| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<head> | <head> | ||
<style> | <style> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
button.accordion { | button.accordion { | ||
background-color: #eee; | background-color: #eee; | ||
| Line 28: | Line 12: | ||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
border: none; | border: none; | ||
| − | text-align: | + | text-align: left; |
outline: none; | outline: none; | ||
font-size: 15px; | font-size: 15px; | ||
| Line 41: | Line 25: | ||
padding: 0 18px; | padding: 0 18px; | ||
display: none; | display: none; | ||
| − | background-color: | + | background-color: white; |
} | } | ||
body { | body { | ||
| Line 48: | Line 32: | ||
} | } | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| + | </head> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="column full_size"> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color: lightcyan;padding:14px; font-family: verdana"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
<div class = "column_full_size_inner"> | <div class = "column_full_size_inner"> | ||
| + | <h2 style="font-family: verdana; font-size: 45px; text-align: center; color: rgb(0, 184, 230)">Results</h2> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | |||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
<div class="column sixth_size"> | <div class="column sixth_size"> | ||
| − | <a href="#section1"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/ | + | <a href="#section1"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/5f/Gga-gfp.png" style="width:100%"><p>Part Plasmids </p></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="column sixth_size"> | <div class="column sixth_size"> | ||
| − | <a href="#section2"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/ | + | <a href="#section2"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/3/39/Plasmidpart.png" style="width:100%"><p>Cassette Assembly</p></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="column fifth_size"> | <div class="column fifth_size"> | ||
| − | <a href="#section3"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/ | + | <a href="#section3"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/archive/e/e7/20171101072448%21GABAFinal.png" style="width:100%"> <p>GABA Production </p></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="column sixth_size"> | <div class="column sixth_size"> | ||
| − | <a href="#section4"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/ | + | <a href="#section4"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/e/e5/Lacto-final.png" style="width:100%"><p><i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i></p></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <strong><h2 style="font-family: verdana; font-size: 17px; text-align: center; color: rgb(0, 184, 230)">Click on one of the images above to learn more about our results!</h2></strong> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 187: | Line 180: | ||
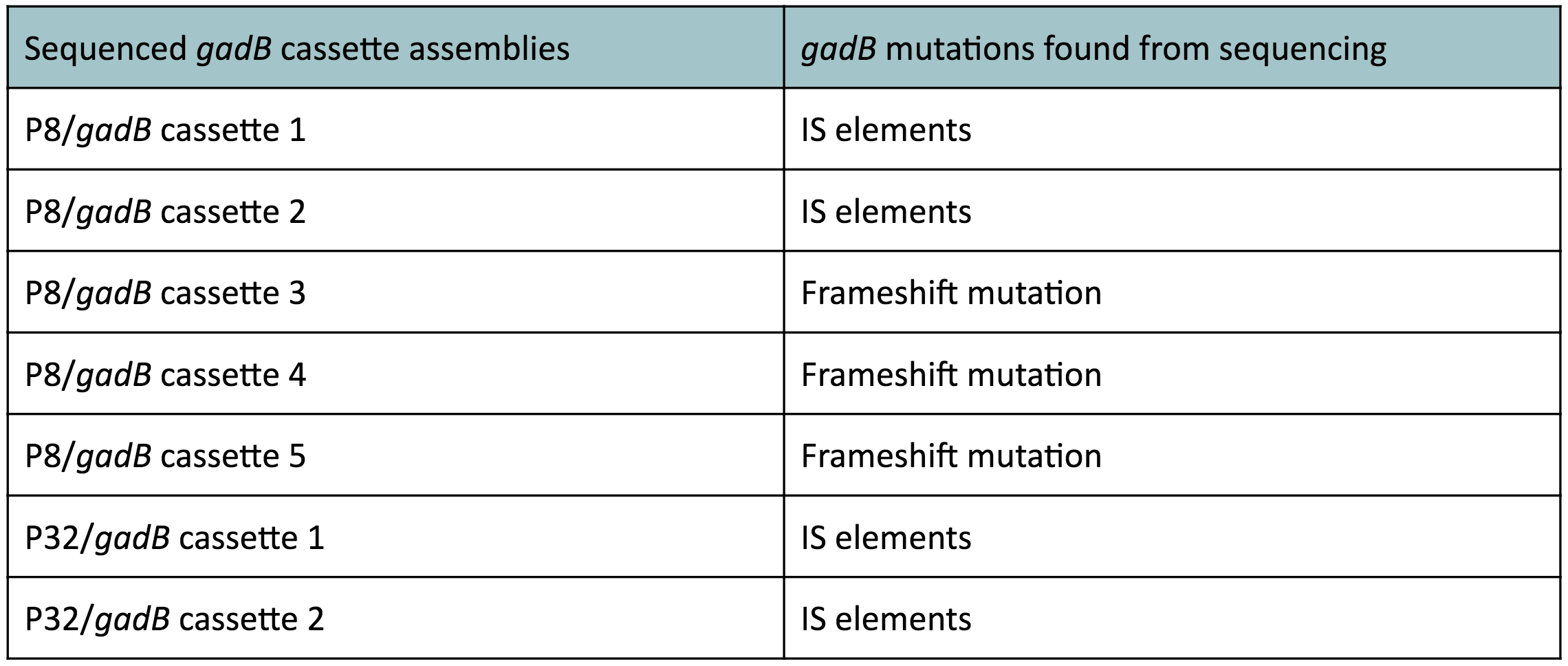
| − | <p | + | <p>Along with being one of the canonical amino acids utilized in protein synthesis, glutamate plays an important role as the main amino-group donor in the biosynthesis of nitrogen-containing compounds such as amino acids and nucleotides (4, 5). Thus, we hypothesized that <i>gadB</i> overexpression via the P8 and P32 constitutive promoters and the high-copy-number ColE1 origin induced a high metabolic load on the cells by shunting away glutamate from essential anabolic pathways. Additionally, having high <i>gadB</i> expression does not confer a selective advantage to the cells. We believed that transformants containing the mutationally degraded <i>gadB</i> gene were favored in the population, as "breaking" the metabolically-taxing <i>gadB</i> gene gave these transformants a competitive advantage, allowing them to utilize glutamate sources towards growth. In contrast, transformants containing the functional <i>gadB</i> gene were selected against due to having a depletion of glutamate needed for important cellular processes. </p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 200: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
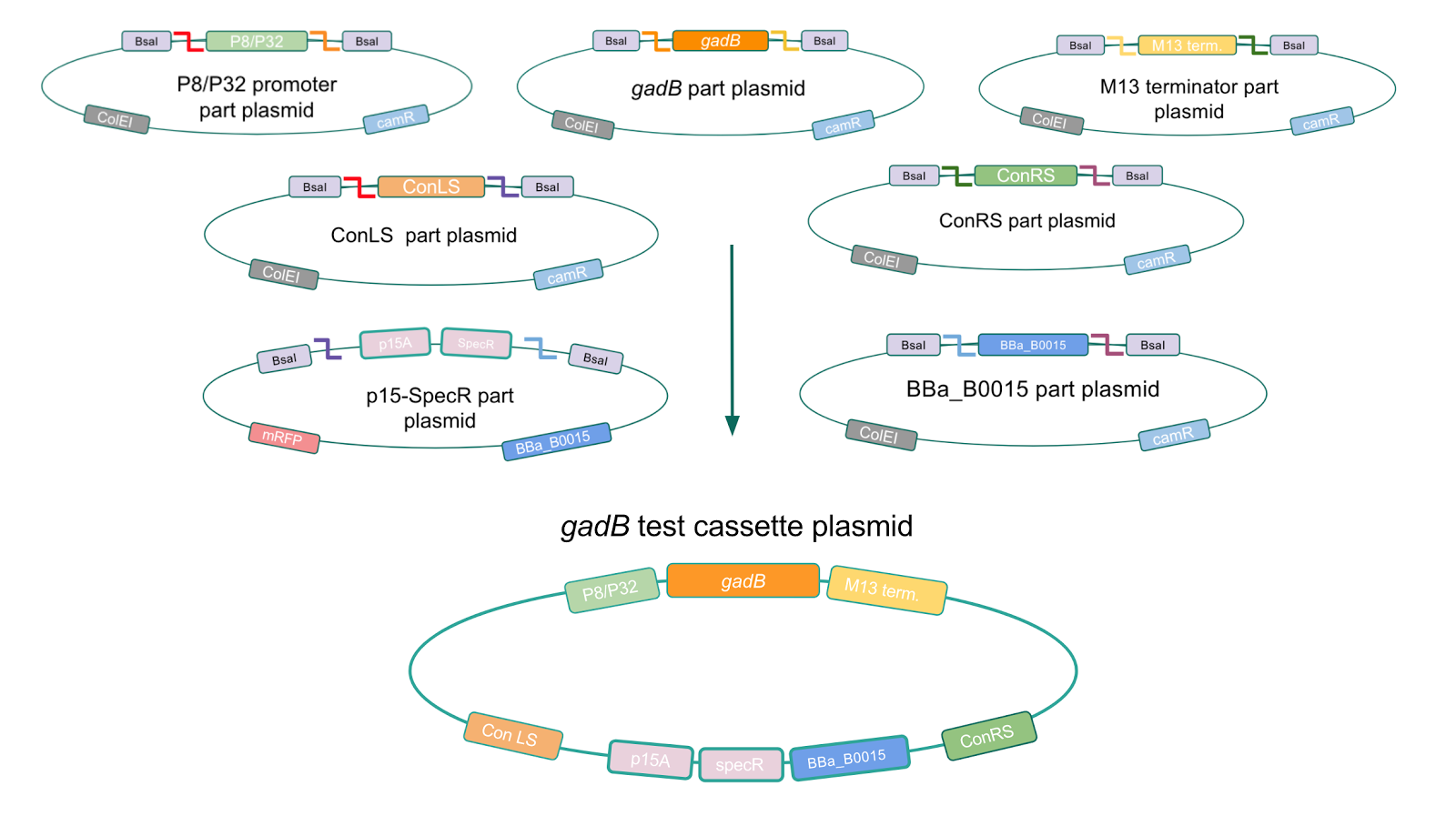
