| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<!-- Normaler Text --> | <!-- Normaler Text --> | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
| − | Zhang <i>et al.</i> used an N-terminal truncated version of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, lacking the first 65 amino acids, since they observed some kind of toxicity resulting from the native N-terminal sequence (Zhang et al., 2017). For our project, we analyzed the amino acid sequence of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 using the prediction software Phobius (Käll et al., 2007). Using Phobius, we analyzed the signal peptide and the transmembrane topology of <i>Pt</i>NTT2. The analysis revealed that the native signal peptide is formed by amino acids 1 30, which means that Zhang et al. removed more than the native signal peptide for their experiment. The results of the prediction are shown in figure (1). Analysis of the transmembrane topology of the transporter, which is integrated into the plastid membrane in its native algal cell, shows iterative non-cytoplasmatic, transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions. The topology might indicate, that the transporter will be integrated into the inner membrane when expressed in <i>E. coli</i>. | + | Zhang <i><i>et al.</i></i> used an N-terminal truncated version of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, lacking the first 65 amino acids, since they observed some kind of toxicity resulting from the native N-terminal sequence (Zhang <i>et al.</i>, 2017). For our project, we analyzed the amino acid sequence of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 using the prediction software Phobius (Käll <i>et al.</i>, 2007). Using Phobius, we analyzed the signal peptide and the transmembrane topology of <i>Pt</i>NTT2. The analysis revealed that the native signal peptide is formed by amino acids 1-30, which means that Zhang <i>et al.</i> removed more than the predicted native signal peptide for their experiment. The results of the prediction are shown in figure (1). Analysis of the transmembrane topology of the transporter, which is integrated into the plastid membrane in its native algal cell, shows iterative non-cytoplasmatic, transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions. The topology might indicate, that the transporter will be integrated into the inner membrane when expressed in <i>E. coli</i>. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
| − | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/ | + | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/fa/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--phobiuspredictcomp.jpeg"> |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 1: Results of the analysis of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 using Phobius.</b><br> The 30 first amino acids are clearly recognized as a signal peptide. Ten transmembrane domains are predicted.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</article> | </article> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/05/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2_plasmids.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/05/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2_plasmids.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 2: Schematic overview of the design of the different transporter variants.</b> The lacUV5 promotor was used together with a strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>) for all parts. All variants except for pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were also tagged with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>). cMyc was used as a linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>).</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | All plasmids except pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were tagged with the same cMyc-GFP construct for imaging and western blots. cMyc was used as a linker to allow the targeting of the fusion protein with two separate antibodies, an anti-GFP antibody and the anti-cMyc antibody. The GFP part was taken from | + | All plasmids except pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were tagged with the same cMyc-GFP construct for imaging and western blots. cMyc was used as a linker to allow the targeting of the fusion protein with two separate antibodies, an anti-GFP antibody and the anti-cMyc antibody. The GFP part was taken from <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>, while the cMyc fragment was taken from <a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>. The fusion proteins were assembled using Gibson Assembly. A schematic overview of the design of the different plasmids is shown in Figure 2. |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 1: Designed and cloned plasmids for the analysis and characterization of <i>Pt</i>NTT2. </b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin: auto"> | <table style="margin: auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PtNTT2</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PtNTT2</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201004</td> | + | <td><b><a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201004">BBa_K2201004</a></b></td> |
<td>Only the cds</td> | <td>Only the cds</td> | ||
| − | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | < | + | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2</td> |
| + | <td><b><a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201000">BBa_K2201000</a></b></td> | ||
| + | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>) </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) </td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) </td> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201001">BBa_K2201001</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS ( | + | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 87: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575)</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575)</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201005</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201005">BBa_K2201005</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), truncated version lacking the first 30 amino acids | + | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>), truncated version lacking the first 30 amino acids</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 94: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 </td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 </td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201006</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201006">BBa_K2201006</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), native signal peptide replaced with the pelB signal peptide | + | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>), native signal peptide replaced with the pelB signal peptide</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201007</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201007">BBa_K2201007</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), native signal peptide replaced with a TAT signal peptide | + | <td>cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">BBa_B0034</a>), native signal peptide replaced with a TAT signal peptide</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 109: | Line 108: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201002</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201002">BBa_K2201002</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201000 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker ( | + | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201000 with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>), Myc epitope tag as linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 115: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575)-GFP</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575)-GFP</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201003</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201003">BBa_K2201003</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201001 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker ( | + | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201001 with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>), Myc epitope tag as linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 125: | Line 122: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575)-GFP</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575)-GFP</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201011</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201011">BBa_K2201011</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201005 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker ( | + | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201005 with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>), Myc epitope tag as linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 129: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201012</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201012">BBa_K2201012</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201006 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker ( | + | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201006 with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>), Myc epitope tag as linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 136: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | <td>pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2-GFP</td> | ||
| − | <td>BBa_K2201013</td> | + | <td><b><a href="<b>http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201013">BBa_K2201013</a></b></td> |
| − | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201007 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker ( | + | <td>Fusion protein of BBa_K2201007 with GFP (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040">BBa_E0040</a>), Myc epitope tag as linker (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2201181">BBa_K2201181</a>)</td> |
| − | + | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
| Line 160: | Line 154: | ||
<!-- Ueberschriften --> | <!-- Ueberschriften --> | ||
<h3> Cultivations of the Different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 Variants </h3> | <h3> Cultivations of the Different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 Variants </h3> | ||
| − | <article>Given that Zhang <i>et al.</i>, 2017 reported some kind of toxicity resulting from the N-terminal sequence of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, we first investigated if we could also observe the same toxicity associated with the N-terminal sequence. We also tested whether our own versions of the transporter | + | <article>Given that Zhang <i><i>et al.</i></i>, 2017 reported some kind of toxicity resulting from the N-terminal sequence of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, we first investigated if we could also observe the same toxicity associated with the N-terminal sequence. We also tested whether our own versions of the transporter results in better growth and reduced toxicity compared to the native transporter. Therefore, after cloning the plasmids in <i>E. coli</i> DH5α and verifying the correct assembly via sequencing, all plasmids were transformed into <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3). The presence of the correct plasmids was again verified by colony PCR. |
The first cultivations were carried out in shake flasks in LB media. A total cultivation volume of 50 mL was used. The cultures were incubated at 37 °C and 180 rpm. All cultures were inoculated with an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.01. OD<sub>600</sub> was measured every hour during lag and stationary phase and every 30 minutes during the exponential phase. The optical density was measured using an Eppendorf Photometer and standard cuvettes. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) without a plasmid and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) harboring pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Two biological replicates of each strain were tested and three technical replicates were measured for each timepoint. | The first cultivations were carried out in shake flasks in LB media. A total cultivation volume of 50 mL was used. The cultures were incubated at 37 °C and 180 rpm. All cultures were inoculated with an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.01. OD<sub>600</sub> was measured every hour during lag and stationary phase and every 30 minutes during the exponential phase. The optical density was measured using an Eppendorf Photometer and standard cuvettes. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) without a plasmid and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) harboring pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Two biological replicates of each strain were tested and three technical replicates were measured for each timepoint. | ||
| Line 166: | Line 160: | ||
