| Line 522: | Line 522: | ||
<h5>Construction of Cre-<i>loxpsym</i> System </h5> | <h5>Construction of Cre-<i>loxpsym</i> System </h5> | ||
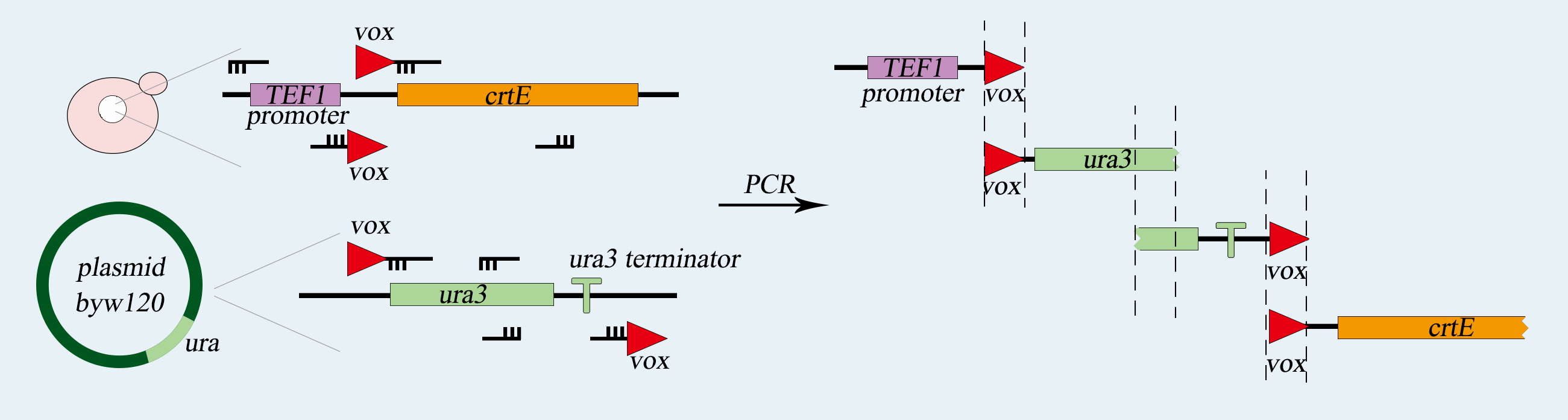
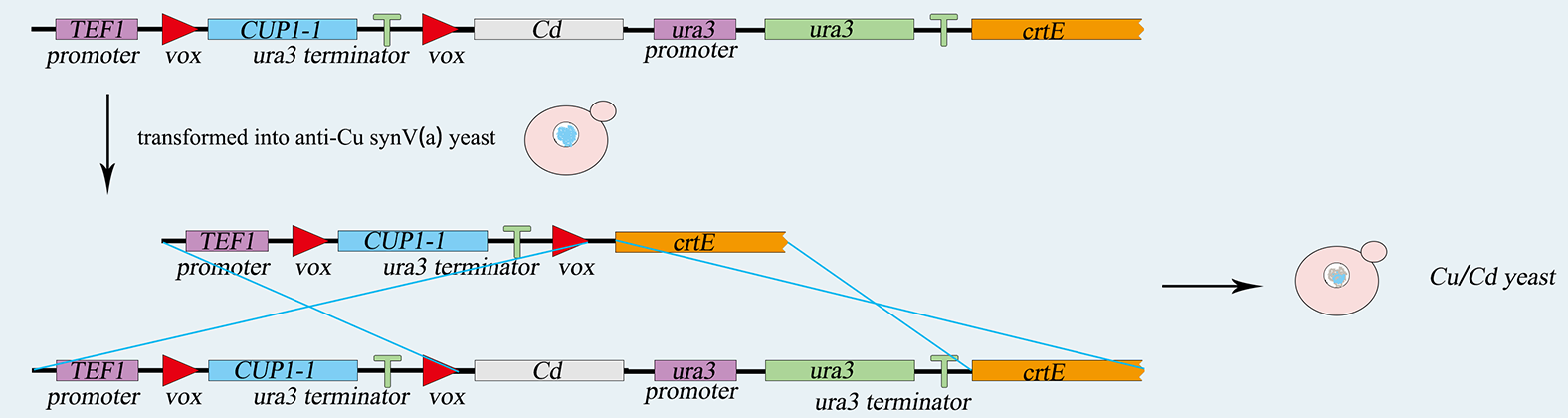
<p>First, We use two common expression vector plasmid, PRS416 and PRS413(with different nutrition label), in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to load our device, which consists of heterologous gene part (PCLB2 promoter, Cre-EBD gene, CYC1 terminator) . Second, we transform the pSCW11-CRE/EBD plasmid into <i>synX</i> strain , respectively and get three strains with Cre-EBD, 079 and 160 with ura tag ,085 with his tag.</p> | <p>First, We use two common expression vector plasmid, PRS416 and PRS413(with different nutrition label), in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to load our device, which consists of heterologous gene part (PCLB2 promoter, Cre-EBD gene, CYC1 terminator) . Second, we transform the pSCW11-CRE/EBD plasmid into <i>synX</i> strain , respectively and get three strains with Cre-EBD, 079 and 160 with ura tag ,085 with his tag.</p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<h5>Screening of Strains with High Tolerance</h5> | <h5>Screening of Strains with High Tolerance</h5> | ||
| − | <p>Aiming at screening strains with tolerance to high concentration of cadmium ion and cupric ion solution, we prepare SC culture medium with 3mM, 4mM, 4.5mM, 5mM, 5.5mM, 6mM, 6.5mM, 7mM copper ion and SC culture medium with 0.01mM, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 0.15mM, 0.2mM cadmium ion. | + | <p>Under the cell culture environment with traces of estradiol(1μL of 5mM estradiol / 5mL media), three strains are incubated at 30℃for 6 hours. After dilute 1000 times and wash 2 times with water to remove estradiol and spot on on SC plates with gradient concentrations of copper ion and cadmium ion.</p> |
| − | <h5>Verification of Cre-EBD Effect (Dilution Assay and Measurement of | + | <p>Incubate plates for 3 days at 30℃ and observe the growth of strains.</p> |
| − | <p>To demonstrate the verification of Cre-EBD effect, we diluted optimal strains to 10- | + | <p>Aiming at screening strains with tolerance to high concentration of cadmium ion and cupric ion solution, we prepare SC culture medium with 3mM, 4mM, 4.5mM, 5mM, 5.5mM, 6mM, 6.5mM, 7mM copper ion and SC culture medium with 0.01mM, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 0.15mM, 0.2mM cadmium ion. Through detecting the number, size of colony of different strains on SC plates with gradient concentrations. We further narrow the range of concentrations and screen strains with optimal characteristics.</p> |
