| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
The purpose of this model is to select promoters used in downstream neurons of <i> C.elegans’</i> which have greatest possibility to be lighted on when AWA and AWB (the main neurons in our project) are actived. | The purpose of this model is to select promoters used in downstream neurons of <i> C.elegans’</i> which have greatest possibility to be lighted on when AWA and AWB (the main neurons in our project) are actived. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = References = | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
<html><a target="_blank" href="https://2017.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/Neuron Network Model" class="btn btn-default"><i class="ion-arrow-right-c"></i> See Details</a></html> | <html><a target="_blank" href="https://2017.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/Neuron Network Model" class="btn btn-default"><i class="ion-arrow-right-c"></i> See Details</a></html> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
{{:Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/wiki-footer}} | {{:Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/wiki-footer}} | ||
{{:Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/themeJs}} | {{:Team:SUSTech_Shenzhen/themeJs}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 05:40, 28 October 2017

Overview
Model
Contents
Modeling is usually used to make sense of the experimental discovery in traditional biological studies. In this synthetic biology project, we believe that carefully carried out modeling will be critical for the experimental design and data analysis at different stages of the project. We hope to demonstrate that the modeling is especially helpful to finalize the microfluidics chip design, and determine the distribution of the C.elegans (Caenorhabditis elegans) in microfliudics, as well as the transfection of the MiniMos in our experiment.
Model for Chemical Diffusion
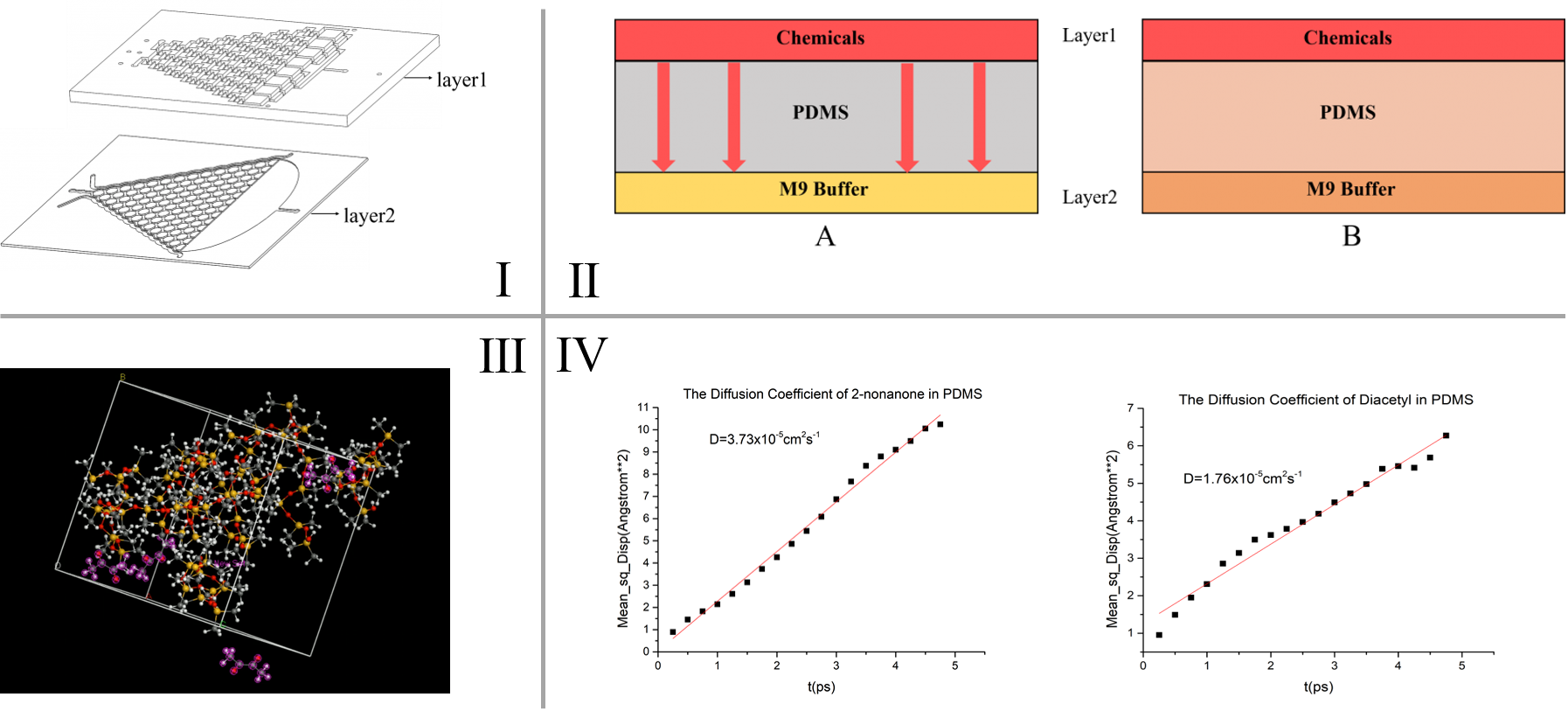
A diffusion model is built to simulate the diffusion process of chemicals in the PDMS chips, and through that we are able to determine the “delaying time” of the C. elegans’ olfactory response in our inducing experiment. The physical basis of this model is Fick’s second law (\frac{\partial C}{\partial t}=D \frac{\partial^2 C}{\partial x^2}) to know the chemical diffusion in PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane). To calculate the time t, the diffusion coefficient D (representing the diffusion rate of chemicals in PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane)) is needed. This parameter is calculated by simulating the force field of the diffusion of gases in silicone polymers in Material Studio®. [1] [2]
Model for Genetic Probability
In our program, we aim to change the physical behaviour of C. elegans using the two specific optogenetic traits.Through microinjection and selection, we are able to get two strains with two phenotypes of the preference to blue light and the aversion to red light , and the next step is to obtain the single worm with the combination ofe these 2 different traits. Therefore, we build a miniMos transfection model to simulate and estimate the final results of our transfection.
Model for Worms Locomotion
This model describes how microfluidics Gaussian distribution plate works when we use this device to test C.elegans’ preference in the plate.
Model for Neuron Network
The purpose of this model is to select promoters used in downstream neurons of C.elegans’ which have greatest possibility to be lighted on when AWA and AWB (the main neurons in our project) are actived.
References
- ↑ Albrecht, D. R. and C. I. Bargmann (2011). “High-content behavioral analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans in precise spatiotemporal chemical environments.” Nature Methods 8(7): 599-605.
- ↑ Troemel, E. R., Kimmel, B. E., & Bargmann, C. I. (1997). Reprogramming chemotaxis responses: sensory neurons define olfactory preferences in C. elegans. Cell, 91(2), 161-9.