| − | <p | + | <p><b>Given our experimental results and the fact that inducibly expressed genetic devices are more evolutionarily stable than constitutively expressed ones (6), we attempted to inducibly express the <i>gadB</i> gene using the regulatory elements of the lac operon to see if expression and maintenance of a stable <i>gadB</i> gene was possible in <i>E. coli</i></b>. Our IPTG-inducible <i>gadB</i> expression cassette plasmid was assembled using a lac promoter and operator part plasmid, the <i>gadB</i> gene part plasmid, the M13 terminator part plasmid, connector part plasmids, a CP25 promoter part plasmid, a lacI part plasmid, and the SpecR and p15A origin part plasmid <b>(Fig. 8)</b>. Under this assembled regulatory system, in the absence of IPTG (an analog of the allolactose inducer) the LacI repressor will bind to the lac operator region to block transcription of the <i>gadB</i> gene. When present, IPTG will act as an inducer and bind to the LacI repressor to decrease its binding affinity for the lac operator, thereby allowing for <i>gadB</i> expression. This IPTG-inducible system provides us with a mechanism of controlling <i>gadB</i> expression. <b>Positive colonies have been identified and sequence verification is currently underway.</b> </p> |
| Line 223: | Line 216: | ||
<h2 style="font-family: verdana; font-size: 28px; text-align: center">Creating a Golden Gate compatible shuttle vector</h2> | <h2 style="font-family: verdana; font-size: 28px; text-align: center">Creating a Golden Gate compatible shuttle vector</h2> | ||
| − | <p style="font-family: verdana">We wanted to assemble our final GABA overexpression cassette plasmid using the shuttle vector pMSP3535 as the backbone <b>(Fig. 9).</b> To do this, we first needed to make pMSP3535 Golden Gate compatible (i.e. free of BsaI restriction sites and containing correct overhangs for cassette assembly). We chose to work with pMSP3535 as it contains both a ColE1 origin for replication in <i>E. coli</i> and a pAMb1 origin for replication in Gram-positive bacteria including <i>Lactobacillus</i> species ( | + | <p style="font-family: verdana">We wanted to assemble our final GABA overexpression cassette plasmid using the shuttle vector pMSP3535 as the backbone <b>(Fig. 9).</b> To do this, we first needed to make pMSP3535 Golden Gate compatible (i.e. free of BsaI restriction sites and containing correct overhangs for cassette assembly). We chose to work with pMSP3535 as it contains both a ColE1 origin for replication in <i>E. coli</i> and a pAMb1 origin for replication in Gram-positive bacteria including <i>Lactobacillus</i> species (7). Additionally, the <strong>pMSP3535 vector contains the resistance gene for erythromycin, of which <i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i> is naturally susceptible (8).</strong></p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 243: | Line 236: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p style="font-family: verdana><b>Since the original pMSP3535 vector contained two illegal BsaI sites within the ColE1 origin, we sought to replace this ColE1 origin with a BsaI-free one isolated from pYTK001.</b> This assembly process involved linearizing and adding BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs to the pMSP3535 backbone and the pYTK001 ColE1 origin via PCR. After the pMSP3535 backbone and ColE1 origin were successfully amplified by PCR <b>(Fig. 11a)</b>, they were joined together using BsmBI assembly. Diagnostic PCR was performed on pMSP3535 + ColE1 minipreps from <i>E. coli</i> transformants to screen for positive samples containing both the pMSP3535 backbone and the ColE1 inserts (Fig. 11b). <b>After confirming the presence of the pMSP3535 vector and ColE1 origin, we partially sequence-confirmed the two miniprep samples.</b></p> | + | <p style="font-family: verdana"><b>Since the original pMSP3535 vector contained two illegal BsaI sites within the ColE1 origin, we sought to replace this ColE1 origin with a BsaI-free one isolated from pYTK001.</b> This assembly process involved linearizing and adding BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs to the pMSP3535 backbone and the pYTK001 ColE1 origin via PCR. After the pMSP3535 backbone and ColE1 origin were successfully amplified by PCR <b>(Fig. 11a)</b>, they were joined together using BsmBI assembly. Diagnostic PCR was performed on pMSP3535 + ColE1 minipreps from <i>E. coli</i> transformants to screen for positive samples containing both the pMSP3535 backbone and the ColE1 inserts (Fig. 11b). <b>After confirming the presence of the pMSP3535 vector and ColE1 origin, we partially sequence-confirmed the two miniprep samples.