
EXPERIMENTS:
STEP 1: Create guideRNA Plasmid
Why
We produced our gRNA plasmids in order to repress targeted fluorescent proteins on our reporter plasmid. This allows more combinations than possible with reporters alone.
How
Refer to step 2 for plasmid construction. The sgRNA plasmid uses static promoter J23119, and sgRNA in place of reporter proteins. We constructed plasmids that contain one gRNA each, although we could expand this to include 3 or more gRNAs per plasmid. In our lab book you can see that we can easily transform this plasmid into E. coli along with pReporter with high efficiency. The gRNA plasmid uses the same ligation strategy as pReporter which means that the process of creating more combinations is simple and minimises the cost associated with many enzymes.
Results
Refer to CRISPRi & gRNA efficiency results.
STEP 2: Create Reporter Plasmid

Why
To create a stepwise and logical order of production, a reporter plasmid was constructed firstly, out of only various promoter types, mRFP and terminators, to allow for testing. This was then escalated to include dCas9 for the final experiment.
How

Each individual Promoter-Reporter-Terminator brick contains interchangeable parts. The three parts are linked together with Bsa1 sites so that there is no preference for any part when ligating together. This allows randomness to be added later. This method is used also for the construction of Promoter-gRNA-Terminator bricks so that this could be randomised in the future. The bricks are then flanked by a prefix and suffix, and these are flanked by restriction sites ABCD on either end. Digestion of bricks with A+B, B+C, and C+D allows any brick to be placed in any position within the plasmid but it would be pre-determined. This means that the no one promoter-reporter-terminator brick would be limited to one specific place in the plasmid, which allows another level of randomness in assembly as we would not know which reporter was being placed where, which could also affect expression levels.
The arrangement of the DCBA restriction system means that any brick can be placed in any position in the plasmid which allows expansion of possibilities whilst maintaining randomness of insertion later. Bricks can be joined together via amplifying each randomly assembled brick through common amplification sites and then cutting them using a set of restriction enzymes which give each plasmid a specific order of bricks, depending on which are cut and then ligated together.

This was then used for the promoter library.
After this, the same method as above was used for the final dCas9 including vector. However with an addition of dCas9 in the final ligation phase. In this way two promoter libraries were produced.
Results
Found in promoter library section.
STEP 3: Promoter Library

Why
A library of promoters with variant expression capacity was constructed for use with reporter proteins. RFP was used as the reporter for ease of screening.How
Results


STEP 4: Random Ligations

Why
The random ligation of different promoter-protein bricks is an experiment to test the viability of a brownian motion driven random ligation process. This random ligation is the basis for the unpredictability of a large scale key design process. The experiment hoped to produce a random mixture of fluorescent protein expression levels. This random mixture of multiple proteins in a single vector would then show the viability of the Key.coli restriction enzyme-ligation process for achieving unpredictability for keys.
How
The strongest and weakest promoters were chosen to give the most easily visible result, promoters E and 4. Promoter 4 gives a high expression of fluorescent proteins, as shown by our promoter library findings. The promoters were then attached to each reporter protein CFP, RFP and GFP via BsaI digestion and ligation along with a terminator to form six "brick" variants. After amplification of the bricks produced via PCR, seven products combinations were ligated to a low copy backbone in the pattern of red, green and blue fluorescent proteins, consistently through the controlled use of the DCBA digestion site. Each ligation has only one ligation slot (due to availability of restriction cut sites) per reporter colour, leaving random chance to produce a combination of all the possible variants in the random ligations where multiple promoters are available.
e= empty promoter, h= high expression promoter
e= empty promoter, h= high expression promoter

