different types and sizes of nanoparticle. With the increased use of nanoparticles in society, Dr. Roam believes that more attention should be placed on waste management, risk assessment and regulations.
After our first visit to the Dihua WWTP, we learned that the sludge removed from wastewater is either 1) sent to landfills, 2) used as fertilizer, or 3) incinerated. We asked Dr. Roam if sludge containing aggregated nanoparticles would still be harmful to the environment if disposed of using current methods. He said that all of these sludge disposal solutions are still harmful to the environment, but they are still better than letting nanoparticles flow into bodies of water. He advised us to target removal of nanoparticles in the wastewater treatment process before it is discharged. (Interviewed by Candice L. and Justin Y.)

Professor Gwo-Dong Roam (left) of National Central University and former general director of the Environmental Analysis Labs (EAL) of Taiwan EPA.

Materials that Dr. Roam provided the team with.
Thomas J. Brown
Thomas J. Brown, the Water Program Specialist of the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) occasionally helps with the Boswell Wastewater Treatment Plant. He has also worked with the EPA in Taiwan on wastewater treatments. We interviewed Mr. Brown about our methods to clean nanoparticles in wastewater treatment plants and how to achieve our goal of implementation. With his expertise in the field of wastewater treatment, he provided us some suggestions as to how we could turn our project into reality.
For example, we asked him if there were differences between rural and urban plants that we should take into consideration when thinking about implementing our project. He responded that the biological processes used for treatment remains the same regardless of facility size. This helped us think about and design our final prototype, which can potentially be used in both rural and urban treatment plants.
Nanoparticle Manufacturers and Disposal Services
Apex Nanotek
To learn more about the applications of nanoparticles, we visited a nanotech company that uses silver nanoparticles to make various antimicrobial products. The researcher and manager of Apex Nanotek, Chery Yang, introduced us to their main product, which is antimicrobial nanosilver activated carbon. Pure activated carbon, commonly used to treat sewage and industrial exhaust, is prone to bacterial growth. To overcome this problem, they integrate crystallized nanosilver into the activated carbon for their antimicrobial effects. One of their products is a showerhead, with nanosilver activated carbon filters to kill bacteria when water flows through the showerhead.
We tested the product by comparing SEM images between tap water and filtered water from the showerhead. The showerhead decreased the number of bacteria and larger particles from tap water! However, we also observed the release of nanoparticles from the filter, which will flow into wastewater. (Interviewed by Christine C., Kelly C., Yvonne W., Chansie Y., and Justin Y.)

Chery Yang (third person from the left), the main researcher of Apex Nanotek Corporation

Product of Apex Nanotek: Silver Spring Shower Head.

Figure 1-3 Tap water under SEM.
The image on the left shows a tap water sample under the SEM, in which we observed some bacteria (round objects that are approximately 1 μm in diameter). The SEM image on the left shows water that was filtered by the showerhead from Apex nanotek. There is less bacteria as the showerhead uses embedded nanosilver antibacterial filters. (SEM images: Christine C. and Florence L.)
THEPS Environmental Protection Engineering Company (中港環保工程股份有限公司)
We contacted the company that removes our nanoparticle waste because we wanted to know what happens when it leaves our lab. They directed us to National Cheng Kung university who actually treats the waste for them. The university uses chemicals and burning to aggregate nanoparticles. Through literature research, we discovered that burning nanoparticles is the most prevalent way for removal, however it is not 100% effective at removing all types of nanomaterials (Marr et. al. 2013). (Interviewed by Katherine H, Audrey T. and Christine C.)
Public Opinion
Survey Results
We created a survey that helped us identify public knowledge and misconceptions about synthetic biology and nanoparticle usage. Over 240 people completed the survey. (Survey created by Abby H., Christine C. and Emily C.)
Here are some results from our survey:
General Questions
- The majority of people think that gene modification is acceptable if the goal is to save or improve quality of life; however, it is not acceptable for non-medical related reasons, such as changing hair or eye color. In addition, most people do not have a preference between chemical or biological drug synthesis. These results suggest that people are accepting of genetic engineering when it is related to health and medicine.
- Environmentally, people are generally concerned with the wastewater that enters the ocean and the river. This gives weight to our project, because the quality of water is an important concern for the general public.