</b></p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 253: | Line 246: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p style="font-family: verdana>To this pMSP3535 + ColE1 assembly, we wanted to add a <i>gfp</i> dropout part containing internal BsaI sites that will generate overhangs compatible with those in the P8/P32 promoter and M13 terminator part plasmids.</b> Additionally, the incorporation of this <i>gfp</i> dropout part will also allow us to visually screen for positive and negative transformants based on their fluorescence. BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs were added to the <i>gfp</i> dropout part by PCR amplifying it from pYTK047. We have been attempting to linearize and add BsmBI sites and overhangs to the positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 assemblies via PCR, with no success. However, results from diagnostic digests suggested that our assemblies may have contained extra, undesired DNA such as IS elements (Fig. 12). Thus, as of right now, we are screening for more positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 transformants. Once we have trouble-shooted this problem, the pMSP3535 + ColE1 and the <i>gfp</i> dropout PCR products will be joined through BsmBI assembly to form the final Golden Gate compatible pMSP3535 vector. | + | <p style="font-family: verdana">To this pMSP3535 + ColE1 assembly, we wanted to add a <i>gfp</i> dropout part containing internal BsaI sites that will generate overhangs compatible with those in the P8/P32 promoter and M13 terminator part plasmids.</b> Additionally, the incorporation of this <i>gfp</i> dropout part will also allow us to visually screen for positive and negative transformants based on their fluorescence. BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs were added to the <i>gfp</i> dropout part by PCR amplifying it from pYTK047. We have been attempting to linearize and add BsmBI sites and overhangs to the positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 assemblies via PCR, with no success. However, results from diagnostic digests suggested that our assemblies may have contained extra, undesired DNA such as IS elements <b>(Fig. 12).</b> <b>Thus, as of right now, we are screening for more positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 transformants.</b> Once we have trouble-shooted this problem, the pMSP3535 + ColE1 and the <i>gfp</i> dropout PCR products will be joined through BsmBI assembly to form the final Golden Gate compatible pMSP3535 vector. </p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
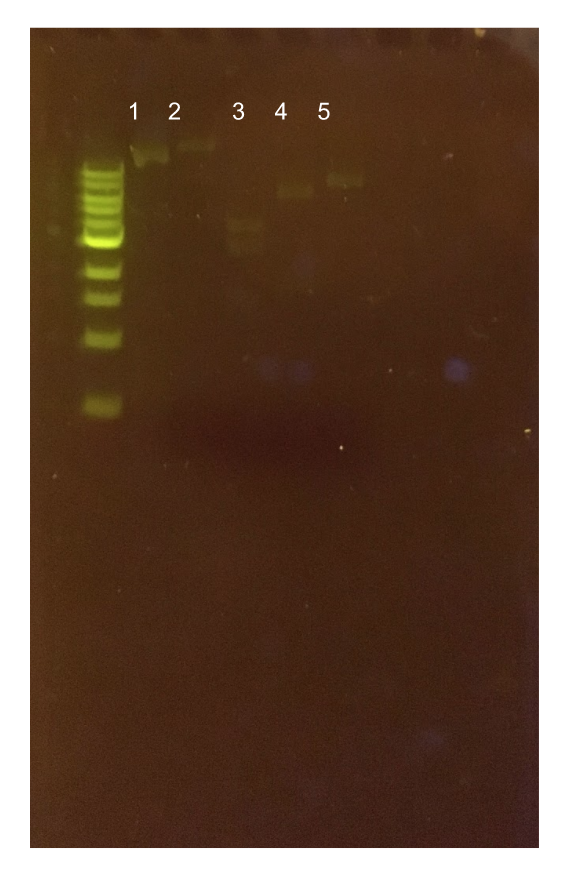
| − | [[File:T--Austin_UTexas--pMSP3535ColE1Diag.jpg|thumb|center| | + | [[File:T--Austin_UTexas--pMSP3535ColE1Diag.jpg|thumb|center|450px|<b>Figure 12.</b> Agarose gel of pMSP3535 + ColE1 assembly diagnostic digests. Lane 1 contains the undigested plasmid assembly. Lane 2 contains the ClaI-digested plasmid with expected 400 bp and 4.6 kb bands. The actual band generated is apparently above 10 kb. Lane 3 contains the XmnI-digested plasmid with expected 200 bp, 1.5 kb, and 3.3 kb bands. The generated band sizes were 2.5 kb and 4 kb. Lane 4 contains the KpnI-digested assembly with an expected 5.1 kb band. The generated band size was 6 kb. Lane 5 contains the Bg1II-digested assembly with an expected 5.1 kb band. The generated band size was 8 kb.]] |
<html> | <html> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | < | + | <h3 style="font-family: verdana"; font-size: 28px; text-align: center">Assessing erythromycin susceptibility of <i>E. coli</i></h3> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 284: | Line 277: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p style="font-family: verdana"><i> Lactobacillus plantarum </i> is a gram-positive lactic acid producing bacteria, so it requires a different growth media than we typically use in our lab. In 1954, Briggs agar was developed ( | + | <p style="font-family: verdana"><i> Lactobacillus plantarum </i> is a gram-positive lactic acid producing bacteria, so it requires a different growth media than we typically