These bricks were ligated with the backbone as follows:
This produced a control for each reporter fluorescent protein in isolation. It also produced a control for all reporters on either highest expression or lowest expression. This finally also produced a random set of colonies for isolation (after transformation) for comparison and test for true randomness.
Results
Twelve colonies were picked from the pilot study of random ligation, which gave the following distribution: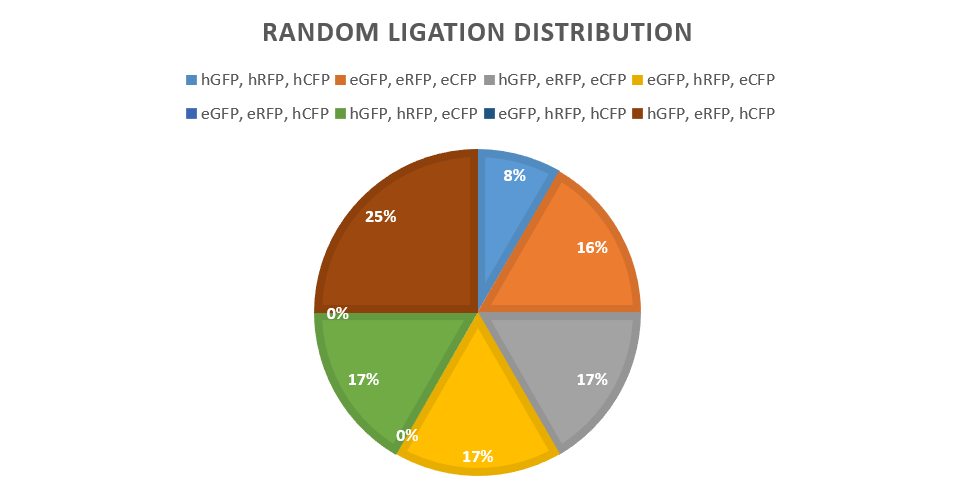
STEP 5: Freeze Drying & Revival

Why
For Key. coli to become a success, the ability to transport the bacterial key in a safe way whilst maintaining a sample of viable cells with similar expression patterns is vital. The Key. coli cells can either be kept in a metabolically active state or in a freeze dried, metabolically inactive state. The first option has two major disadvantages: a continues supply of nutrients will have to be provided and through successive bacterial generations genetic drift will occur, meaning that cells will lose certain traits, traits that are not essential for the applied growth conditions. The reporters we will be expressing inside the cell will not be essential for cell survival and thus will be lost, hence the key will no longer be functional. The second option, storing freeze dried cells inside a sealed capsule, allows ‘semi’ long term storage with very little phenotypic change and no need for nutrients. In addition, they are very quickly activated when properly mixedwith recovery medium and nutrients.
When the cells are revived, their reporter levels will need to be measured to ascertain the key’s identity. This brings into question how fast and accurately this process can and should occur. When cells are freeze dried, any proteins are also locked; after revival, there will be residual amounts of the reporter present in approximately the correct proportions. Although these signals are present and representative, they will be low and not optimal, after 4 hours the cells will have grown substantially to produce an appropriate level of reporter to measure. With the experiment described below we show that freeze drying cells is a reliable and reproducible way to store the Key. coli cells.
How
The cells were freeze dried in accordance with a protocol we devised, for further details click here. To summarise, colonies of our bacteria were grown overnight to produce a batch of our specimen. New media was inoculated with our bacteria and grown for 24 hours, with OD600nm absorbance and fluorescence intensity at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 hour timepoints. Just before the bacteria enter the stationary growth phase, a 1 ml sample was taken for freeze drying. The cells were washed twice with water before resuspending the cells in a 10% sterile sucrose solution.The sucrose solution acts as our cryo-protectant, therefore the cell resuspension was incubated for 5 minutes on the becnh to allow the sucrose to build up inside the cell. Subsequently, the samples were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen at -200°C and placed on dry ice. After all samples were frozen, the tube lids were pierced and placed in a chilled vacuum chamber overnight to remove all present moisture
Results
The results presented in figure 1 show that the two promoters, SP4 and WP1, are clearly distinct from each other at every stage of revival and storage time. This information is important as we will need to calibrate the thresholds for identification accordingly. The data also shows that storing the cells for two weeks at different temperatures has no to little effect on the reporter expression.