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/57/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--shakeflask_PtNTT2.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/57/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--shakeflask_PtNTT2.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 3: Shake flask cultivation of all <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants. </b> <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201004</b>), not expressing <i>Pt</i>NTT2, were used as negative controls. Two biological replicates of each strain were cultivated and three technical replicates taken for each measurement. A clear difference in the growth rates can be observed, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201000</b>) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201007</b>) showing the weakest growth. Both strains also show the longest lag phase, which is nearly twice as long as the lag phase of <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3). <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (<b>BBa_K2201001</b>) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201006</b>) show the best growth of all <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants, reaching the highest OD<sub>600</sub>. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) without any plasmid shows the best growth, with the highest specific growth rate and the highest final OD<sub>600</sub> of 5.178 ± 0.046. The second negative control, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) harboring pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201004) reached the second highest OD<sub>600</sub> with 4.638 ± 0.029. Of the functional <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants, strains harboring pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (BBa_K2201001) and pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201006) reached the highest ODs with 4.397 ± 0.062 and 4.171 ± 0.051, respectively. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) (BBa_K2201005) showed similar growth to the two previous strains during the lag phase and early exponential phase, but reaching a lower OD<sub>600</sub> of 3.802 ± 0.135. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201000) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201007) grew | + | <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) without any plasmid shows the best growth, with the highest specific growth rate and the highest final OD<sub>600</sub> of 5.178 ± 0.046. The second negative control, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) harboring pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201004</b>) reached the second highest OD<sub>600</sub> with 4.638 ± 0.029. Of the functional <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants, strains harboring pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (<b>BBa_K2201001</b>) and pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201006</b>) reached the highest ODs with 4.397 ± 0.062 and 4.171 ± 0.051, respectively. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) (<b>BBa_K2201005</b>) showed similar growth to the two previous strains during the lag phase and early exponential phase, but reaching a lower OD<sub>600</sub> of 3.802 ± 0.135. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201000</b>) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201007</b>) grew substantially weaker compared to all previous strains, with a lag phase nearly four hours long and final ODs of 2.499 ± 0.134 and 2.735 ± 0.150, respectively. The difference in growth between the two negative controls can be explained by the metabolic burden caused by plasmid replication and expression of the chloramphenicol resistance. Therefore, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201004</b>) is the more accurate control, since all samples contain the same plasmid backbone and were also grown in LB media supplemented with chloramphenicol. If not indicated otherwise, pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (<b>BBa_K2201004</b>) was used as the main reference. The difference in growth between strains expressing the native, full length transporter and the truncated version <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575), observed by Zhang <i>et al.</i> 2017, could also be shown. This negative effect might be associated with the native signal peptide of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, which <i>E. coli</i> might not be able to process correctly. Another explanation for the weak growth could be that the native transporter variant has a higher activity compared to the other variants. If the activity is too high, this might lead to a toxic effect and to the observed weak growth. Given that all transporter variants were expressed with the same promotor, this difference in growth cannot be explained by differences in the expression. |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 2: Final OD<sub>600</sub> of all cultures.</b> The highest OD<sub>600</sub> was reached by the wildtype <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3), the lowest by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2.</p> |
<table style="margin: auto"> | <table style="margin: auto"> | ||
| Line 232: | Line 226: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | To determine the maximum specific growth rate (µ<sub>max</sub>), the natural logarithm of the OD<sub>600</sub> values was plotted against the cultivation time. The slope of the linear regression through the exponential phase gives µ<sub>max</sub>. The graphical determination of µmax for the shake flask cultivation is shown in | + | To determine the maximum specific growth rate (µ<sub>max</sub>), the natural logarithm of the OD<sub>600</sub> values was plotted against the cultivation time. The slope of the linear regression through the exponential phase gives µ<sub>max</sub>. The graphical determination of µmax for the shake flask cultivation is shown in Figure 4 |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bb/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5max_shakeflask.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bb/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5max_shakeflask.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 4: Graphical determination of µ<sub>max</sub>. </b> The highest specific growth rate was determined for each culture by plotting the natural logarithm of OD<sub>600</sub> against the cultivation time. The slope of the linear regression through the exponential phase gives µ<sub>max</sub>. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | The highest specific growth rate can be observed for the negative controls <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 with values of 1.201 ± 0.070 h<sup>-1</sup> and 1.212 ± 0.029 h<sup>-1</sup>, respectively. The lowest specific growth rate could be observed for <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 with a value of 0.946 ± 0.030 h<sup>-1</sup>. Based on the specific growth rate, the minimal doubling time was calculated using the following equation: | |
<br> | <br> | ||
<div class="equation-line"> | <div class="equation-line"> | ||
| Line 247: | Line 241: | ||
With <i>t<sub>d</sub></i> being the doubling time in hours and <i>µ</i> the specific growth rate in <i>h<sup>-1</sup></i>. The maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times are show in table (3) for all cultures. | With <i>t<sub>d</sub></i> being the doubling time in hours and <i>µ</i> the specific growth rate in <i>h<sup>-1</sup></i>. The maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times are show in table (3) for all cultures. | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 3: Maximum specific growth rates and minimum doubling times for all cultures. </b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin: auto"> | <table style="margin: auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 325: | Line 319: | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
| − | Due to the high price of unnatural nucleoside triphosphates, performing experiments such as cultivations in a small volume is desirable. Therefore, we validated whether cultivations in micro well plates can achieved the same results as cultivations performed in shake flasks and optimized the method | + | Due to the high price of unnatural nucleoside triphosphates, performing experiments such as cultivations in a small volume is desirable. Therefore, we validated whether cultivations in micro well plates can achieved the same results as cultivations performed in shake flasks and <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/unnatural_base_pair/preservation_system">optimized the method</a>. The optimal conditions for cultivations in a small volume were determined as follows: 12 well plates with a cultivation volume of 1 mL, 37 °C and 600 rpm. To analyze the growth of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants in a micro cultivation, the shake flask cultivation was repeated in a 12 well plate. All cultures were inoculated with an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.1. Three biological replicates of each strain were tested and three technical replicates were measured at each time point. The results are shown in Figure 5. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4d/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/4d/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 5: Microcultivation of all <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants</b><i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201004) were again used as negative controls. The same growth pattern as in the shake flask cultivation can be observed, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) reaching the highest ODs, followed by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575), <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 335: | Line 329: | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 4: Final OD<sub>600</sub> of all cultures.</b><br> The highest OD<sub>600</sub> was reached by the wildtype <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) with 5,487 ± 0.038, the lowest by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 with 1.623 ± 0.481.</p> |
<table style="margin: auto"> | <table style="margin: auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 394: | Line 388: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Like for the shake flask cultivation, µ<sub>max</sub> was determined graphically ( | + | Like for the shake flask cultivation, µ<sub>max</sub> was determined graphically (Figure 6). Bases on the obtained values, the minimum doubling time was calculated. The results are summarized in Table 5. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e6/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5max_microcultivation.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e6/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5max_microcultivation.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 6: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rate µ<sub>max</sub> for the microcultivations. </b> </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
All cultures showed extended doubling times when compared to the shake flask cultivations. This is not surprising, since the oxygen transfer is much better in shake flasks compared to well plates. Nonetheless, similar final OD<sub>600</sub> values were reached in the micro cultivations. Furthermore, the same differences in growth between the different strains can be observed, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 growing the weakest. | All cultures showed extended doubling times when compared to the shake flask cultivations. This is not surprising, since the oxygen transfer is much better in shake flasks compared to well plates. Nonetheless, similar final OD<sub>600</sub> values were reached in the micro cultivations. Furthermore, the same differences in growth between the different strains can be observed, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 growing the weakest. | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 5: Maximum specific growth rate and minimum doubling time for all cultures cultivated in 12 well plates. </b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin: auto"> | <table style="margin: auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 471: | Line 465: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | To investigate the effect of smaller well plates, a cultivation of two of our strains was performed by the iGEM team UNIFI from Florence, Italy. The team cultivated <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) in a 96 well plate. The cultivation was performed at 37 °C and 130 rpm in 3 mL of LB media. Three biological replicates were cultivated and measured at each time point. The results are shown in | + | To investigate the effect of smaller well plates, a cultivation of two of our strains was performed by the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UNIFI">iGEM team UNIFI</a> from Florence, Italy. The team cultivated <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) in a 96 well plate. LB media was used as a reference. The cultivation was performed at 37 °C and 130 rpm in 3 mL of LB media. Three biological replicates were cultivated and measured at each time point. The results are shown in Figure 7. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/02/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation96_well.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/02/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation96_well.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 7: Microcultivation in a 96 well plate performed by <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UNIFI">iGEM team UNIFI</a> from Florence, Italy.</b><br> <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) were cultivated in a total volume of 3 mL at 37 °C and 130 rpm. The growth difference between the two strains observed in previous cultivations could also be observed in this experiment carried out by the team from Florence. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 reached a final OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.329 ± 0.037 while <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) reached a final OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.664 ± 0.033. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | The results obtained by iGEM team UNIFI validate our results, since the same difference in growth can be observed between the truncated version <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) and <i>Pt</i>NTT2. Also in a 96 well plate, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 reached only 49.5 % of the final cell density of <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (40.2 % for the cultivation carried out in 12 well plates). After 27 hours, the final OD<sub>600</sub> of the strain carrying the full-length version of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 was 0.329 ± 0.037, while the final OD<sub>600</sub> of the strain expressing the truncated version <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) was 0.664 ± 0.033. These results clearly indicate that it is highly beneficial for higher cell densities and better growth to cultivate in larger well plates. Furthermore, shaking at higher frequencies can improve the growth, as show in the validation of | + | The results obtained by iGEM team UNIFI validate our results, since the same difference in growth can be observed between the truncated version <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) and <i>Pt</i>NTT2. Also in a 96 well plate, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 reached only 49.5 % of the final cell density of <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (40.2 % for the cultivation carried out in 12 well plates). After 27 hours, the final OD<sub>600</sub> of the strain carrying the full-length version of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 was 0.329 ± 0.037, while the final OD<sub>600</sub> of the strain expressing the truncated version <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) was 0.664 ± 0.033. These results clearly indicate that it is highly beneficial for higher cell densities and better growth to cultivate in larger well plates. Furthermore, shaking at higher frequencies can improve the growth, as show in the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/unnatural_base_pair/preservation_system">validation of microcultivations</a>. |