use in our lab. In 1954, Briggs agar was developed (9). This media was designed for <i>Lactobacilli</i>, but was not sufficient for many species, including <i> Lactobacillus plantarum </i>, so a different non-selective media for general lactobacilli was developed in 1960 by Man, Rogosa and Sharpe and named MRS (10). We have exclusively grown our <i> Lactobacillus plantarum </i> on MRS media. Further, we grew <i> Lactobacillus plantarum </i> in a CO2 incubator as referenced in most literature we studied (11-13). The metabolic pathways in the bacteria alter when grown aerobically to produce excess acetate (14) and less lactic acid. Because we intend to utilize this bacteria in a fermentable food, a change in this metabolic pathway would not benefit our ultimate goal.</p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 300: | Line 293: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p style="font-family: verdana">Once we could successfully grow our chosen bacteria, we needed to transform the gram positive, <i> Lactobacillus plantarum</i>, with pMSP3535. In order to do this, we identified and worked with a different protocol than we had ever used in our lab. We attempted several protocols, including Landete 2014 ( | + | <p style="font-family: verdana">Once we could successfully grow our chosen bacteria, we needed to transform the gram positive, <i> Lactobacillus plantarum</i>, with pMSP3535. In order to do this, we identified and worked with a different protocol than we had ever used in our lab. We attempted several protocols, including Landete 2014 (11) and Speer 2012 (12). However, we found success using a variation of the Welker protocol(13). Welker et al. transformed multiple strains of <i>Lactobacillus casei</i> using varying reagents and yielded different efficiencies between each strain of the species with each variation.</p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 391: | Line 384: | ||
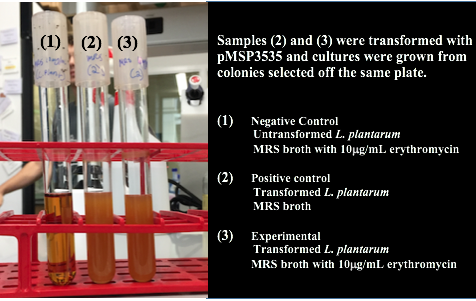
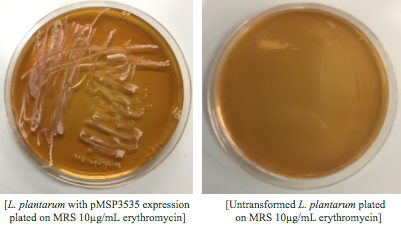
<p style="font-family: verdana">Colonies from each transformation plate were grown up in MRS broth supplemented with 10μg/mL erythromycin. The subsequent day, they were streaked on 10μg/mL erythromycin MRS agar plates to verify resistance.</p> | <p style="font-family: verdana">Colonies from each transformation plate were grown up in MRS broth supplemented with 10μg/mL erythromycin. The subsequent day, they were streaked on 10μg/mL erythromycin MRS agar plates to verify resistance.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <strong><p style="font-family: verdana"> Genomic and plasmid sequence verification is underway.</p></strong> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 425: | Line 420: | ||
<li>Sarkar, P.K. and Nout, M.J.R. (Eds.) 2014. Handbook of Indigenous Foods Involving Alkaline Fermentation. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group, p. 629.</il> | <li>Sarkar, P.K. and Nout, M.J.R. (Eds.) 2014. Handbook of Indigenous Foods Involving Alkaline Fermentation. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group, p. 629.</il> | ||
| + | <li>Sleight, S. C. et al. Designing and engineering evolutionary robust genetic circuits. Journal of Biological Engineering. (4):12 (2010).</il> | ||
<li>Pérez-Arellano, I. et al. Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and <i>Escherichia coli</i>. Plasmid. 46(2): 106-16 (2001).</li> | <li>Pérez-Arellano, I. et al. Construction of Compatible Wide-Host-Range Shuttle Vectors for Lactic Acid Bacteria and <i>Escherichia coli</i>. Plasmid. 46(2): 106-16 (2001).</li> | ||
| Line 448: | Line 444: | ||
| − | |||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:21, 1 November 2017
Results
Click on one of the images above to learn more about our results!
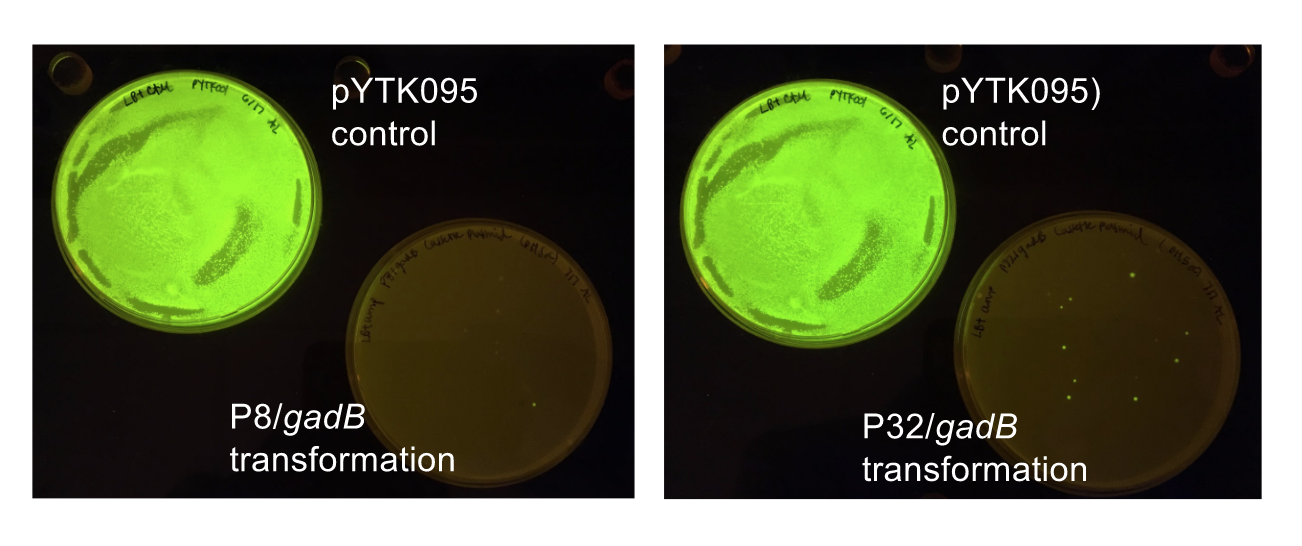
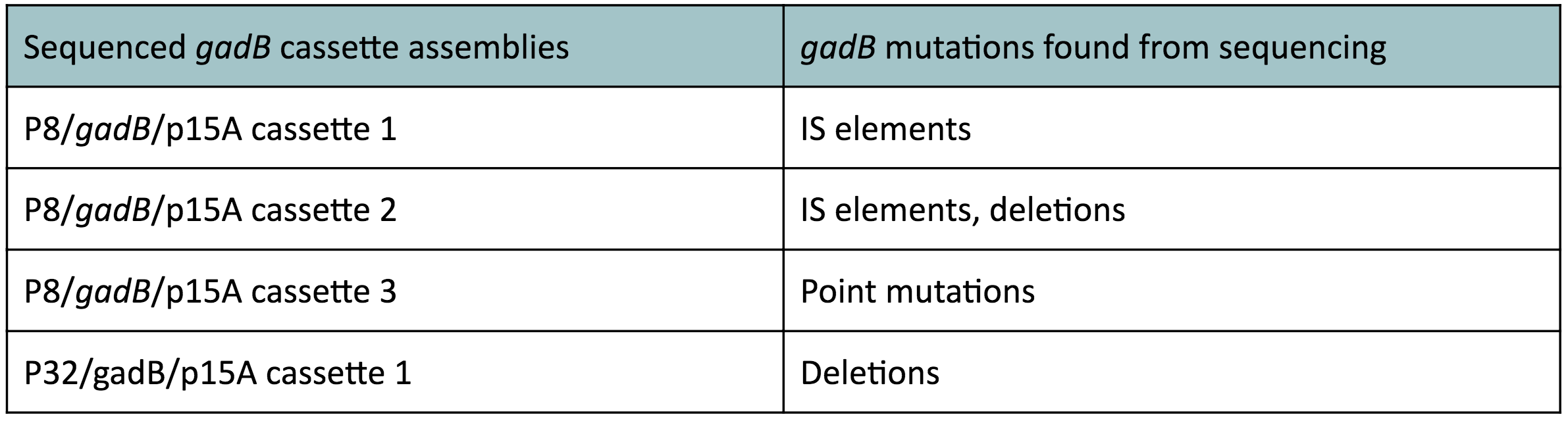
Although bacteria can naturally synthesize GABA, we wanted to increase expression of the gadB gene and subsequently GABA production in order to imbue our probiotic with a more potent medicinal quality, with the idea that this GABA-overproducing probiotic can then be consumed by patients with bowel disorders or anxiety (1). Overexpression of the gadB gene will be accomplished by placing it under the control of either the P8 or P32 constitutive promoters from Lactococcus lactis (2).