| − | <p>What's more, we measure the survivial rate of optimal strains with original strains <i>synX</i>. After cultivating yeasts in YPD overnight, we take 200μL culture medium into ultrahigh concentration copper ion and cadmium ion solution. Then, | + | <img> |
| + | <h5>Verification of Cre-EBD Effect (Dilution Assay and Measurement of Cell Survival Rate)</h5> | ||
| + | <p>To demonstrate the verification of Cre-EBD effect, we diluted optimal strains to 10<sup>-1</sup>、10<sup>-2</sup>、10<sup>-3</sup>、10<sup>-4</sup>、10<sup>-5</sup> and made dilution assay on SC culture medium with copper ion and cadmium ion. Obviously if optimal strains grow better than other blanks, the answer is YES.</p> | ||
| + | <img> | ||
| + | <p>What's more, we measure the survivial rate of optimal strains with original strains <i>synX</i>. After cultivating yeasts in YPD overnight, we take 200μL culture medium into ultrahigh concentration copper ion and cadmium ion solution. Then, plate after 10min, 30min, 1h and 2h. Through counting the number of colony, we can obtain and compare the curve describing the cell survival rate of optimal strain and <i>synX</i>.</p> | ||
| + | <img> | ||
<div class="collapse-card__close_handler mt1 align-right mouse-pointer"> | <div class="collapse-card__close_handler mt1 align-right mouse-pointer"> | ||
Revision as of 03:30, 31 October 2017
/* OVERRIDE IGEM SETTINGS */
Design
Background
Human existence on earth is almost impossible without the heavy metals. Even though important to mankind, exposure to them during production, usage and their uncontrolled discharge in to the environment has caused lots of hazards to man, other organisms and the environment itself. Heavy metals can enter human tissues and organs via inhalation, diet, and manual handling. As the process of urbanization and industrialization goes deeper and deeper, heavy metal pollution, a noticeable threaten to almost all the creatures, has become an essential problem to solve.
According to our human practice, the situation of heavy metal pollution (copper and cadmium ions) is marked on a world map, and the severity of heavy metal pollution has been increasing all over this map. Places with serious pollution includes middle Asia, eastern Asia, southern Europe, and Latin America. In addition, not only fresh water sources, but also soil and crops are seriously contaminated by heavy metals. On average, during three out of ten suppers we have, we absorb excess heavy metals over the standard concentration.
Considering the rigorous situation we face, our team decided to design an advanced system for typical toxic heavy metal disposal based on Saccharomyces cerevisiae.