Brittneywick (Talk | contribs) |
Evan pepper (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
font-size: 120%; | font-size: 120%; | ||
| − | font-weight: | + | font-weight: 400; |
} | } | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
font-style: normal !important; | font-style: normal !important; | ||
font-size: 140% !important; | font-size: 140% !important; | ||
| − | font-weight: | + | font-weight: 400 !important; |
width: 100% !important; | width: 100% !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
opacity: 1; | opacity: 1; | ||
display: inline-block; | display: inline-block; | ||
| − | width: | + | width: 30%; |
height: auto; | height: auto; | ||
transition: .5s ease; | transition: .5s ease; | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
opacity: 1; | opacity: 1; | ||
display: inline-block; | display: inline-block; | ||
| − | width: | + | width: 65%; |
height: auto; | height: auto; | ||
transition: .5s ease; | transition: .5s ease; | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
.proj-button:hover .proj-button-image { | .proj-button:hover .proj-button-image { | ||
| − | opacity: 0. | + | opacity: 0.2; |
} | } | ||
.proj-button:hover .proj-button-image-solo { | .proj-button:hover .proj-button-image-solo { | ||
| − | opacity: 0. | + | opacity: 0.2; |
} | } | ||
.proj-button:hover .proj-button-desc { | .proj-button:hover .proj-button-desc { | ||
| − | opacity: 0. | + | opacity: 0.8; |
} | } | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
font-size: 20px; | font-size: 20px; | ||
font-family: "Objektiv-mk1" !important; | font-family: "Objektiv-mk1" !important; | ||
| − | font-weight: | + | font-weight: 400 !important; |
padding: 16px 32px; | padding: 16px 32px; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
font-style: italic !important; | font-style: italic !important; | ||
| − | + | font-size: 28px; | |
| − | font-size: | + | line-height: 130%; |
| − | line-height: | + | |
} | } | ||
.quote-person { | .quote-person { | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
| − | font-size: | + | font-size: 22px; |
width: 100% !important; | width: 100% !important; | ||
text-align: right !important; | text-align: right !important; | ||
| Line 144: | Line 143: | ||
.titleimg { | .titleimg { | ||
vertical-align: middle; | vertical-align: middle; | ||
| − | width: | + | width: 25%; |
} | } | ||
| Line 153: | Line 152: | ||
.diagram-image { | .diagram-image { | ||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
| − | padding-left: 20px | + | padding-left: 20px; |
} | } | ||
| Line 177: | Line 176: | ||
} | } | ||
| + | .diagram-image-right-1 { | ||
| + | width: 45%; | ||
| + | padding-left: 30px; | ||
| + | float: right; | ||
| + | text-align: center; | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | padding-bottom: 15px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .row { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: inherit; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: inherit; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container-3 { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: inherit; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .col-md-4 { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | } | ||
@media (min-width: 1144px) { | @media (min-width: 1144px) { | ||
.container { | .container { | ||
| + | width: 100% !important; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container-3 { | ||
width: 100% !important; | width: 100% !important; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 214: | Line 244: | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
font-style: italic !important; | font-style: italic !important; | ||
| − | + | font-size: 26px; | |
| − | font-size: | + | |
} | } | ||
.quote-person { | .quote-person { | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
| − | font-size: | + | font-size: 20px; |
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