Two examples of general questions from our survey. (Left) 87% (201 out of 243 total responses) think that genes should be modified if the goal is to save or improve quality of life. (Right) 96.7% of the people surveyed care about the quality of wastewater (236 out of 244 total responses).Figure: Christine C.
Project-Specific Questions
- The majority of people have heard of nanoparticles and know that nanoparticles are used in consumer products; however, they do not know why nanoparticles are used.
- Most people believe that the government and nanoparticle manufacturers should share responsibility for the regulation of nanoparticle usage and disposal.

Two examples of project-specific questions from our survey. (Left) A majority of the people we asked (58.6%) do not know why nanoparticles are used in consumer products (143 out of 244 total responses). (Right) People believe that nanoparticle manufacturers and the government (including WWTPs) are most responsible for the regulation of nanoparticle usage and disposal. Figure: Christine C.
Bioethics Panel
We hosted a Bioethics Panel, where we invited students and teachers to discuss the moral, social and environmental concerns of our project. To encourage participants to consider the problems from multiple perspectives, we created a role-playing game and assigned different roles to participants. We then asked for their opinions on nanoparticle usage and disposal from the perspective of their assigned role. (Whole team activity)
For instance, one of our questions was:
“Dihua WWTP has no nanoparticle removal plan. Should this be the job of the wastewater plant? Or the nanoparticle manufacturer?”
The following roles were assigned:
- Wastewater plant manager
- Nanoparticle manufacturer
- Citizen
- Fisherman
- Fish
Most of the wastewater plant managers thought that nanoparticle manufacturers should be responsible for removing nanoparticles, because they have more information (e.g., solubility, toxicity, etc.) about their own products. However, many other participants were skeptical that manufacturers could be trusted to remove their own contamination and agreed that WWTPs should ultimately be responsible for cleaning water contaminated with nanoparticles.
This activity gave us great insight on how the public perceives nanoparticle usage and regulation in society. This also gave us a chance to talk to people about both the benefits and the dangers of using nanoparticles.

IMPACT
Even though we can’t implement our project in an actual wastewater treatment system, we still wanted to make a difference! We decided on two areas where we could make an immediate impact: 1) Creating an policy brief to highlight current obstacles in effective nanoparticle regulation and propose new policy solutions, and 2) Raising funds for two organizations that promote environmental protection.
Policy Brief -- Nanoparticle Regulation Issues and Case Studies
Our team has conducted extensive research on existing regulatory laws and policies regarding nanoparticles and nanomaterials. We have investigated chemical regulations, including the Restriction, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), A Toxic Substances Control Act (TCSA), CLP, and the Clean Air Act (CAA). There are significant obstacles to successfully regulating nanoparticles, such as conflicting definitions on nanoparticles that lead to an inability to successfully regulate manufacturers. Research has also been conducted on the hazardous effects of nanoparticles on the human body and environment. We decided to compose a policy brief highlighting the existing challenges in nanoparticle regulation and the lessons learned from previous failure to regulate new chemical substances. The brief was sent out to regulatory agencies, government agencies, and news outlets to raise awareness about the issue. We feel responsible to let others know about the damage nanoparticle waste can do to the environment. (Policy Brief created by Ashley L.)
We sent this policy brief to the Environmental Protection Administration (EPA) minister in Taiwan, and they responded! They read our policy brief and said that they will take it into consideration when they make policy regulations on the use of nanoparticles in the future. They understand that nanotechnology is still developing and definitely needs more attention and regulation. (Correspondence: Christine C.)

We were interviewed by News Lens International about nanoparticle regulation. Many of the questions focused on why we chose to target nanoparticles and how nanoparticles are dealt with in Taiwan. We emphasized that the lack of regulatory legislation prevents agencies from acquiring regulatory power. We also talked about the lack of nanoparticle filtration in wastewater treatment plants. (Interviewed by Ashley L.)
Fundraising and Donation
We held multiple fundraising sales, selling small ice cream dots (resembling nanoparticles!) and Oreo fudge during our lunch periods in school, and making “glitter slime” at our school’s annual spring fair (see Spring Fair in the Outreach section above). (Team activity)
In total, we raised around 500 USD, and donated the money to two organizations:

WaterisLife is an organization that provides clean drinking water, as well as sanitation and hygiene education programs to schools and communities in need. We donated to this organization in hopes that more people will have access to clean water. Visit WaterisLife here.