Figure 1: Graph of strong promoter 4 and weak promoter 1 transformed cells RFP fluorescence assay after freeze-drying revival two weeks and three weeks after samples were freeze dried.
However, there is a notable decease in fluorescence from 2 to 3 weeks at room temperature, especially pronounced at 4 and 6 hour after revival.. This problem may be mitigated in that the drop offs seem proportional to both WP1 and SP4, so the ratios of expression may remain the same. Having said this, the differences in expression would be within the bounds of the thresholds set to compare the two, as even with the changes they would still be identifiable. One might argue that the need to set so many time and storage dependent thresholds makes the system unnecessary complicated. To minimise the described variables that need to be taken into consideration keys stored at room temperature should be replaced after two weeks. Keys which require long term storage should be stored at -20°C.
Interestingly, as predicted there is a substantial amount of fluorescence detectable 2 hours after revival, suggesting that a bacterial key could possibly be identifiable with little waiting period. However, they are undoubtedly more pronounced at 4 and 6 hours which would likely to be a more accurate time to measure.
In conclusion, these results are very promising and show that cells remain viable and reliably express the reporter for up to three weeks at convenient storage conditions necessary for our key to work in a practical sense.
For future research, this process could be optimised to produce even more reproducible results and yield a more robust identification process. Distinct 0 hour expression levels might also be possible, greatly increasing the potential of Key. coli becoming a common security system. Multiple reporters should be the next focus to strengthen the security of the key. All reporters will need to be tested for their stability and reproducibility.
STEP 6: CRISPRi & gRNA Efficiency

Why
In our experiment, the production of differentially identifiable expression patterns is paramount. A library of promoters with robust expression patterns was generated to achieve this (step 3 to 5). To further modulate the expression patterns, a promoter targeted short guide RNA (sgRNA)-dcas9 repression system was devised. Using such a system will add a third expression level to the already existing ON and OFF states of our system, expanding the options further.
The sgRNAs have a 20bp ‘SEED’ region homologous to the promoters (used in step 3) between the -10 and -35 box, which will form a complex with a deactivated Cas9. The complex will be directed to the promoter through the homology between promoter sequence and the sgRNA. Binding of this very big RNA-protein complex to the promoter sequence will inhibit recognition and binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region due to allosteric hindrance. The strength of inhibition is related to the binding affinity of the complex to the target DNA. Ideally, each promoter will have its own unique sgRNA which only inhibits the intended promoter to prevent cross interference.
How
To exemplify that the presence of a repression system would allow an increase in possible key outputs so we decided to start with a simple proof of function experiment. Therefore, we decided to go for a two plasmid based system.
One low copy vector was used to express both the catalytically inactive Cas9 protein and the RFP reporter, fused to any of the five promoters previously tested in step 3. Using a low-copy plasmid for the expression of reporter and dCas9 was a precautionary measure, as high levels of dCas9 can be toxic to the cells due to unspecific binding to other regions of the genome. Starting the experiments with only one reporter would allow us to easily establish how well each sgRNA represses the complementary promoter. The second plasmid was comprised of the sgRNAs and a high copy origin of replication (ori). Confining the sgRNAs to a separate vector is advantageous in that it can be easily substituted out for another vector, potentially detailing sgRNAs with a differing affinity to the promoter. This interchangeability can facilitate a ‘plug and play’ system to produce a multitude of expression levels with ease.
To select for a dual transformation, each vector backbone requires separate antibiotic resistances. Consequently, the high copy vector (containing sgRNAs) was given an chloramphenicol resistant cassette, the low copy backbone was given a erythromycin resistance cassette.
As a control, a sgRNA 0 was added to the library. The ‘SEED’ region of this sgRNA is not homologous to any of the promoters. This will act as a control, to signify how the expression will differ when inhibition is occurring. It will also serve later to increase the pool of possible expression patterns when we come to the random ligation experiments . These were cloned using traditional type II restriction cloning with BsaI sites.
To construct the sgRNAs, primer dimers were PCR amplified to generate the initial fragments of the sgRNA, it’s promoter, and terminator; also with their complimentary BsaI sites. After digestion with BsaI, the fragments were linearly ligated to produce promoter-sgRNA-terminator ‘bricks’. These were then amplified using a set of ‘universal’ primers designed to be capable of amplifying all of our ‘bricks’, these primers were complementary to a multiple cloning site(MCS) flanking each brick we produced. These sgRNA bricks were then digested using this MCS and ligated into their associated high copy backbone.
Results

The above graph shows characterization of the sgRNAs. As you can see, gRNA3, 4 and 5 are repressing well. gRNA 1 and 2 have no repression, and PE shows that there is very little expression as a background level.