| − | The graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates is shown in | + | The graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates is shown in Figure 8. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/fb/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation96.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/f/fb/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation96.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 8: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates for the cultivations carried out in 96 well plates by the <a href="https://2017.igem.org/Team:UNIFI">iGEM team UNIFI</a>.</b><br> </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | Graphical determination of the specific growth rates and the minimum doubling times revealed | + | Graphical determination of the specific growth rates and the minimum doubling times revealed substantially weaker growth of the cultures in 96 well plates compared to 12 well plates or shake flasks. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) reached the highest specific growth rate with 0,11 ± 0,002 h-1. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 showed much weaker growth with a maximum specific growth rate of 0,041 ± 0,004 h-1. The maximum specific growth rates and minimum doubling times are summarized in table (6). |
<p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table (6): Maximum specific growth rate and minimum doubling time for all cultures cultivated in 12 well plates. </b><br> </p> | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table (6): Maximum specific growth rate and minimum doubling time for all cultures cultivated in 12 well plates. </b><br> </p> | ||
| Line 527: | Line 521: | ||
<h3>Verification of the Function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2</h3> | <h3>Verification of the Function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2</h3> | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
| − | To verify that <i>Pt</i>NTT2 fulfills its desired function, a simple experiment was designed. Usually, the function of nucleotide transporters is determined using radioactively labeled nucleotides. Given that we did not want to work with radioactively labeled nucleotides and that not every lab has access to suitable equipment, we focused on verifying the function | + | To verify that <i>Pt</i>NTT2 fulfills its desired function, a simple experiment was designed. Usually, the function of nucleotide transporters is determined using radioactively labeled nucleotides. Given that we did not want to work with radioactively labeled nucleotides and that not every lab and iGEM team has access to suitable equipment, we focused on verifying the function using a less dangerous and better accesible method. |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Under phosphate starvation, <i>E. coli</i> secretes phosphatases to utilize the phosphates from nucleotides as phosphate source. On the other hand, cells expressing <i>Pt</i>NTT2 and integrating it into the inner membrane should be able to take up nucleoside triphosphates directly. By taking up nucleoside triphosphates directly from the media, the cells can directly take up three phosphates and the nucleobase. Given that the uptake of NTPs by <i>Pt</i>NTT2 is facilitated by counter exchange of ATP, ATP is exported and consequently converted to AMP by extracellular phosphatases. | ||
| + | <div class="figure large"> | ||
| + | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/0/01/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2proposeduptake.jpeg"> | ||
| + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 9: Proposed function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2.</b> . A) ATP is exported in presence of the unnatural nucleotides iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, leading to a constant loss of ATP, negatively influencing growth. B) If the media is supplemented with ATP in slightly higher concentrations than the intracellular concentration, ATP is likely taken up in exchange for ATP, ADP as well as other NTPs. A beneficial effect of expression of the transporter on the growth of the cells is achieved due to a small net uptake of ATP.C) In case of much higher extracellular concentrations compared to the intracellular concentration of ATP, ATP will be taken up efficiently in exchange for NTPs, ADP and AMP. This would lead to a net uptake of ATP, but a net loss of NTPs, leading to reduced growth.</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
The experiment we designed consists of two parts and is based on the disability of <i>E. coli</i> to take up nucleoside triphosphates from the media. The first part consists of cultivations performed in MOPS minimal media which is supplemented with either 1.32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> or 1 mM ATP. Calculation of the Odds-ratio as shown in equation (A) allows to evaluate how beneficial expression of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 is for the cell if extracellular ATP or unnatural base pairs represent the sole phosphate source. The second part of the experiment consists of liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (LC-MS) measurements for the quantification of AMP in the supernatant. Combined, these methods provide a way to investigate the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 without the application of radioactively labeled nucleotides. Furthermore, these experiments might also serve as a way for future iGEM teams to easily characterize the function of membrane proteins. | The experiment we designed consists of two parts and is based on the disability of <i>E. coli</i> to take up nucleoside triphosphates from the media. The first part consists of cultivations performed in MOPS minimal media which is supplemented with either 1.32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> or 1 mM ATP. Calculation of the Odds-ratio as shown in equation (A) allows to evaluate how beneficial expression of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 is for the cell if extracellular ATP or unnatural base pairs represent the sole phosphate source. The second part of the experiment consists of liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (LC-MS) measurements for the quantification of AMP in the supernatant. Combined, these methods provide a way to investigate the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 without the application of radioactively labeled nucleotides. Furthermore, these experiments might also serve as a way for future iGEM teams to easily characterize the function of membrane proteins. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Figure 9 shows the proposed function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2. In presence of the unnatural nucleotides iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, ATP is exported. Therefore, uptake of iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP leads to a constant loss of ATP, negatively influencing growth. If the media is supplemented with ATP in slightly higher concentrations than the intracellular concentration, ATP is likely taken up in exchange for ATP, ADP as well as other NTPs. This would lead to a small net uptake of ATP, and therefore to a beneficial effect of expression of the transporter on the growth of the cells. In case of much higher extracellular concentrations compared to the intracellular concentration of ATP, ATP will be taken up efficiently in exchange for NTPs, ADP and AMP. This would lead to a net uptake of ATP, but a net loss of NTPs, leading to reduced growth. | Figure 9 shows the proposed function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2. In presence of the unnatural nucleotides iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, ATP is exported. Therefore, uptake of iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP leads to a constant loss of ATP, negatively influencing growth. If the media is supplemented with ATP in slightly higher concentrations than the intracellular concentration, ATP is likely taken up in exchange for ATP, ADP as well as other NTPs. This would lead to a small net uptake of ATP, and therefore to a beneficial effect of expression of the transporter on the growth of the cells. In case of much higher extracellular concentrations compared to the intracellular concentration of ATP, ATP will be taken up efficiently in exchange for NTPs, ADP and AMP. This would lead to a net uptake of ATP, but a net loss of NTPs, leading to reduced growth. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
For the first part of the experiment, two sets of cultivations were carried out in parallel. All transporter variants as well as two negative controls, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2, were cultivated in MOPS minimal media containing either 1,32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> or 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated in 1 mL of media in a 12 well plate at 37 °C and 600 rpm. For each measurement point, three technical replicates were measured. Figure X shows the growth curves of the cultivations carried out with 1,32 mM of K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> as the sole phosphate source. | For the first part of the experiment, two sets of cultivations were carried out in parallel. All transporter variants as well as two negative controls, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2, were cultivated in MOPS minimal media containing either 1,32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> or 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated in 1 mL of media in a 12 well plate at 37 °C and 600 rpm. For each measurement point, three technical replicates were measured. Figure X shows the growth curves of the cultivations carried out with 1,32 mM of K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> as the sole phosphate source. | ||
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/64/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation_K2HPO4.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/64/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation_K2HPO4.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 10: Cultivation of all transporter variants in MOPS media with K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> acting as the sole phosphate source.</b><br> The cultivation was carried out in 12 well plates and three biological replicates were cultivated of each strain. For measurement of the optical density at 600 nm, three technical replicates were taken. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | The final OD<sub>600</sub> values varied widely, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 reaching the highest OD<sub>600</sub> of 3.907 ± 0.018. The lowest OD<sub>600</sub> was reached by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 with a value of 1.537 ± 0.045. All final optical densities at 600 nm are shown in | + | The final OD<sub>600</sub> values varied widely, with <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 reaching the highest OD<sub>600</sub> of 3.907 ± 0.018. The lowest OD<sub>600</sub> was reached by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 with a value of 1.537 ± 0.045. All final optical densities at 600 nm are shown in Table 7. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | The cultivations were performed in parallel in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Again, three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated and three technical replicates measured for each time point. The growth curves are shown in | + | The cultivations were performed in parallel in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Again, three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated and three technical replicates measured for each time point. The growth curves are shown in Figure 11. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/14/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation_ATP.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/1/14/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microcultivation_ATP.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 11: Cultivation of all strains in MOPS media with 1 mM ATP acting as the sole phosphate source.</b><br> Three biological replicates were cultivated and three technical replicates measured for each time point.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | In ATP supplemented media, the wildtype strain reached the highest OD<sub>600</sub> with 4.967 ± 0.143. Of the transporter variants, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 again reached the highest OD<sub>600</sub> and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 the lowest. The results for both cultivations are summarized in | + | In ATP supplemented media, the wildtype strain reached the highest OD<sub>600</sub> with 4.967 ± 0.143. Of the transporter variants, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 again reached the highest OD<sub>600</sub> and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 the lowest. The results for both cultivations are summarized in Table 7. |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 7: Final OD<sub>600</sub> values for all cultivations carried out in MOPS media with 1,32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub>. </b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin:auto"> | <table style="margin:auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 616: | Line 613: | ||
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/3c/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5maxK2HPO4.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/3c/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5maxK2HPO4.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 12: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates for all cultures cultivated in MOPS media with 1.32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub>.</b><br></p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | Based on the maximum specific growth rates, the minimum doubling time was calculated. The results are shown in | + | Based on the maximum specific growth rates, the minimum doubling time was calculated. The results are shown in Table 8. Once again, the strains expressing the native transporter and the transporter with a TAT signal peptide showed the weakest growth. The best growth characteristics were achieved by the strains expressing the truncated versions <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) and <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575), and <i>Pt</i>NTT2 with a pelB signal peptide. |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 8: Maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times of the cultivations in MOPS media with 1.32 mM K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub>.</b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin:auto"> | <table style="margin:auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 679: | Line 676: | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
</table><br> | </table><br> | ||