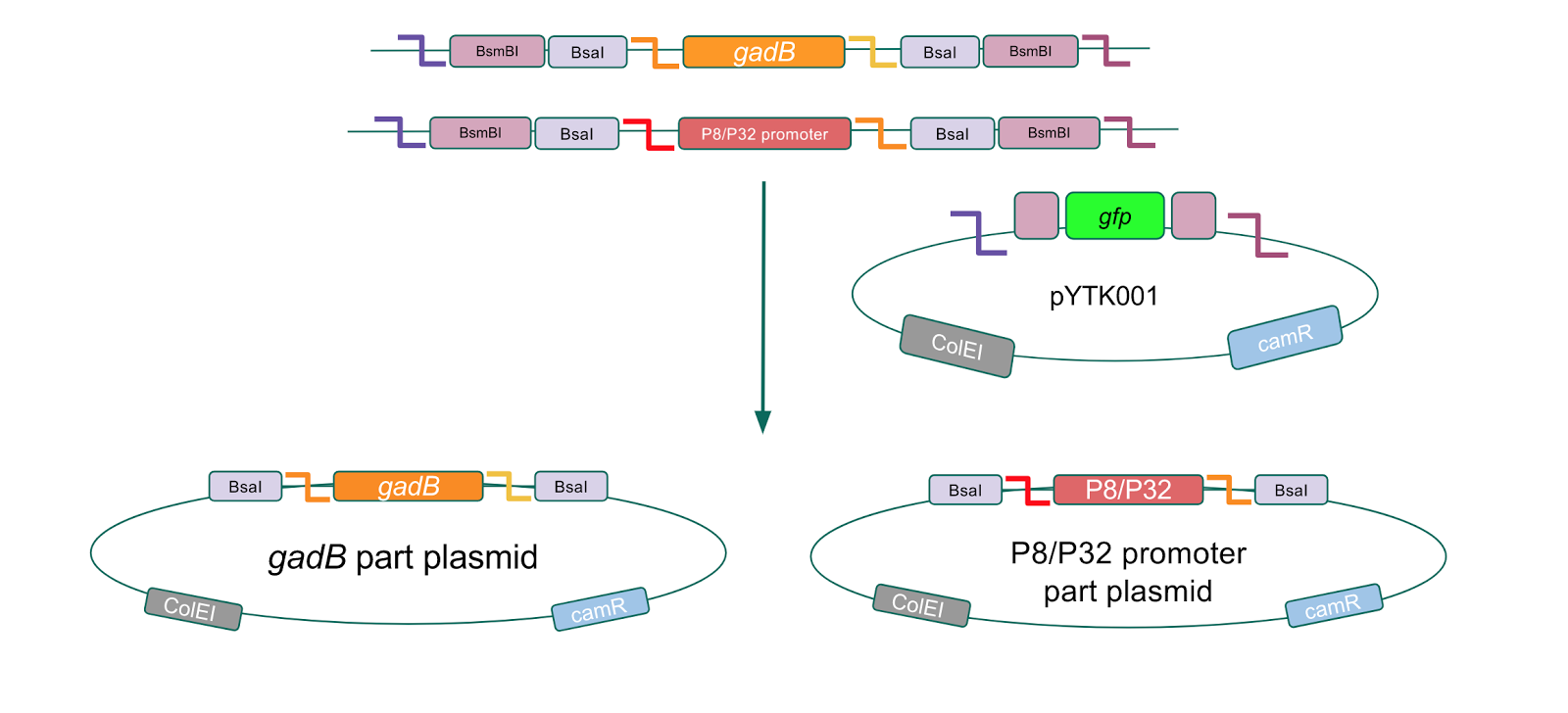
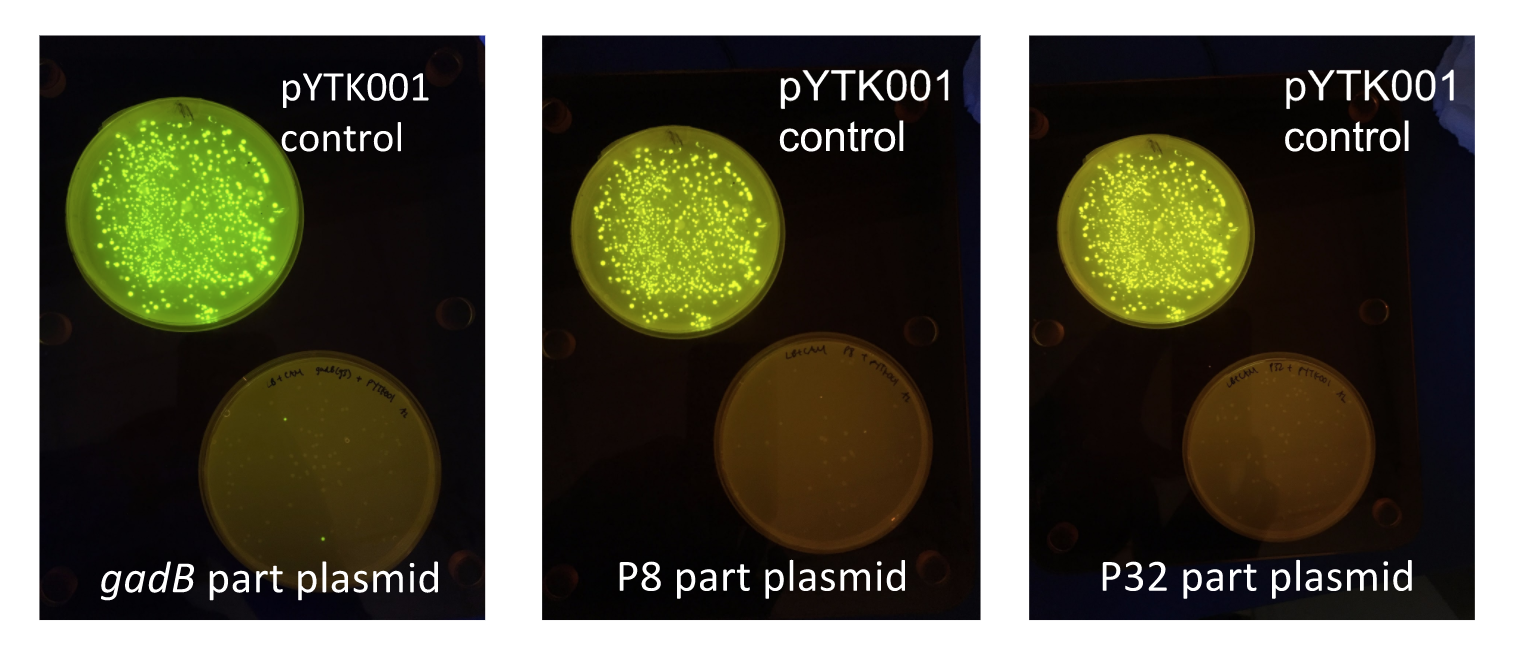
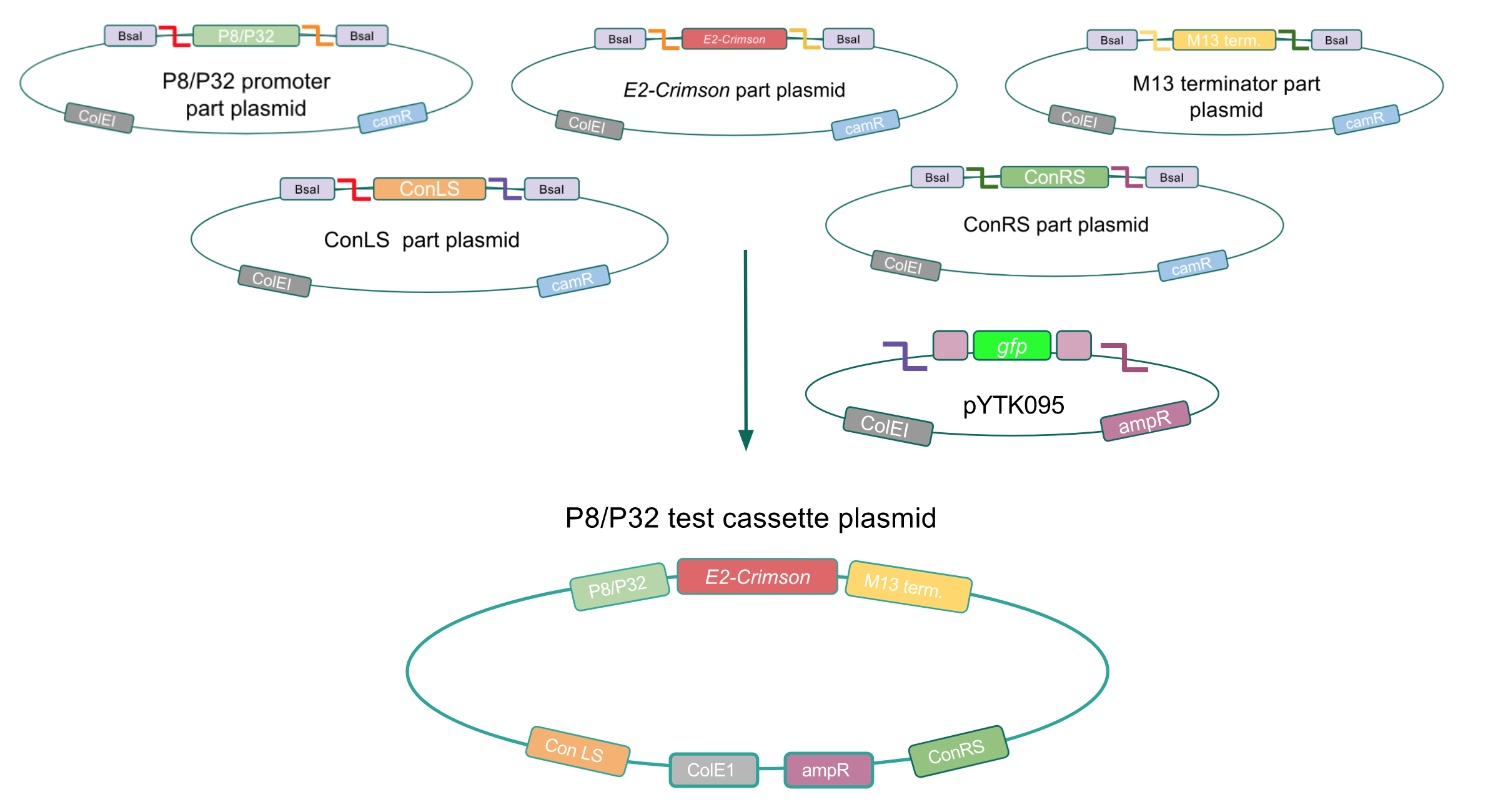
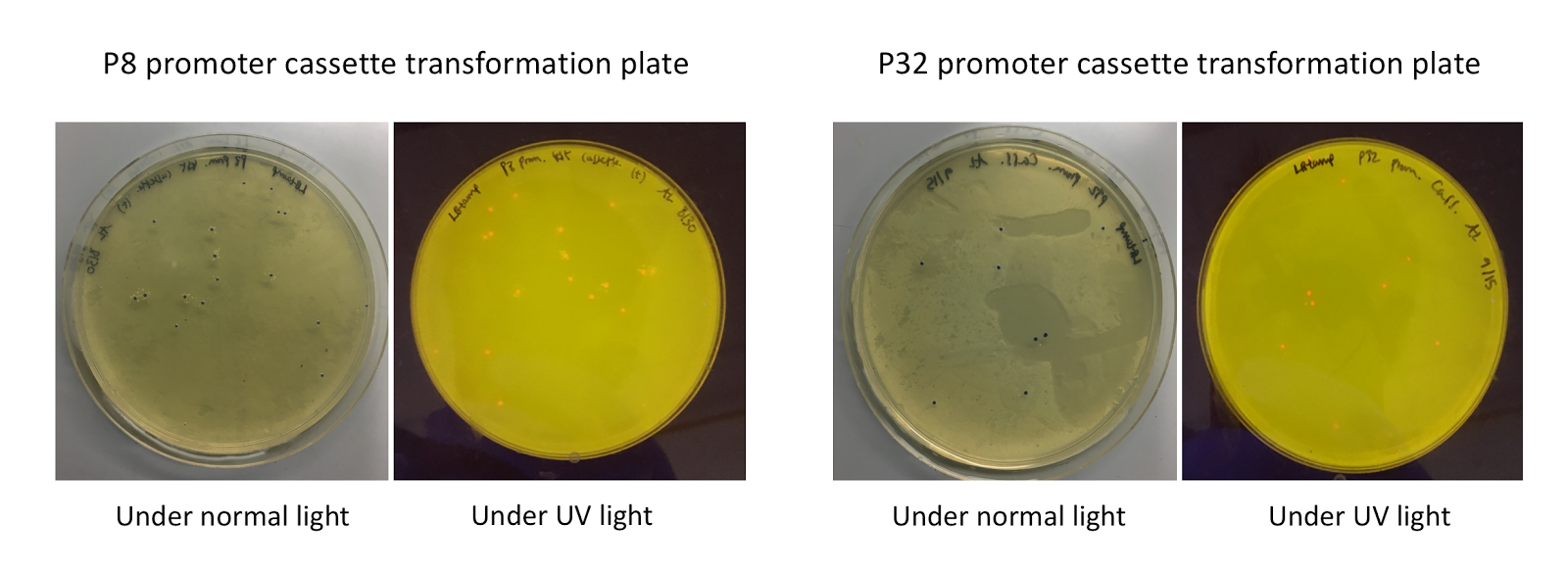
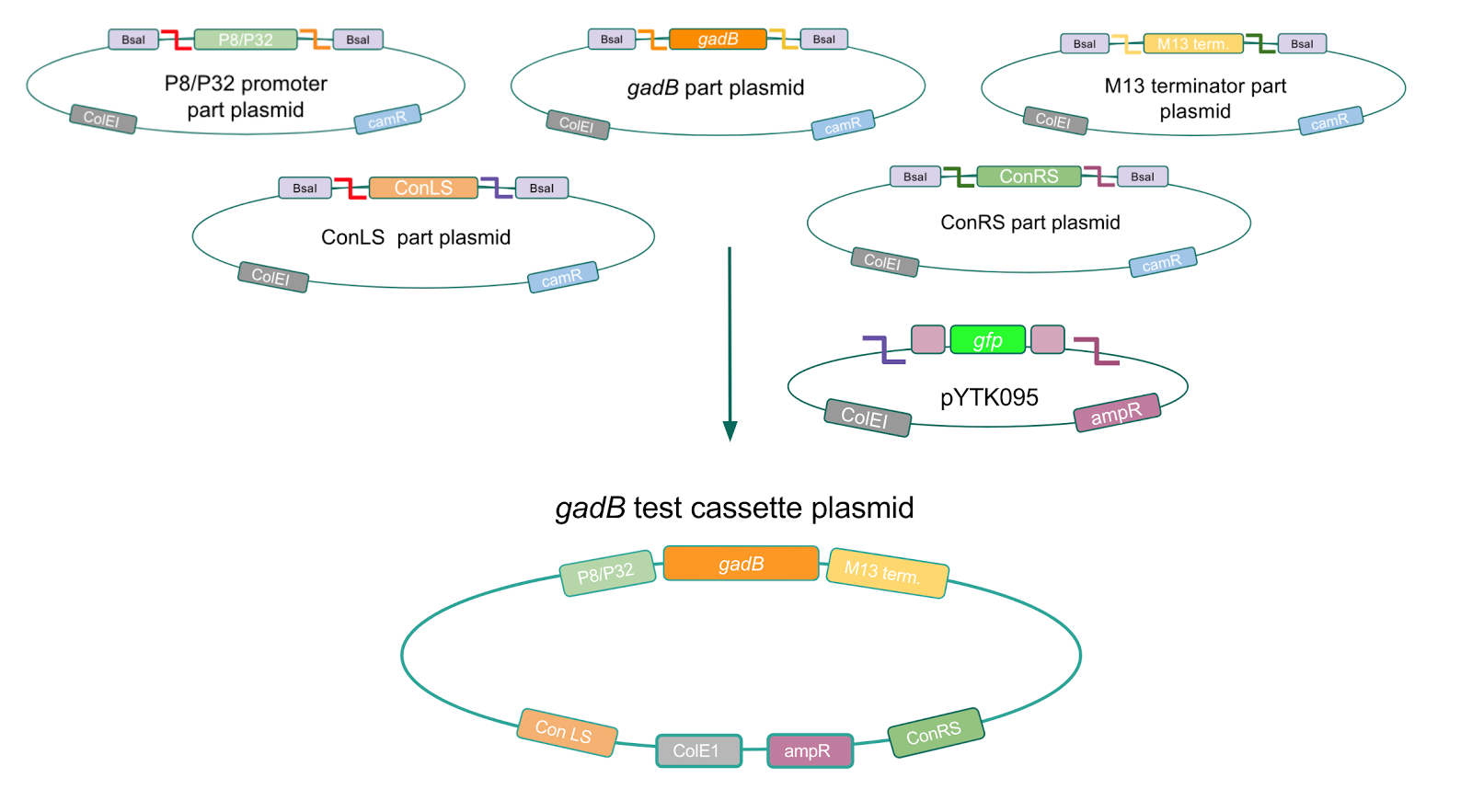
To make our GABA-producing probiotic we first needed to assemble a GABA overexpression cassette plasmid using the Golden Gate assembly method. The intention here is that bacteria containing this GABA overexpression cassette plasmid should produce high levels of GABA. In short, Golden Gate Assembly is a new cloning method that allows for the creation of a multi-part DNA assembly (i.e. cassette plasmid) in a single reaction through the use of DNA parts containing specific, predefined suffixes and prefixes with recognition sites for Type IIs restriction enzymes (e.g. BsmBI and BsaI). The specificity of these suffixes and prefixes provides directionality of the desired DNA parts during the assembly process. For our purposes, we used the MoClo Yeast Tool Kit developed by John Dueber (3).