text-align: right; | text-align: right; | ||
| Line 233: | Line 262: | ||
.container { | .container { | ||
| + | width: 80% !important; | ||
| + | padding-left: 0px !important; | ||
| + | padding-right: 0px !important; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container-3 { | ||
width: 80% !important; | width: 80% !important; | ||
padding-left: 0px !important; | padding-left: 0px !important; | ||
| Line 260: | Line 295: | ||
opacity: 1; | opacity: 1; | ||
display: inline-block; | display: inline-block; | ||
| − | width: | + | width: 32%; |
height: auto; | height: auto; | ||
transition: .5s ease; | transition: .5s ease; | ||
| Line 284: | Line 319: | ||
-ms-transform: translate(-50%, -50%) | -ms-transform: translate(-50%, -50%) | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .overlap-button-text { | ||
| + | background-color: rgba(94, 94, 94, 0.4); | ||
| + | border-radius: 60px; | ||
| + | color: white; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .diagram-image-right-1 { | ||
| + | padding-left: 10px; | ||
| + | padding-right: 10px; | ||
| + | font-size: 65%; | ||
| + | line-height: 1.5; | ||
| + | width: 60%; | ||
| + | } | ||
h1 { | h1 { | ||
| Line 307: | Line 356: | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
font-style: italic !important; | font-style: italic !important; | ||
| − | + | font-size: 20px; | |
| − | font-size: | + | |
} | } | ||
| Line 326: | Line 374: | ||
figcaption { | figcaption { | ||
| − | font-size: | + | font-size: 14px; |
| − | line-height: | + | line-height: 140%; |
} | } | ||
| Line 338: | Line 386: | ||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
padding-left: 0px; | padding-left: 0px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .reference-list { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: 12px; | ||
| + | text-align: left; | ||
| + | list-style-type: none; | ||
| + | line-height: 100%; | ||
| + | margin-bottom: 80px; | ||
| + | margin-right: -70px; | ||
| + | margin-left: -70px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .row-3 { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: 75%; | ||
| + | line-height: 1.5; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .row { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | line-height: 1.5; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | line-height: 1.5; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container-3 { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: 65%; | ||
| + | line-height: 1.5; | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 350: | Line 431: | ||
opacity: 1; | opacity: 1; | ||
display: inline-block; | display: inline-block; | ||
| − | width: | + | width: 50%; |
height: auto; | height: auto; | ||
transition: .5s ease; | transition: .5s ease; | ||
| Line 374: | Line 455: | ||
-ms-transform: translate(-50%, -50%) | -ms-transform: translate(-50%, -50%) | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .overlap-button-text { | ||
| + | background-color: rgba(94, 94, 94, 0.5); | ||
| + | border-radius: 60px; | ||
| + | color: white; | ||
| + | font-size: 12px; | ||
| + | } | ||
.firstword { | .firstword { | ||
| Line 407: | Line 495: | ||
font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1' !important; | ||
font-style: italic !important; | font-style: italic !important; | ||
| − | + | font-size: 17px; | |
| − | font-size: | + | |
} | } | ||
| Line 431: | Line 518: | ||
figcaption { | figcaption { | ||
| − | font-size: | + | font-size: 12px; |
| − | line-height: | + | line-height: 130%; |
} | } | ||
| Line 438: | Line 525: | ||
margin-left: -10px !important; | margin-left: -10px !important; | ||
margin-right: -10px !important; | margin-right: -10px !important; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .reference-list { | ||
| + | font-family: 'objektiv-mk1'; | ||
| + | font-size: 12px; | ||
| + | text-align: left; | ||
| + | list-style-type: none; | ||
| + | line-height: 100%; | ||