| − | The graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates of the cultures cultivated in ATP supplemented media is shown in | + | The graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates of the cultures cultivated in ATP supplemented media is shown in Figure 13. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bf/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5maxATP.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bf/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--%C2%B5maxATP.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 13: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates of all cultivations performed in MOPS media and 1 mM ATP. </b><br> </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | The determined values for µmax and the minimal doubling times are shown in | + | The determined values for µmax and the minimal doubling times are shown in Table 9. |
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Table 9: Maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times of the cultivations in MOPS media with 1 mM ATP.</b><br> </p> |
<table style="margin:auto"> | <table style="margin:auto"> | ||
<thead> | <thead> | ||
| Line 746: | Line 743: | ||
</tbody> | </tbody> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | Based on the results of the two cultivations, the relative beneficial effect (RBE) of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 was calculated using | + | Based on the results of the two cultivations, the relative beneficial effect (RBE) of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 was calculated using Equation 2. |
<br> | <br> | ||
<div class="equation-line"> | <div class="equation-line"> | ||
<img class="equation" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b5/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--equationRBE.png" style="width:350px;"> | <img class="equation" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b5/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--equationRBE.png" style="width:350px;"> | ||
| − | <p class="equation-nr"> | + | <p class="equation-nr">2</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | For each measurement point <i>n</i>, the optical density at 600 nm of the cultivation of a transporter variant in ATP supplemented media (<i>OD<sub>AT</sub></i>) was divided by the optical density of the reference <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 in ATP supplemented media (<i>OD<sub>AR</sub></i>). The same was done for the cultures in K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> supplemented media(<i>OD<sub>KT</sub></i> and <i>OD<sub>KR</sub></i>). The value for ATP was then divided by the value for K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub>. The sum of the quotient for all measurement points <i>n</i> was then divided by <i>n</i> to obtain the final value for the relative beneficial effect of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 shown in | + | For each measurement point <i>n</i>, the optical density at 600 nm of the cultivation of a transporter variant in ATP supplemented media (<i>OD<sub>AT</sub></i>) was divided by the optical density of the reference <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 in ATP supplemented media (<i>OD<sub>AR</sub></i>). The same was done for the cultures in K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub> supplemented media(<i>OD<sub>KT</sub></i> and <i>OD<sub>KR</sub></i>). The value for ATP was then divided by the value for K<sub>2</sub>HPO<sub>4</sub>. The sum of the quotient for all measurement points <i>n</i> was then divided by <i>n</i> to obtain the final value for the relative beneficial effect of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 shown in Figure 14. The final error was calculated through error propagation of the standard error of each measured optical density. |
<div class="figure seventy"> | <div class="figure seventy"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/9f/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2RBE1mM.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/9/9f/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2RBE1mM.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 14: Relative beneficial effect of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants.</b><br> As expected, the native transporter variant shows the highest positive effect since it most likely also exhibits the highest activity. Surprisingly, the two truncated versions show a higher effect than the versions with a pelB and TAT signal peptide.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 768: | Line 765: | ||
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/68/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2RBE10mM.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/6/68/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--PtNTT2RBE10mM.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 15: Relative Beneficial Effect of the different transporter variants when cultivated in MOPS minimal media supplemented with 10 mM ATP.</b> No substantial beneficial effect could be observed for any of the transporter variants. The highest beneficial effects were reached by <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (+17.2 % ± 7.2 %) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) (+14.0 % ± 4.7 %).</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | The highest beneficial effect was reached by TAT-SP-PtNTT2 with a value of +17.2 % ± 7.2 %, followed by <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575) with +14.0 % ± 4.7 %. All other strains did not show a | + | The highest beneficial effect was reached by TAT-SP-PtNTT2 with a value of +17.2 % ± 7.2 %, followed by <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575) with +14.0 % ± 4.7 %. All other strains did not show a substantial beneficial effect. These results suggest, that the activity of the different transporter variants is concentration dependent and that expression of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 in media supplemented with higher concentrations of ATP equalizes the effects of uptake and export of NTPs. Therefore, no substantial beneficial effect could be observed, but also no negative effect. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | The experiment was repeated once again with MOPS media supplemented with 100 µM of iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP. | + | The experiment was repeated once again with MOPS media supplemented with 100 µM of iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP. Substantial differences were observed for all transporter variants. <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) reached the highest beneficial effect with +38 % ± 10 %. All other transporter variants reached showed a negative effect compared to the reference. This confirms that ATP is exported in presence of the unnatural nucleotides, leading to a net loss of ATP and inhibition of growth. Therefore, it can be concluded that the native transporter variant <i>Pt</i>NTT2 has the highest activity towards iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, followed by <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575). |
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/cc/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--RBEUBP.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/c/cc/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--RBEUBP.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 16: Relative beneficial effect of the best <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 100 µM of iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP each.</b> Substantial differences can be observed for all transporter variants, with <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) reaching the highest beneficial effect +38 % ± 10 %. All other transporter variants reached showed a negative effect compared to the reference, which means that ATP is exported in exchange for iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, leading to a net loss of ATP.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | The supernatants of the cultures cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM and 10 mM ATP were further analyzed with LC-MS. Therefore, the cultures were centrifuged, and the supernatant analyzed with LC-MS. AMP, ADP and ATP were measured, but only AMP was | + | The supernatants of the cultures cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM and 10 mM ATP were further analyzed with LC-MS. Therefore, the cultures were centrifuged, and the supernatant analyzed with LC-MS. AMP, ADP and ATP were measured, but only AMP was substantially above the detection limit in nearly all samples. AMP was quantified based on the standard curve shown in Figure 18. ADP and ATP could not be quantified. The results are shown in Figure 17. |
<div class="figure large"> | <div class="figure large"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b2/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--HPLCcombined.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/b2/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--HPLCcombined.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 17: : Results of the LC-MS analysis of the supernatants of the cultures cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM and 10 mM ATP.</b> Measured AMP concentrations were standardized to the corresponding final optical densities.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
AMP could be detected in all samples except for the supernatants of the strains expressing pelB-SP-PtNTT2 and TAT-SP-PtNTT2 cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 10 mM ATP. | AMP could be detected in all samples except for the supernatants of the strains expressing pelB-SP-PtNTT2 and TAT-SP-PtNTT2 cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 10 mM ATP. | ||
| Line 789: | Line 786: | ||
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/40/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--Standardkurve.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/4/40/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--Standardkurve.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 18: Standard curve for AMP using 10 mM, 1 mM, 0.1 mM, 0.01 mM and 0.001 mM of AMP. </b> The standard curve was used to quantify AMP in the supernatant of the cultivations carried out in ATP supplemented MOPS media. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 796: | Line 793: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Concluding, we were able to verify the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 without using radioactively labeled nucleotides. The native transporter variant shows the highest activity in all experiments. Uptake of the unnatural nucleotides was verified by determination of the RBE of the different transporter variants when cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with the unnatural nucleotides. Since ATP is constantly exported in exchange for iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, leading to | + | Concluding, we were able to verify the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 without using radioactively labeled nucleotides. The native transporter variant shows the highest activity in all experiments. Uptake of the unnatural nucleotides was verified by determination of the RBE of the different transporter variants when cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with the unnatural nucleotides. Since ATP is constantly exported in exchange for iso-dC<sup>m</sup>TP and iso-dGTP, leading to substantial negative influence on the growth of the cultures. |
</article> | </article> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 807: | Line 804: | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
| − | To investigate the subcellular localization of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants, GFP fusion proteins were constructed. Each <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variant was tagged with a cMyc epitope tag as a linker and GFP (BBa_E0040). The cells were cultivated and prepared for microscopy as described in the methods section. Microscopy was performed using the Zeiss LSM 700. The pictures shown in | + | To investigate the subcellular localization of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants, GFP fusion proteins were constructed as listed in Table 1. Each <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variant was tagged with a cMyc epitope tag as a linker and GFP (BBa_E0040). The cells were cultivated and prepared for microscopy as described in the methods section. Microscopy was performed using the Zeiss LSM 700. The pictures shown in Figure 19 were taken at 100x magnification and clearly show the subcellular localization of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants. |
<div class="figure large"> | <div class="figure large"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/a1/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microscopy.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/a/a1/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--microscopy.