TNCR_Korea

What is the problem with gluten food?
Gluten-contaning food is staple food in the daily human diet, including wheat, barley and rye. It is used to give the chewy texture to the final products. Gliadins and glutenins are the two main components of the gluten. Especially, incomplete breakdown of gliadin which is rich in proline is associated with the development of celiac disease(CD) and disorder such as depression and schizophrenia. Gliadinomorphin-7 (Tyr-Pro-Gln-Pro-Gln-Pro-Phe), is an intermediate product of gliadin, are finally cleaved by Dipeptidyl peptidase IV(DPP4) that can cleave N-terminal dipeptides with proline at the second position. Remaining tripeptide acts as a inhibitor of DPP4. DPP4 inactivity leads to the incomplete breakdown of gluten and can increase the diseases mentioned above. Thus, people who have gluten sensitivity need to additional DPP4 for gluten digestion.
Question
What's the difference between health people and gluten sensitivity people? Is it coming from genetic defect? or digestion activity of intestinal bacteria? That's what we want to address by experimental approaches.
Approach
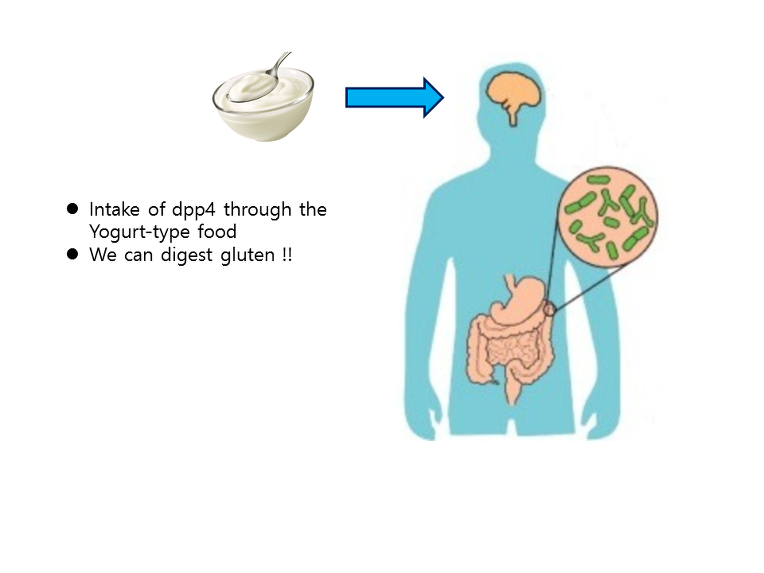
Team TNCR-Korea is focusing on the intestinal bacteria (Gut microflora) and has set hypothesis that introducing the DPP4 gene into intestinal bacteria of gluten sensitivity people may help their gluten indigestion caused by incomplete breakdown.
Method
1. Analysis of intestinal bacterial flora in gluten sensitivity people
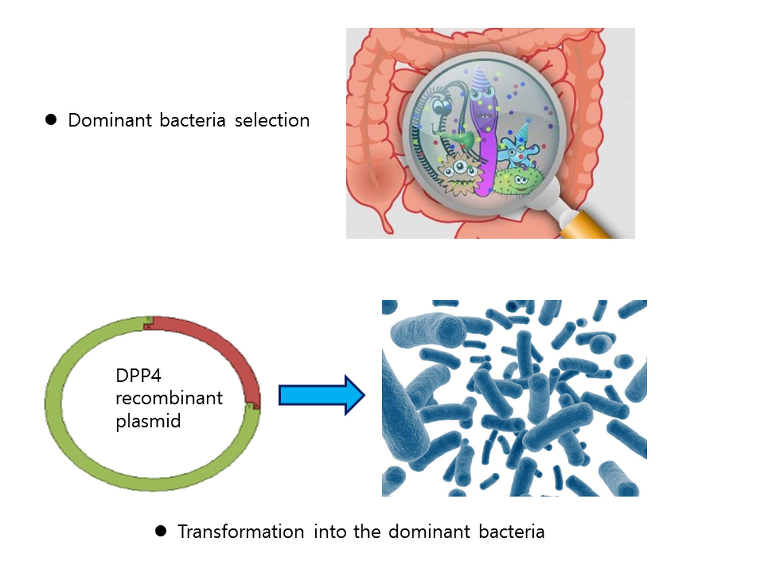
2. Dominant bacteria selection which have strong activity of DPP4.
3. Introduction of DPP4 to the dominant gut bacteria of weak DPP4 activities by gene cloning and transformation methods.
4. Yogurt-type intake of probiotics (beneficial bacteria) with recombinant DPP4 construct.
reference
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gluten
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gliadin
3. Pruimboom L, de Punder K. (2015). The opioid effects of gluten exorphins: asymptomatic celiac disease. J Health Popul Nutr. 33:24
4. Detel D, Persić M, Varljen J. (2007). Serum and intestinal dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV/CD26) activity in children with celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 45(1):65-70.
Image reference
1. https://www.glutenfreegigi.com/celiac-disease-versus-gluten-sensitivity/
2. https://www.organicfacts.net/coeliac-disease-gluten-intolerance.html
3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dipeptidyl_peptidase-4
4. http://www.ezbalance.com/how-to-colonize-your-gut-with-beneficial-bacteria/
5, http://www.di.uq.edu.au/proj4aproc
6. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/05/130515113744.htm
7. http://uinkin.tistory.com/
8.http://www.yesvegetarian.com/is-yogurt-your-favorite-then-you-need-to-read-this
UPLOAD FILES