| + | margin-bottom: 80px; | ||
| + | margin-right: -50px; | ||
| + | margin-left: -50px; | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 454: | Line 552: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <img class="titleimg" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/ | + | <img class="titleimg" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/88/Spirulinatitle.png"> |
<h1>TARGET ORGANISM</h1> | <h1>TARGET ORGANISM</h1> | ||
| Line 464: | Line 563: | ||
<div class="text-container"> | <div class="text-container"> | ||
<div class="container"> | <div class="container"> | ||
| − | <p><span class="quote">"The concentration of protein and vitamins in Spirulina has led many to classify it as the 'most nutrient dense food on the planet.' Compared to other foods gram for gram, it lives up to this reputation | + | <p><span class="quote">"The concentration of protein and vitamins in Spirulina has led many to classify it as the 'most nutrient dense food on the planet.' Compared to other foods gram for gram, it lives up to this reputation"</span></p> |
<div class="quote-person">~Wellness Mama on Spirulina Benefits<sup>[1]</sup></div> | <div class="quote-person">~Wellness Mama on Spirulina Benefits<sup>[1]</sup></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 477: | Line 576: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <div class="diagram-image-right-1"> | |
| − | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/7/76/Biomass_Diagram.png" style="width: 100%;"> | |
| − | + | <i>Biological composition of Arthrospira platensis, commonly known as Spirulina.</i> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | </div | + | |
<p>In researching host organisms, we discovered that the cyanobacteria <i>A. platensis</i> produces a wide range of essential vitamins and supplements. <i>A. platensis</i> is a cyanobacteria that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for consumption by the FDA<sup>[2]</sup>. The nutrient composition of <i>A. platensis</i> consists of 65% protein (including all 8 essential amino acids), 15% carbohydrates, 6% lipids, carotenoids, vitamins B<sub>1</sub>, B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>3</sub>, B<sub>5</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>7</sub>, B<sub>9</sub>, D, E, antioxidants, and minerals including potassium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, sodium, and zinc<sup>[3]</sup>.</p> | <p>In researching host organisms, we discovered that the cyanobacteria <i>A. platensis</i> produces a wide range of essential vitamins and supplements. <i>A. platensis</i> is a cyanobacteria that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for consumption by the FDA<sup>[2]</sup>. The nutrient composition of <i>A. platensis</i> consists of 65% protein (including all 8 essential amino acids), 15% carbohydrates, 6% lipids, carotenoids, vitamins B<sub>1</sub>, B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>3</sub>, B<sub>5</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>7</sub>, B<sub>9</sub>, D, E, antioxidants, and minerals including potassium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, sodium, and zinc<sup>[3]</sup>.</p> | ||
| Line 493: | Line 591: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p>Therefore, an axenic strain of <i>A. platensis</i>, UTEX 2340, is being created for eventual sequencing and release to NCBI. This is being done in an effort to help the | + | <p>Therefore, an axenic strain of <i>A. platensis</i>, UTEX 2340, is being created for eventual sequencing and release to NCBI. This is being done in an effort to help the scientific community by providing a better understanding of <i>A. platensis</i> genetics. Sequencing the whole genome opens the possibility of applying the genetic modifications in PCC 7942, described in the Metabolic Engineering section for <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Acetaminophen">acetaminophen</a> and <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/B-12">vitamin B<sub>12</sub></a>, into <i>A. platensis</i> as well.</p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 499: | Line 597: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <div class="container"> | + | <!-- <div class="container-3"> --> |