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 19: Confocal laser scanning microscopy of the different <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants fused to GFP (BBa_E0040). </b> The pictures were taken with 100x magnification and show from <b>A</b> to <b>E</b>: <<i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2, <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575), <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575), <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | All <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants can be localized within the membrane, since the fluorescence signals of the GFP tag are concentrated there. Judging from the pictures, the variant with the pelB signal peptide is weakly integrated into the inner membrane, which would explain the good growth characteristics and the weak functionality of this variant. The TAT-signal peptide variant, which showed bad growth characteristics and no function, seems to be located within the cell envelope nonetheless. Given that peptides containing the TAT signal peptide are usually folded within the cytoplasm and then secreted via the twin-arginine translocation pathway, this could be a possible explanation for the non-existent function of the TAT variant. All other variants that also showed a detectable function are successfully integrated into the membrane. The variants without a signal peptide are also located within the membrane, which is not surprising, given that the integration of membrane proteins does not necessarily require a signal peptide (Facey and Kuhn, 2004) . <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) seems to be better integrated into the membrane than any other variant. The native <i>Pt</i>NTT2, and <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575) are integrated in a similar scale, but a little bit weaker compared to <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575). These results are consistent with the results of the verification of the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, since all variants that showed a relative beneficial effect and also the highest AMP concentrations in the supernatant do integrate the transporter into the membrane. For the TAT signal peptide variant, it is most likely that the transporter is integrated incorrectly, leading to a correct subcellular localization while lacking the correct function. | + | All <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants can be localized within the membrane, since the fluorescence signals of the GFP tag are concentrated there. Judging from the pictures, the variant with the pelB signal peptide is weakly integrated into the inner membrane, which would explain the good growth characteristics and the weak functionality of this variant. The TAT-signal peptide variant, which showed bad growth characteristics and no substantial function, seems to be located within the cell envelope nonetheless. Given that peptides containing the TAT signal peptide are usually folded within the cytoplasm and then secreted via the twin-arginine translocation pathway, this could be a possible explanation for the non-existent function of the TAT variant. All other variants that also showed a detectable function are successfully integrated into the membrane. The variants without a signal peptide are also located within the membrane, which is not surprising, given that the integration of membrane proteins does not necessarily require a signal peptide (Facey and Kuhn, 2004) . <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575) seems to be better integrated into the membrane than any other variant. The native <i>Pt</i>NTT2, and <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575) are integrated in a similar scale, but a little bit weaker compared to <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575). These results are consistent with the results of the verification of the function of <i>Pt</i>NTT2, since all variants that showed a relative beneficial effect and also the highest AMP concentrations in the supernatant do integrate the transporter into the membrane. For the TAT signal peptide variant, it is most likely that the transporter is integrated incorrectly, leading to a correct subcellular localization while lacking the correct function. |
</article> | </article> | ||
| Line 830: | Line 827: | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
For further analysis of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 the isolation of the transporter from the cell was attempted. This task proved to be challenging, given that <i>Pt</i>NTT2 comprises ten transmembrane domains and is therefore highly hydrophobic. For that reason, several different methods and procedures were tested to achieve the best results. | For further analysis of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 the isolation of the transporter from the cell was attempted. This task proved to be challenging, given that <i>Pt</i>NTT2 comprises ten transmembrane domains and is therefore highly hydrophobic. For that reason, several different methods and procedures were tested to achieve the best results. | ||
| − | The first two attempts were based on the isolation of the periplasmic protein fraction through cold osmotic shock and fast cell lysis followed by analysis via SDS PAGE. Unsurprisingly, both methods did not lead to the desired results, since | + | The first two attempts were based on the isolation of the periplasmic protein fraction through cold osmotic shock and fast cell lysis followed by analysis via SDS PAGE. Unsurprisingly, both methods did not lead to the desired results, since no bands for <i>Pt</i>NTT2 could be observed. Figure 20 shows the SDS PAGE of the samples prepared using the fast cell lysis for SDS PAGE. |
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/34/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEkochen.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/34/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEkochen.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 20: SDS-PAGE of the GFP-fusion constructs of <i>Pt</i>NTT2</b><br> The cells were prepared using the fast cell lysis for SDS PAGE protocol. <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Unsurprisingly, no thick band can be observed around 90.3 kDa, which would be the size of <i>Pt</i>NTT2-cMyc-GFP. No bands can be observed for the other <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | A second gel was used for a western blot using an anti-GFP antibody. The result is shown in | + | A second gel was used for a western blot using an anti-GFP antibody. The result is shown in Figure 21. |
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://2017.igem.org/wiki/images/f/ff/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotkochen.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://2017.igem.org/wiki/images/f/ff/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotkochen.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 21: Western Blot of the samples prepared using the fast cell lysis for SDS PAGE protocol. </b><br> An anti-GFP antibody was used for the detection of <i>Pt</i>NTT2-cMyc-GFP variants. E . coli BL21(DE3) and <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Much unspecific binding of the anti-GFP antibody could be observed, which is not surprising given that the entire proteome of the cells was analyzed. Thick band can be observed for <i>Pt</i>NTT2-cMyc-GFP, <i>Pt</i>NTT2(66-575)-cMyc-GFP, <i>Pt</i>NTT2(31-575)-cMyc-GFP and <i>Pt</i>NTT2(pelB)-cMyc-GFP around 35 kDa. This indicates that only the cMyc-GFP linker was detected and that the linker might be cleaved of from <i>Pt</i>NTT2 due to the high difference in hydrophobicity. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | In a second approach, the cells were lysed using a nitrogen cooled Precellys Homogenizer. After three cycles, cells were centrifuged at 4 °C and the membrane fraction was isolated as described in the methods section . After boiling the membrane fraction, the samples were loaded onto two SDS PAGEs, one of which was consequently used for a western blot, if the fusion proteins were used. For the western blot, two different antibodies were tested, an anti-GFP antibody and an anti-cMyc antibody. Figure | + | In a second approach, the cells were lysed using a nitrogen cooled Precellys Homogenizer. After three cycles, cells were centrifuged at 4 °C and the membrane fraction was isolated as described in the methods section. After boiling the membrane fraction, the samples were loaded onto two SDS PAGEs, one of which was consequently used for a western blot, if the fusion proteins were used. For the western blot, two different antibodies were tested, an anti-GFP antibody and an anti-cMyc antibody. Figure 22 shows the SDS-PAGE after isolation of the membrane fraction. Again, no clear difference between the negative controls and the samples could be observed around 90 kDa. |
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bf/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEribo.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/b/bf/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEribo.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 22: SDS PAGE performed with the isolated membrane fractions.</b><br> The cMyc-GFP fusion proteins were used, which should be visible around ~90 kDa, differing slightly based on the <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variant used. No bands could be observed around 90 kDa, which was subsequently proofed by performing a western blot. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 857: | Line 854: | ||
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ec/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotRibo.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ec/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotRibo.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 23: Western Blot of the isolated membrane fractions of the strains expressing the cMyc-GFP fusion proteins.</b><br> Thick bands can be observed around 28 kDa for all samples except for <i>Pt</i>NTT2-cMyc-GFP with a TAT signal peptide. The negative controls do not show the same band, but some unspecific binding of the anti-GFP antibody could be observed. Compared to the previous western blot, unspecific binding was substantially reduced. These results indicate, that the linker is most likely separated from the transporter either during the isolation process or already within the cell. This would be no surprise, given that the transporter is highly hydrophobic while the linker is hydrophilic. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 864: | Line 861: | ||
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/51/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotcmycribo.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/51/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--WesternBlotcmycribo.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 24: Western Blot of the isolated membrane fraction using an anti-cMyc antibody. </b><br> Again, fragments can be observed around 35 kDa for all samples except for <i>Pt</i>NTT2-cMyc-GFP with a TAT signal peptide. No bands can be observed for the full construct, but a very weak band can be seen between 55 and 70 kDa for the fusion protein of the native transporter. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
Once again, bands could be observed for all transporter variants except for the TAT signal peptide variants around 35 kDa. One very weak can be observed for the fusion protein of the native transporter between 55 and 70 kDa. | Once again, bands could be observed for all transporter variants except for the TAT signal peptide variants around 35 kDa. One very weak can be observed for the fusion protein of the native transporter between 55 and 70 kDa. | ||
| − | All these results show how difficult the isolation of integral membrane proteins can be. A number of reasons can be brought forward to explain why isolation of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 from the membrane proved to be so challenging. First of all, <i>Pt</i>NTT2 has 10 transmembrane domains, making it a highly hydrophobic protein. To find a correct detergent to solubilize the protein from the isolated membrane fraction also proves challenging. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) lists dozens of possible detergents on their site (European Molecular Biology Laboratory - Protein Purification). To find a best suited detergent is also a challenge. Another reason why the visualization of membrane proteins on SDS PAGEs and western blots is challenging is that membrane proteins tend to aggregate when boiled and that they often exhibit “gel shifting” (Rath et al., 2009). For that reason, another SDS PAGE was run using the isolated membrane fractions of the <i>Pt</i>NTT2 constructs without cMyc-GFP tag, but this time the samples were loaded onto the gel without previous boiling. | + | All these results show how difficult the isolation of integral membrane proteins can be. A number of reasons can be brought forward to explain why isolation of <i>Pt</i>NTT2 from the membrane proved to be so challenging. First of all, <i>Pt</i>NTT2 has 10 transmembrane domains, making it a highly hydrophobic protein. To find a correct detergent to solubilize the protein from the isolated membrane fraction also proves challenging. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) lists dozens of possible detergents on their site (European Molecular Biology Laboratory - Protein Purification). To find a best suited detergent is also a challenge. Another reason why the visualization of membrane proteins on SDS PAGEs and western blots is challenging is that membrane proteins tend to aggregate when boiled and that they often exhibit “gel shifting” (Rath <i>et al.</i>, 2009). For that reason, another SDS PAGE was run using the isolated membrane fractions of the <i>Pt</i>NTT2 constructs without cMyc-GFP tag, but this time the samples were loaded onto the gel without previous boiling. |
<div class="figure sixty"> | <div class="figure sixty"> | ||
<img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2b/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEnoboiling.jpeg"> | <img class="figure image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/2/2b/T--Bielefeld-CeBiTec--SDSPAGEnoboiling.jpeg"> | ||
| − | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure | + | <p class="figure subtitle"><b>Figure 25: SDS PAGE of the isolated membrane fraction without previous boiling</b><br> No thick bands can be observed around 70 kDa. Slightly above 100 kDa, bands can be observed for all <i>Pt</i>NTT2 variants but not for the negative controls. But given that the samples ran quite different on the gel compared to the boiled samples, no definite conclusion can be drawn from this gel. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 885: | Line 882: | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3> References</h3> | <h3> References</h3> | ||
| − | + | <article> | |
| + | <b>EMBL Protein Purification - Extraction and Clarification - Solubilisation of Membrane Proteins.</b> https://www.embl.de/pepcore/pepcore_services/protein_purification/extraction_clarification/solubilisation_membrane_proteins/index.html, Date Accessed: 1st of November, 2017 | ||
| + | </article> | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
<b>Facey, S.J. and Kuhn, A. </b>(2004). Membrane integration of <i>E. coli</i> model membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 1694: 55–66. | <b>Facey, S.J. and Kuhn, A. </b>(2004). Membrane integration of <i>E. coli</i> model membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 1694: 55–66. | ||
| Line 892: | Line 891: | ||
<b>Käll, L., Krogh, A., and Sonnhammer, E.L.L. </b> (2007). Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction-the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 35: 429–432. | <b>Käll, L., Krogh, A., and Sonnhammer, E.L.L. </b> (2007). Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction-the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 35: 429–432. | ||
</article> | </article> | ||
| + | <article> | ||
| + | <b>Rath, A., Glibowicka, M., Nadeau, V.G., Chen, G., and Deber, C.M. </b>(2009). Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. <b>106</b>: 1760–1765. | ||
| + | </article> | ||
<article> | <article> | ||
<b>Zhang, Y., Lamb, B.M., Feldman, A.W., Zhou, A.X., Lavergne, T., Li, L., and Romesberg, F.E.</b> (2017). A semisynthetic organism engineered for the stable expansion of the genetic alphabet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114: 1317–1322. | <b>Zhang, Y., Lamb, B.M., Feldman, A.W., Zhou, A.X., Lavergne, T., Li, L., and Romesberg, F.E.</b> (2017). A semisynthetic organism engineered for the stable expansion of the genetic alphabet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114: 1317–1322. | ||
Revision as of 21:43, 1 November 2017





