(→Applied Design) |
(→Applied Design) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Our design is an alternative solution for detecting the presence of H3N2 virus using DNA 3-dimensional nanostructure as the diagnostic device. | Our design is an alternative solution for detecting the presence of H3N2 virus using DNA 3-dimensional nanostructure as the diagnostic device. | ||
| − | Currently, there are a few conventional methods to detect | + | |
| − | + | [[File:lpad.png| center | 500px| Comparison of different diagnostic method for H3N2 virus]] | |
| − | + | ||
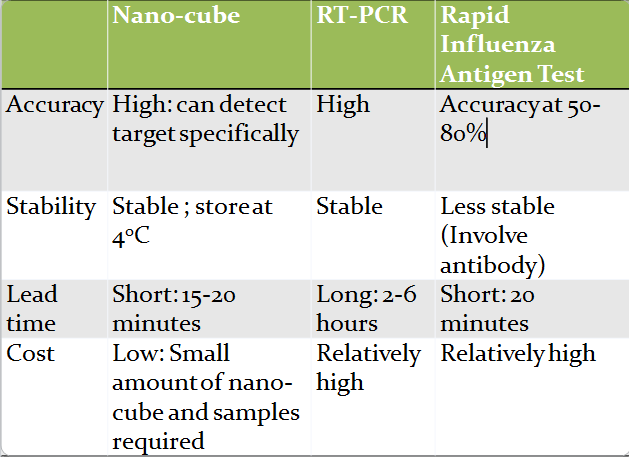
| + | Currently, there are a few conventional methods to detect influenza virus. One of them is to use real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). It is a reliable method with a high accuracy rate. However, the detection process takes around 2-6 hours, which may not be suitable for emergency cases which requires a short lead time for detection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another method is rapid influenza antigen test. This method can detect influenza virus shortly from 15 to 20 minutes. Nevertheless, using rapid influenza antigen test has its drawbacks. False negative result may be given due to the difference in viral activity and the amount of virus. Hence, the accuracy for this test lies between 50-80%, showing that the result may not fully reflect the situation of the patients. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another drawback is that the antibody used in rapid influenza antigen test is quite expensive. The cost of diagnosis of H3N2 virus would be very high. Plus, the storage of antibody is less stable than that of chemicals, which also affects sensitivity of the diagnosis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | detecting virus using DNA nanostructure as a diagnostic device may be a possible way out. DNA nanostructure is formed from several DNA strands. They have the ability to detect RNA of specific virus. Compared to current methods, this diagnostic method is more stable and cheaper because it does not involve any antibody. Chemicals used for detection is cheap and easy to store, which makes our diagnosis more feasible for public use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Concluded from the above table, it is obvious that our nano-cube could provide a cheaper, faster yet more precise detection for H3N2 virus. | ||
Revision as of 01:51, 2 November 2017
Applied Design
Our design is an alternative solution for detecting the presence of H3N2 virus using DNA 3-dimensional nanostructure as the diagnostic device.
Currently, there are a few conventional methods to detect influenza virus. One of them is to use real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). It is a reliable method with a high accuracy rate. However, the detection process takes around 2-6 hours, which may not be suitable for emergency cases which requires a short lead time for detection.
Another method is rapid influenza antigen test. This method can detect influenza virus shortly from 15 to 20 minutes. Nevertheless, using rapid influenza antigen test has its drawbacks. False negative result may be given due to the difference in viral activity and the amount of virus. Hence, the accuracy for this test lies between 50-80%, showing that the result may not fully reflect the situation of the patients.
Another drawback is that the antibody used in rapid influenza antigen test is quite expensive. The cost of diagnosis of H3N2 virus would be very high. Plus, the storage of antibody is less stable than that of chemicals, which also affects sensitivity of the diagnosis.
detecting virus using DNA nanostructure as a diagnostic device may be a possible way out. DNA nanostructure is formed from several DNA strands. They have the ability to detect RNA of specific virus. Compared to current methods, this diagnostic method is more stable and cheaper because it does not involve any antibody. Chemicals used for detection is cheap and easy to store, which makes our diagnosis more feasible for public use.
Concluded from the above table, it is obvious that our nano-cube could provide a cheaper, faster yet more precise detection for H3N2 virus.