| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
<h2 class="header-subsection"> Gene randomizer </h2><br> | <h2 class="header-subsection"> Gene randomizer </h2><br> | ||
<p>Gene randomizer utilizes the ability of site-specific recombinases to perform dynamic DNA inversion, and has been utilized by researchers to develop the brainbow system (2) to label individual cells:</p> | <p>Gene randomizer utilizes the ability of site-specific recombinases to perform dynamic DNA inversion, and has been utilized by researchers to develop the brainbow system (2) to label individual cells:</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align: center;"><img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b9/T--Edinburgh_UG--Randomizer.png"></div><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | Using biobricks from our toolkit, they can be assembled using standard biobrick assembly protocols. The SSR systems in our toolkit are also characterized in terms of orthogonality so that it is possible to have multiple gene randomizers working parallel within the same cell: | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align: center;"><img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/f2/T--Edinburgh_UG--parallel_randomizer.png"></div><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | We envision that such a design could be used for generating a heterogeneous population that can each cell carries a distinct combination of gene expression, and can be screened with single cell technology. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <h2 class="header-subsection"> Logic gates </h2><br> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | Biological logic gates can be very useful to create sophisticated genetic circuits (3). We have used tyrosine recombinases in our toolkit to design six logic gates (OR, AND, NOR, NAND, XOR, XNOR) using only excision mechanism: | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/53/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_AND_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">AND gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/1c/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_OR_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">OR gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/cf/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_NAND_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">NAND gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/d/d7/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_NOR_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">NOR gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/39/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_XOR_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">XOR gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | <img class="same-width" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/ca/T--Edinburgh_UG--design_XNOR_gate.png"> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 20px">XNOR gate</figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | This kind of construct is possible only when the recombinases and their target sites are well defined to be non-interfering (i.e. orthogonal), so that they can be designed according to engineering principle, building from simple biobricks. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2 class="header-subsection"> References </h2><br> | ||
| + | <p> 1. Singha, T.K., Gulati, P., Mohanty, A., Khasa, Y.P., Kapoor, R.K., Kmuar, S. (2017) Efficient genetic approaches for improvement of plasmid based expression of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli: A review. Process biochemistry. 55: 17-31 | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | 2. Livet, J., Weissman, T.A., Kang, H., Draft, R.W., Lu, J., Bennis, R.A., Sanes, J.R., Lichtman, J.W. (2007) Transgenic strategies for combinatorial expression of fluorescent proteins in the nervous system. Nature. 450: 56-62 | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | 3. Weinberg, B.H., Hang Pham, N.T., Caraballo, L.D., Lozanoski, T., Engel, A., Bhatia, S., Wong, W.W. (2017) Large-scale design of robust genetic circuits with multiple inputs and outputs for mammalian cells. Nature biotechnology. 35(5): 453-462 | ||
| + | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 05:51, 31 October 2017
Design
In our project, we view a single recombinase and a pair of its target site as a functional unit for building dynamic switches. With this concept in mind, we designed more sophisticated composite parts such as the measurement devices, gene randomizer, logic gates, and pulse generator.
Measurement devices
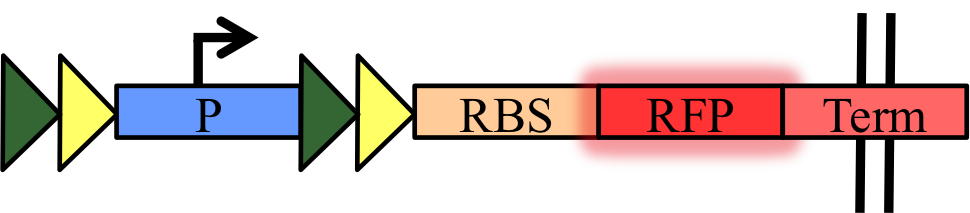
To quantify orthogonality and recombination efficiency, we have designed simple measurement devices to characterize our basic parts – the five recombinases (Cre, Dre, VCre, SCre, Vika) and their target sites (LoxP, Rox, Vlox, Slox, Vox). They are a set of fifteen biobricks that have a target sites-flanked transcriptional terminator inserted between a constitutive promoter and a RFP:

Thus, when recombination occurred, the transcriptional terminator will be excised, expressing the RFP. We propose to use this set of device and our protocol for standardized measurement of recombination progression using plate reader.
Pulse generator
Aware of the potential for SSR to mediate genetic engineering in a highly dynamic way, we have designed a novel construct that once initiate, will express multiple genes in separated pulses of transcription and translation.






The functionality of the pulse generator has been simulated in the model page , where we have performed stochastic modeling and used it to predict the behavior of the pulse generator in different conditions. The pulse generator may find applications in metabolic engineering, where one can separate temporally the expression of several genes, thus lowering the metabolic stress of a cell (1).
Gene randomizer
Gene randomizer utilizes the ability of site-specific recombinases to perform dynamic DNA inversion, and has been utilized by researchers to develop the brainbow system (2) to label individual cells:

Using biobricks from our toolkit, they can be assembled using standard biobrick assembly protocols. The SSR systems in our toolkit are also characterized in terms of orthogonality so that it is possible to have multiple gene randomizers working parallel within the same cell:

We envision that such a design could be used for generating a heterogeneous population that can each cell carries a distinct combination of gene expression, and can be screened with single cell technology.
Logic gates
Biological logic gates can be very useful to create sophisticated genetic circuits (3). We have used tyrosine recombinases in our toolkit to design six logic gates (OR, AND, NOR, NAND, XOR, XNOR) using only excision mechanism:





This kind of construct is possible only when the recombinases and their target sites are well defined to be non-interfering (i.e. orthogonal), so that they can be designed according to engineering principle, building from simple biobricks.
References
1. Singha, T.K., Gulati, P., Mohanty, A., Khasa, Y.P., Kapoor, R.K., Kmuar, S. (2017) Efficient genetic approaches for improvement of plasmid based expression of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli: A review. Process biochemistry. 55: 17-31
2. Livet, J., Weissman, T.A., Kang, H., Draft, R.W., Lu, J., Bennis, R.A., Sanes, J.R., Lichtman, J.W. (2007) Transgenic strategies for combinatorial expression of fluorescent proteins in the nervous system. Nature. 450: 56-62
3. Weinberg, B.H., Hang Pham, N.T., Caraballo, L.D., Lozanoski, T., Engel, A., Bhatia, S., Wong, W.W. (2017) Large-scale design of robust genetic circuits with multiple inputs and outputs for mammalian cells. Nature biotechnology. 35(5): 453-462