Short Summary
Computational Analysis of PtNTT2

Figure 1: Results of the analysis of PtNTT2 using Phobius.
The 30 first amino acids are clearly recognized as a signal peptide. Ten transmembrane domains are predicted.
Plasmid Design

Figure 2: Schematic overview of the design of the different transporter variants. The lacUV5 promotor was used together with a strong RBS (BBa_B0034) for all parts. All variants except for pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were also tagged with GFP (BBa_E0040). cMyc was used as a linker (BBa_K2201181).
Table 1: Designed and cloned plasmids for the analysis and characterization of PtNTT2.
| Plasmid Name | BioBrick Number | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | BBa_K2201004 | Only the cds |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | BBa_K2201000 | cds with lacUV5 promotor and strong RBS (BBa_B0034) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | BBa_K2201001 | cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | BBa_K2201005 | cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), truncated version lacking the first 30 amino acids |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | BBa_K2201006 | cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), native signal peptide replaced with the pelB signal peptide |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | BBa_K2201007 | cds with lacUV5 promotor and a strong RBS (BBa_B0034), native signal peptide replaced with a TAT signal peptide |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2-GFP | BBa_K2201002 | Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201000 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker (BBa_K2201181) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575)-GFP | BBa_K2201003 | Fusion protein of BBa_ K2201001 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker (BBa_K2201181) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575)-GFP | BBa_K2201011 | Fusion protein of BBa_K2201005 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker (BBa_K2201181) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2-GFP | BBa_K2201012 | Fusion protein of BBa_K2201006 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker (BBa_K2201181) |
| pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2-GFP | BBa_K2201013 | Fusion protein of BBa_K2201007 with GFP (BBa_E0040), Myc epitope tag as linker (BBa_K2201181) |
Cultivations of the Different PtNTT2 Variants

Figure 3: Shake flask cultivation of all PtNTT2 variants. E. coli BL21(DE3) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201004), not expressing PtNTT2, were used as negative controls. Two biological replicates of each strain were cultivated and three technical replicates taken for each measurement. A clear difference in the growth rates can be observed, with E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201000) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201007) showing the weakest growth. Both strains also show the longest lag phase, which is nearly twice as long as the lag phase of E. coli BL21(DE3). E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) (BBa_K2201001) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201006) show the best growth of all PtNTT2 variants, reaching the highest OD600.
Table 2: Final OD600 of all cultures. The highest OD600 was reached by the wildtype E. coli BL21(DE3), the lowest by E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2.
| Strain | Final OD600 [-] | |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 5.178 ± 0.046 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 4.638 ± 0.029 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 2.499 ± 0.134 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 4.397 ± 0.062 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 3.802 ± 0.135 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 4.171 ± 0.051 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 2.735 ± 0.150 |
To determine the maximum specific growth rate (µmax), the natural logarithm of the OD600 values was plotted against the cultivation time. The slope of the linear regression through the exponential phase gives µmax. The graphical determination of µmax for the shake flask cultivation is shown in Figure 4

Figure 4: Graphical determination of µmax. The highest specific growth rate was determined for each culture by plotting the natural logarithm of OD600 against the cultivation time. The slope of the linear regression through the exponential phase gives µmax.