| − | <div class="row"> | + | <!-- <div class="row-3"> --> |
<div class="col-md-4"> | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/aa/Spirulina2_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/aa/Spirulina2_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | ||
| + | <i>TRITC HYQ (EX 530-550, DM 565, BA 590-650) filter</i> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="col-md-4"> | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4e/Spirulina1_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4e/Spirulina1_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | ||
| + | <i>Open filter</i> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="col-md-4"> | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/80/Spirulina3_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/80/Spirulina3_pic.png" style="width: 100%;"> | ||
| + | <i>FITC-HYQ (EX 460-500, DM 505, BA 510-560) filter</i> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | </div> | + | <!-- </div> --> |
| − | </div> | + | <br> |
| + | <!-- </div> --> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p style="padding-top: 10px; text-align: center;"><i>Images of A. platensis using an epifluorescence microscope Nikon Eclipse E400.</i></p> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 520: | Line 625: | ||
<p>The UTEX Culture Collection of Algae at the University of Texas at Austin provided a xenic strain, UTEX 2340, of <i>A. platensis</i> along with a modified SAG medium to raise a base culture. Due to a lack of detailed axenicity protocols for <i>A. platensis</i>, a new protocol was constructed from several protocols<sup>[5, 6, 7]</sup>. This new protocol was implemented and includes ultrasonication/bead-beating, filtration, pH treatment, antibiotic treatment, and serial dilutions in order to rid <i>A. platensis</i> of xenic microorganisms. To learn more about the protocols involved, check out our notebook page <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Notebook">here!</a> </p> | <p>The UTEX Culture Collection of Algae at the University of Texas at Austin provided a xenic strain, UTEX 2340, of <i>A. platensis</i> along with a modified SAG medium to raise a base culture. Due to a lack of detailed axenicity protocols for <i>A. platensis</i>, a new protocol was constructed from several protocols<sup>[5, 6, 7]</sup>. This new protocol was implemented and includes ultrasonication/bead-beating, filtration, pH treatment, antibiotic treatment, and serial dilutions in order to rid <i>A. platensis</i> of xenic microorganisms. To learn more about the protocols involved, check out our notebook page <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Notebook">here!</a> </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="container" style="width: 100%"> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
| + | <h3>P R O J E C T</h3> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Project" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/64/UCSCproject.png" class="proj-button-image-solo"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">HOMEPAGE</div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="col-md-8"> | ||