Taiwan Environmental Protection Union (TEPU) is a local organization founded in 1987 to promote public awareness and participation to prevent pollution and damage to public resources. Visit TEPU here.
OUTREACH
In Outreach, we raised awareness of the beneficial qualities and harmful consequences associated with nanoparticles. We also educated the general public about nanoparticle usage, synthetic biology, and science in general. Lastly, we communicated with other iGEM teams to share ideas and collaborate on experiments.
Education
Kindergarten -- Observing the “invisible”
Our iGEM team hosted over 120 kindergarten students to teach them the power of observation and the basics of science. For example, we taught them how to use microscopes to look at anti-counterfeiting measures on paper money and how to use refraction lenses to see that white light is made up of various colors. (Whole Team activity)


7th Grade Introduction to Synthetic Biology
We introduced iGEM and the basics of synthetic biology to all 200+ students in the seventh grade. They learned how to use micropipettes, as well as how to load and run dyes through an agarose gel. We also gave students different real world problems. Using paper biobrick parts, students put together constructs that would solve the given problems. (Whole Team activity)



Spring Fair -- Spreading Public Awareness of Nanoparticles
At our school’s annual spring fair, we manned a booth where people could create their own glitter slime by mixing polyvinyl alcohol and sodium borate solutions. The slime was meant to simulate the biofilm we use to trap nanoparticles (in this demo, glitter) in wastewater treatment plants. We also showed a few SEM images of bacteria, as well as everyday products that contain nanoparticles such as toothpaste and sunscreen. Everyone who came by our booth was encouraged to take our survey so we could record opinions on bioethics and concerns about nanoparticles. (Whole team activity)

iGEM Slime booth at Spring Fair along with the iPad surveys set up next to the tables.


SEM images that show nanoparticles in daily products (ex: toothpaste and sunscreen)
Research Symposium -- Poster and Oral Presentations
At TAS we conduct research symposiums twice a year to showcase the research of students who take a variety of research courses. Before we decided our project topic, we developed 4 different project ideas to present at our first research symposium (poster session). We received feedback from both students and teachers, then decided on our current project. At our second research symposium, we presented on our current project, Nanotrap! (Presenters: Candice L., William C., Chansie Y., Christine C., Yvonne, W., Justin Y., Dylan L., and Catherine Y.)
5th Annual Asia-Pacific iGEM Conference -- NCTU
In preparation for the Giant Jamboree, we attended the 5th annual Asia-Pacific iGEM conference at NCTU to share and receive valuable feedback from other college and high school teams in Taiwan. This event allowed us to consider different aspects of our project using feedback from other teams. (Presenters: William C., Yvonne W., and Justin Y.)


Public Outreach -- A Tour of Taipei
Some members of the iGEM team went to various popular sites in Taipei to pass out fliers and conduct surveys. We visited National Taiwan University, Chiang Kai-Shek Memorial Hall, and Taipei 101. This helped us collect feedback from different age groups and backgrounds. This was a great and fun way to spread awareness of nanoparticle pollution! (Team members: Ashley L., Emily C., Florence L., Candice L., Yvonne W., Justin Y., Avery W., Christine C., Jesse K., and Laurent H.)

Here's a video we made for this event.
Collaborations
NYMU_TAIPEI
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Quidem officia sit amet omnis deleniti veritatis ut. Placeat reprehenderit quas in non a quidem vitae aspernatur, nihil vero pariatur rerum nobis est eum, minima aliquid neque quaerat quibusdam quis. Repellendus neque voluptas reiciendis, id dolorum, asperiores dolores debitis libero autem quibusdam.
CGU_Taiwan
We first met the CGU_Taiwan team at the end of our presentation for the 5th Annual Asia Pacific iGEM Conference hosted in National Chiao Tung University (NCTU). They were excited that our biofilms were able to trap nanoparticles and wanted to know whether they might trap ink particles as well. We offered to test this for CGU_Taiwan.
CGU_Taiwan also helped us independently test biofilm production using a different dye, crystal violet. Their results verified that overexpression of OmpR234 (BBa_K2229200) produces more biofilm than control (BBa_K342003).