(1)
With td being the doubling time in hours and µ the specific growth rate in h-1. The maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times are show in table (3) for all cultures.
Table 3: Maximum specific growth rates and minimum doubling times for all cultures.
| Strain | µmax [h-1] | td [h] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 1.201 ± 0.070 | 0.577 ± 0.058 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 1.212 ± 0.029 | 0.572 ± 0.024 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 0.978 ± 0.033 | 0.709 ± 0.034 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 1.194 ± 0.026 | 0.581 ± 0.022 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 1.143 ± 0.045 | 0.606 ± 0.039 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 1.189 ± 0.028 | 0.583 ± 0.024 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.946 ± 0.030 | 0.733 ± 0.032 |
These results clearly show that expression of PtNTT2 leads to a reduced final cell density and slower growth. Furthermore, the different variants of PtNTT2 differ highly, indicating that some variants of PtNTT2 negatively affect the growth rate and final cell density.
Microcultivations of the Different PtNTT2 Variants

Figure 5: Microcultivation of all PtNTT2 variantsE. coli BL21(DE3) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 (BBa_K2201004) were again used as negative controls. The same growth pattern as in the shake flask cultivation can be observed, with E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2, E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) reaching the highest ODs, followed by E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575), E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2.
Table 4: Final OD600 of all cultures.
The highest OD600 was reached by the wildtype E. coli BL21(DE3) with 5,487 ± 0.038, the lowest by E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 with 1.623 ± 0.481.
| Strain | Final OD600 [-] | |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 5.487 ± 0.038 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 4.337 ± 0.010 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 1.623 ± 0.481 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 4.035 ± 0.051 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 3.865 ± 0.008 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 4.110 ± 0.005 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 2.280 ± 0.337 |
Like for the shake flask cultivation, µmax was determined graphically (Figure 6). Bases on the obtained values, the minimum doubling time was calculated. The results are summarized in Table 5.

Figure 6: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rate µmax for the microcultivations.
Table 5: Maximum specific growth rate and minimum doubling time for all cultures cultivated in 12 well plates.
| Strain | µmax [h-1] | td [h] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 1.059 ± 0.143 | 0.655 ± 0.135 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 1.016 ± 0.133 | 0.682 ± 0.131 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 0.829 ± 0.071 | 0.836 ± 0.086 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 1.023 ± 0.105 | 0.678 ± 0.103 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 1.021 ± 0.096 | 0.679 ± 0.094 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 1.047 ± 0.097 | 0.662 ± 0.093 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.924 ± 0.113 | 0.750 ± 0.122 |
To investigate the effect of smaller well plates, a cultivation of two of our strains was performed by the iGEM team UNIFI from Florence, Italy. The team cultivated E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) in a 96 well plate. LB media was used as a reference. The cultivation was performed at 37 °C and 130 rpm in 3 mL of LB media. Three biological replicates were cultivated and measured at each time point. The results are shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Microcultivation in a 96 well plate performed by iGEM team UNIFI from Florence, Italy.
E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) were cultivated in a total volume of 3 mL at 37 °C and 130 rpm. The growth difference between the two strains observed in previous cultivations could also be observed in this experiment carried out by the team from Florence. E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 reached a final OD600 of 0.329 ± 0.037 while E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) reached a final OD600 of 0.664 ± 0.033.

Figure 8: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates for the cultivations carried out in 96 well plates by the iGEM team UNIFI.
Table (6): Maximum specific growth rate and minimum doubling time for all cultures cultivated in 12 well plates.
| Strain | µmax [h-1] | td [h] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 0.042 ± 0.004 | 16.504 ± 0.095 | |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 0.110 ± 0.002 | 6.301 ± 0.018 |
Verification of the Function of PtNTT2
Under phosphate starvation, E. coli secretes phosphatases to utilize the phosphates from nucleotides as phosphate source. On the other hand, cells expressing PtNTT2 and integrating it into the inner membrane should be able to take up nucleoside triphosphates directly. By taking up nucleoside triphosphates directly from the media, the cells can directly take up three phosphates and the nucleobase. Given that the uptake of NTPs by PtNTT2 is facilitated by counter exchange of ATP, ATP is exported and consequently converted to AMP by extracellular phosphatases.

Figure 9: Proposed function of PtNTT2. . A) ATP is exported in presence of the unnatural nucleotides iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP, leading to a constant loss of ATP, negatively influencing growth. B) If the media is supplemented with ATP in slightly higher concentrations than the intracellular concentration, ATP is likely taken up in exchange for ATP, ADP as well as other NTPs. A beneficial effect of expression of the transporter on the growth of the cells is achieved due to a small net uptake of ATP.C) In case of much higher extracellular concentrations compared to the intracellular concentration of ATP, ATP will be taken up efficiently in exchange for NTPs, ADP and AMP. This would lead to a net uptake of ATP, but a net loss of NTPs, leading to reduced growth.
Figure 9 shows the proposed function of PtNTT2. In presence of the unnatural nucleotides iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP, ATP is exported. Therefore, uptake of iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP leads to a constant loss of ATP, negatively influencing growth. If the media is supplemented with ATP in slightly higher concentrations than the intracellular concentration, ATP is likely taken up in exchange for ATP, ADP as well as other NTPs. This would lead to a small net uptake of ATP, and therefore to a beneficial effect of expression of the transporter on the growth of the cells. In case of much higher extracellular concentrations compared to the intracellular concentration of ATP, ATP will be taken up efficiently in exchange for NTPs, ADP and AMP. This would lead to a net uptake of ATP, but a net loss of NTPs, leading to reduced growth. For the first part of the experiment, two sets of cultivations were carried out in parallel. All transporter variants as well as two negative controls, E. coli BL21(DE3) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2, were cultivated in MOPS minimal media containing either 1,32 mM K2HPO4 or 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated in 1 mL of media in a 12 well plate at 37 °C and 600 rpm. For each measurement point, three technical replicates were measured. Figure X shows the growth curves of the cultivations carried out with 1,32 mM of K2HPO4 as the sole phosphate source.

Figure 10: Cultivation of all transporter variants in MOPS media with K2HPO4 acting as the sole phosphate source.
The cultivation was carried out in 12 well plates and three biological replicates were cultivated of each strain. For measurement of the optical density at 600 nm, three technical replicates were taken.
The cultivations were performed in parallel in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM ATP as sole phosphate source. Again, three biological replicates of each strain were cultivated and three technical replicates measured for each time point. The growth curves are shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11: Cultivation of all strains in MOPS media with 1 mM ATP acting as the sole phosphate source.
Three biological replicates were cultivated and three technical replicates measured for each time point.
Table 7: Final OD600 values for all cultivations carried out in MOPS media with 1,32 mM K2HPO4.
| Strain | Final OD600, K2HPO4 [-] | Final OD600, ATP [-] |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 2.923 ± 0.028 | 4.967 ± 0.143 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 3.507 ± 0.048 | 3.673 ± 0.091 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 1.537 ± 0.045 | 3.033 ± 0.028 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 3.560 ± 0.011 | 3.347 ± 0.032 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 3.797 ± 0.065 | 3.580 ± 0.006 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 3.907 ± 0.018 | 3.710 ± 0.177 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 3.307 ± 0.029 | 2.177 ± 0.007 |

Figure 12: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates for all cultures cultivated in MOPS media with 1.32 mM K2HPO4.
Table 8: Maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times of the cultivations in MOPS media with 1.32 mM K2HPO4.
| Strain | µmax [h-1] | td [h] |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 0.444 ± 0.053 | 1.561 ± 0.199 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 0.499 ± 0.050 | 1.389 ± 0.100 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 0.385 ± 0.044 | 1.800 ± 0.114 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 0,568 ± 0.057 | 1.220 ± 0.100 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 0.532 ± 0.022 | 1.303 ± 0.041 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.549 ± 0.017 | 1.263 ± 0.031 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.463 ± 0.028 | 1.497 ± 0.060 |
The graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates of the cultures cultivated in ATP supplemented media is shown in Figure 13.