| + | <h3>Click here to learn more!</h3> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Acetaminophen" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/6c/Acetaminophenicon.png" class="proj-button-image"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">ACETAMINOPHEN</div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/B-12" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/8/89/B12_title.png" class="proj-button-image"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">VITAMIN B<sub>12</sub></div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Model" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/be/Modeling_button.png" class="proj-button-image"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">MODELING</div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Demonstrate" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/ad/Resulticon.png" class="proj-button-image"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">RESULTS</div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UCSC/Part_Collection" class="proj-button"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/9c/Parts_icon.png" class="proj-button-image"> | ||
| + | <div class="proj-button-desc"> | ||
| + | <div class="overlap-button-text">PARTS</div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 534: | Line 702: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:08, 2 November 2017

TARGET ORGANISM
"The concentration of protein and vitamins in Spirulina has led many to classify it as the 'most nutrient dense food on the planet.' Compared to other foods gram for gram, it lives up to this reputation"
We are currently using the cyanobacteria genus Synechococcus elongatus as a model for the FDA-approved Arthrospira platensis, commonly known as Spirulina. By focusing on an edible cyanobacteria, we hope to generate an easily consumable, photosynthetic culture of vitamins or pharmaceutical synthesizers.
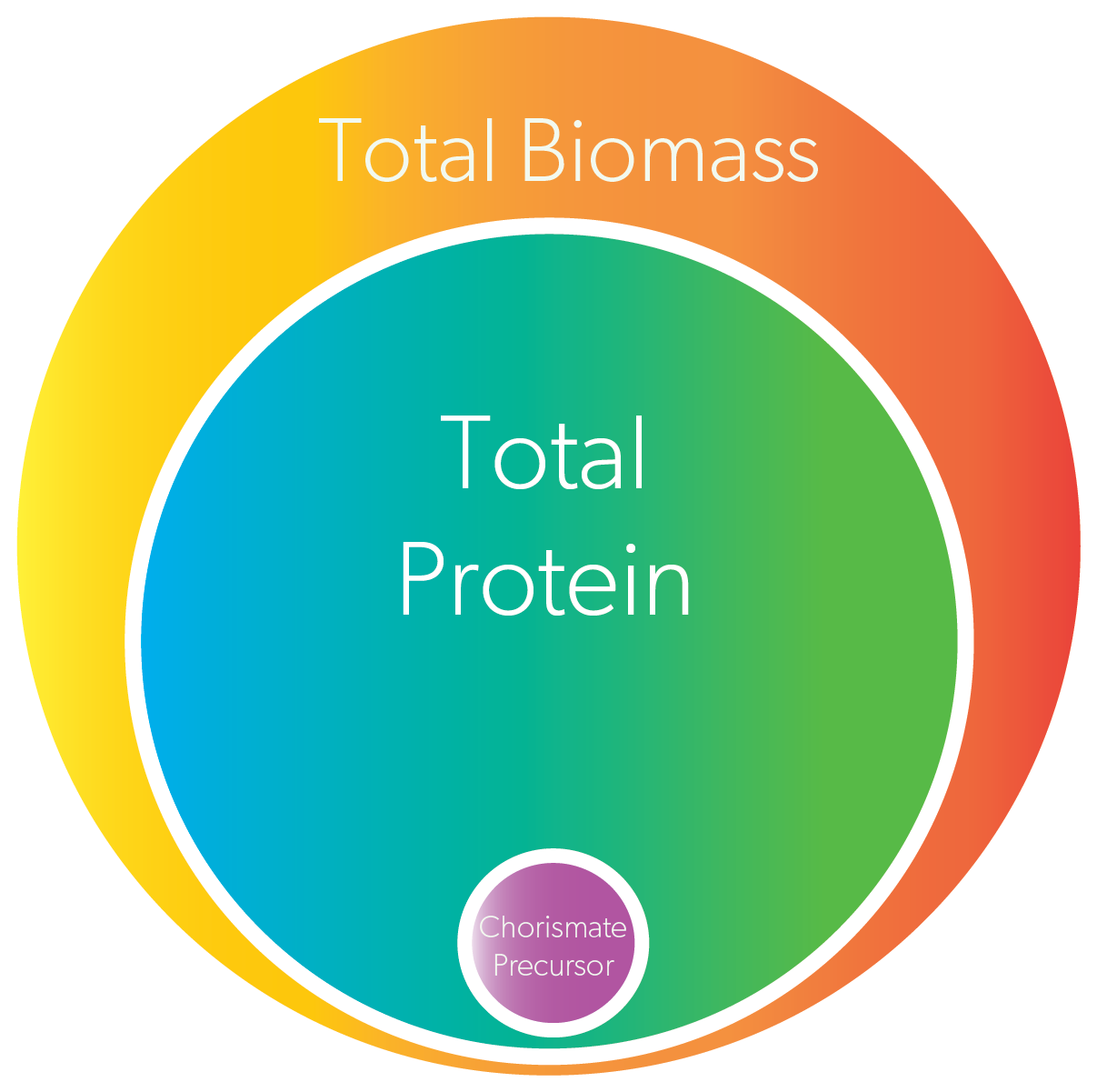 Biological composition of Arthrospira platensis, commonly known as Spirulina.
Biological composition of Arthrospira platensis, commonly known as Spirulina.
In researching host organisms, we discovered that the cyanobacteria A. platensis produces a wide range of essential vitamins and supplements. A. platensis is a cyanobacteria that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for consumption by the FDA[2]. The nutrient composition of A. platensis consists of 65% protein (including all 8 essential amino acids), 15% carbohydrates, 6% lipids, carotenoids, vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, D, E, antioxidants, and minerals including potassium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, sodium, and zinc[3].
Upon further investigation, it became apparent that a system for genetic manipulation in A. platensis hadn’t been well-established[4] and developing such a system would not be possible within the iGEM time constraints, not to mention that it is near impossible to obtain an axenic live culture within the United States.
Therefore, an axenic strain of A. platensis, UTEX 2340, is being created for eventual sequencing and release to NCBI. This is being done in an effort to help the scientific community by providing a better understanding of A. platensis genetics. Sequencing the whole genome opens the possibility of applying the genetic modifications in PCC 7942, described in the Metabolic Engineering section for acetaminophen and vitamin B12, into A. platensis as well.
 TRITC HYQ (EX 530-550, DM 565, BA 590-650) filter
TRITC HYQ (EX 530-550, DM 565, BA 590-650) filter
 Open filter
Open filter
 FITC-HYQ (EX 460-500, DM 505, BA 510-560) filter
FITC-HYQ (EX 460-500, DM 505, BA 510-560) filter
Images of A. platensis using an epifluorescence microscope Nikon Eclipse E400.
The UTEX Culture Collection of Algae at the University of Texas at Austin provided a xenic strain, UTEX 2340, of A. platensis along with a modified SAG medium to raise a base culture. Due to a lack of detailed axenicity protocols for A. platensis, a new protocol was constructed from several protocols[5, 6, 7]. This new protocol was implemented and includes ultrasonication/bead-beating, filtration, pH treatment, antibiotic treatment, and serial dilutions in order to rid A. platensis of xenic microorganisms. To learn more about the protocols involved, check out our notebook page here!