Figure 13: Graphical determination of the maximum specific growth rates of all cultivations performed in MOPS media and 1 mM ATP.
Table 9: Maximum specific growth rates and minimal doubling times of the cultivations in MOPS media with 1 mM ATP.
| Strain | µmax [h-1] | td [h] |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21(DE3) | 0.673 ± 0.012 | 1.030 ± 0.018 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 | 0.600 ± 0.021 | 1.155 ± 0.035 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2 | 0.463 ± 0.035 | 1.497 ± 0.076 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575) | 0.644 ± 0.069 | 1.076 ± 0.107 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) | 0.428 ± 0.091 | 1.620 ± 0.213 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.518 ± 0.043 | 1.338 ± 0.083 |
| E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 | 0.334 ± 0.047 | 2.075 ± 0.141 |

2

Figure 14: Relative beneficial effect of the different PtNTT2 variants.
As expected, the native transporter variant shows the highest positive effect since it most likely also exhibits the highest activity. Surprisingly, the two truncated versions show a higher effect than the versions with a pelB and TAT signal peptide.
This data suggests that the expression of different PtNTT2 variants, especially of the native PtNTT2, is beneficial for the cell when cultivated in MOPS minimal media supplemented with ATP as the sole phosphate source. Given that the reference strain does not express PtNTT2, the expression of PtNTT2 must have a beneficial effect for the cells since they grow better compared to the reference in ATP when compared to the reference in K2HPO4. Therefore, the beneficial effect is larger than the metabolic burden associated with recombinant protein expression. Consequently, the transporter exhibits a function beneficial to the cell in ATP supplemented media, meaning it can facilitate the direct uptake of ATP from the media. Therefore, the proposed activity of PtNTT2 in media supplemented with low concentrations of ATP could be verified.
Consequently, the same experiment was conducted with MOPS minimal media supplemented with 10 mM ATP. The relative beneficial effects of the experiment are summarized in Figure 15.

Figure 15: Relative Beneficial Effect of the different transporter variants when cultivated in MOPS minimal media supplemented with 10 mM ATP. No substantial beneficial effect could be observed for any of the transporter variants. The highest beneficial effects were reached by E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2 (+17.2 % ± 7.2 %) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575) (+14.0 % ± 4.7 %).
The experiment was repeated once again with MOPS media supplemented with 100 µM of iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP. Substantial differences were observed for all transporter variants. PtNTT2(66-575) reached the highest beneficial effect with +38 % ± 10 %. All other transporter variants reached showed a negative effect compared to the reference. This confirms that ATP is exported in presence of the unnatural nucleotides, leading to a net loss of ATP and inhibition of growth. Therefore, it can be concluded that the native transporter variant PtNTT2 has the highest activity towards iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP, followed by PtNTT2(31-575).

Figure 16: Relative beneficial effect of the best PtNTT2 variants cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 100 µM of iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP each. Substantial differences can be observed for all transporter variants, with PtNTT2(66-575) reaching the highest beneficial effect +38 % ± 10 %. All other transporter variants reached showed a negative effect compared to the reference, which means that ATP is exported in exchange for iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP, leading to a net loss of ATP.

Figure 17: : Results of the LC-MS analysis of the supernatants of the cultures cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with 1 mM and 10 mM ATP. Measured AMP concentrations were standardized to the corresponding final optical densities.

Figure 18: Standard curve for AMP using 10 mM, 1 mM, 0.1 mM, 0.01 mM and 0.001 mM of AMP. The standard curve was used to quantify AMP in the supernatant of the cultivations carried out in ATP supplemented MOPS media.
Concluding, we were able to verify the function of PtNTT2 without using radioactively labeled nucleotides. The native transporter variant shows the highest activity in all experiments. Uptake of the unnatural nucleotides was verified by determination of the RBE of the different transporter variants when cultivated in MOPS media supplemented with the unnatural nucleotides. Since ATP is constantly exported in exchange for iso-dCmTP and iso-dGTP, leading to substantial negative influence on the growth of the cultures.
Subcellular Localization of PtNTT2

Figure 19: Confocal laser scanning microscopy of the different PtNTT2 variants fused to GFP (BBa_E0040). The pictures were taken with 100x magnification and show from A to E: <E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2, E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(66-575), E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-PtNTT2(31-575), E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-pelB-SP-PtNTT2 and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PlacUV5-TAT-SP-PtNTT2.
Isolation of PtNTT2 from the Inner Membrane

Figure 20: SDS-PAGE of the GFP-fusion constructs of PtNTT2
The cells were prepared using the fast cell lysis for SDS PAGE protocol. E. coli BL21(DE3) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Unsurprisingly, no thick band can be observed around 90.3 kDa, which would be the size of PtNTT2-cMyc-GFP. No bands can be observed for the other PtNTT2 variants.
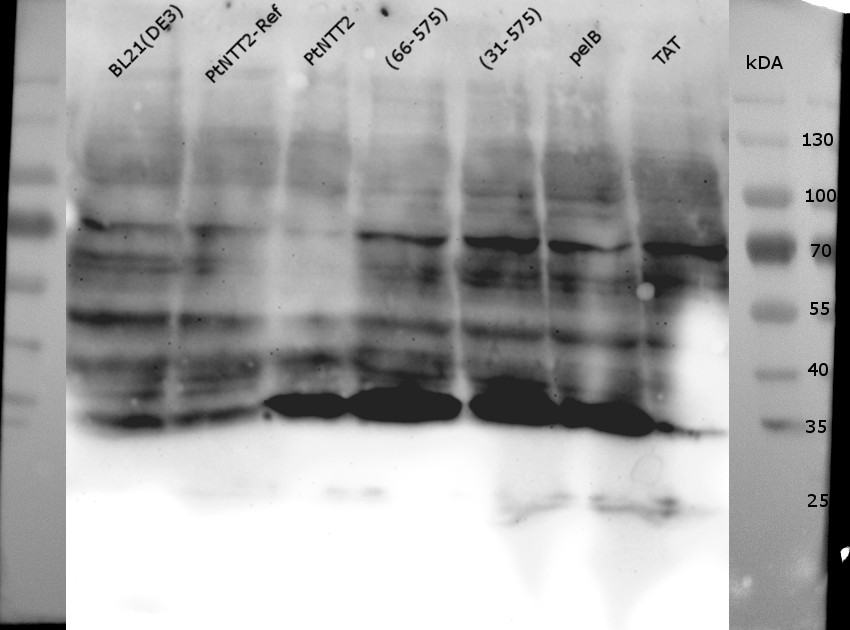
Figure 21: Western Blot of the samples prepared using the fast cell lysis for SDS PAGE protocol.
An anti-GFP antibody was used for the detection of PtNTT2-cMyc-GFP variants. E . coli BL21(DE3) and E. coli BL21(DE3) pSB1C3-PtNTT2 were used as negative controls. Much unspecific binding of the anti-GFP antibody could be observed, which is not surprising given that the entire proteome of the cells was analyzed. Thick band can be observed for PtNTT2-cMyc-GFP, PtNTT2(66-575)-cMyc-GFP, PtNTT2(31-575)-cMyc-GFP and PtNTT2(pelB)-cMyc-GFP around 35 kDa. This indicates that only the cMyc-GFP linker was detected and that the linker might be cleaved of from PtNTT2 due to the high difference in hydrophobicity.

Figure 22: SDS PAGE performed with the isolated membrane fractions.
The cMyc-GFP fusion proteins were used, which should be visible around ~90 kDa, differing slightly based on the PtNTT2 variant used. No bands could be observed around 90 kDa, which was subsequently proofed by performing a western blot.

Figure 23: Western Blot of the isolated membrane fractions of the strains expressing the cMyc-GFP fusion proteins.
Thick bands can be observed around 28 kDa for all samples except for PtNTT2-cMyc-GFP with a TAT signal peptide. The negative controls do not show the same band, but some unspecific binding of the anti-GFP antibody could be observed. Compared to the previous western blot, unspecific binding was substantially reduced. These results indicate, that the linker is most likely separated from the transporter either during the isolation process or already within the cell. This would be no surprise, given that the transporter is highly hydrophobic while the linker is hydrophilic.

Figure 24: Western Blot of the isolated membrane fraction using an anti-cMyc antibody.
Again, fragments can be observed around 35 kDa for all samples except for PtNTT2-cMyc-GFP with a TAT signal peptide. No bands can be observed for the full construct, but a very weak band can be seen between 55 and 70 kDa for the fusion protein of the native transporter.

Figure 25: SDS PAGE of the isolated membrane fraction without previous boiling
No thick bands can be observed around 70 kDa. Slightly above 100 kDa, bands can be observed for all PtNTT2 variants but not for the negative controls. But given that the samples ran quite different on the gel compared to the boiled samples, no definite conclusion can be drawn from this gel.
References