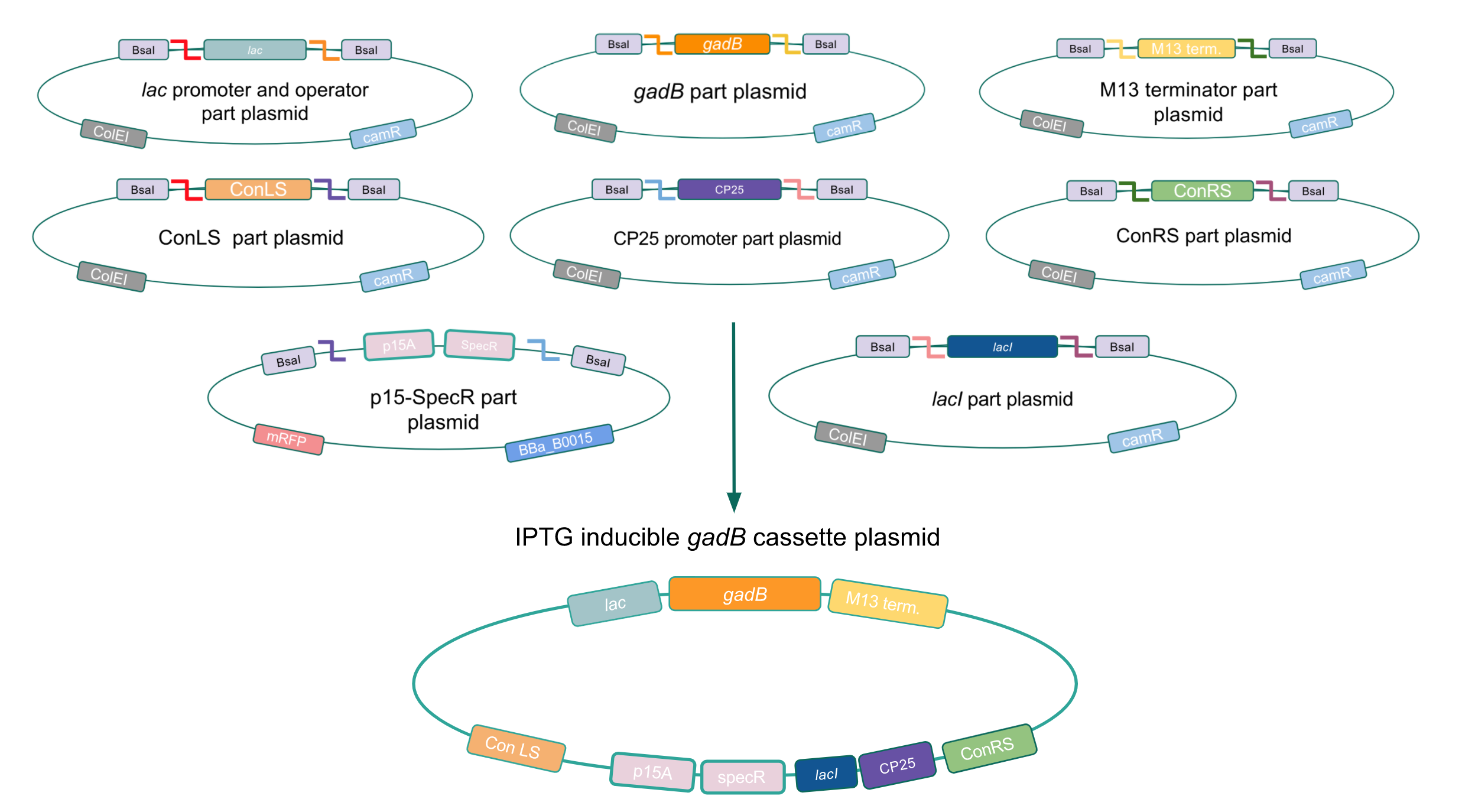
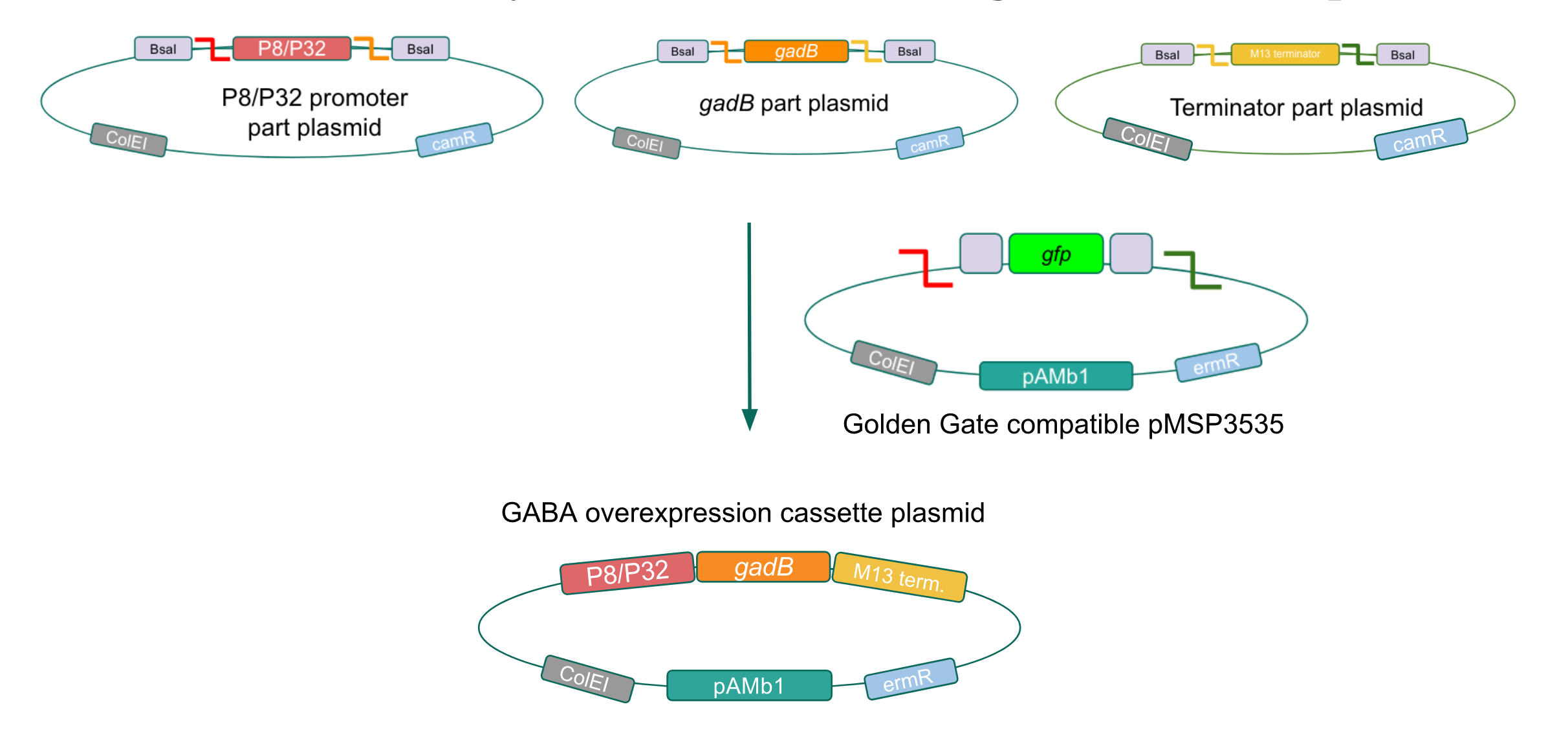
Creating a Golden Gate compatible shuttle vector
We wanted to assemble our final GABA overexpression cassette plasmid using the shuttle vector pMSP3535 as the backbone (Fig. 9). To do this, we first needed to make pMSP3535 Golden Gate compatible (i.e. free of BsaI restriction sites and containing correct overhangs for cassette assembly). We chose to work with pMSP3535 as it contains both a ColE1 origin for replication in E. coli and a pAMb1 origin for replication in Gram-positive bacteria including Lactobacillus species (7). Additionally, the pMSP3535 vector contains the resistance gene for erythromycin, of which Lactobacillus plantarum is naturally susceptible (8).
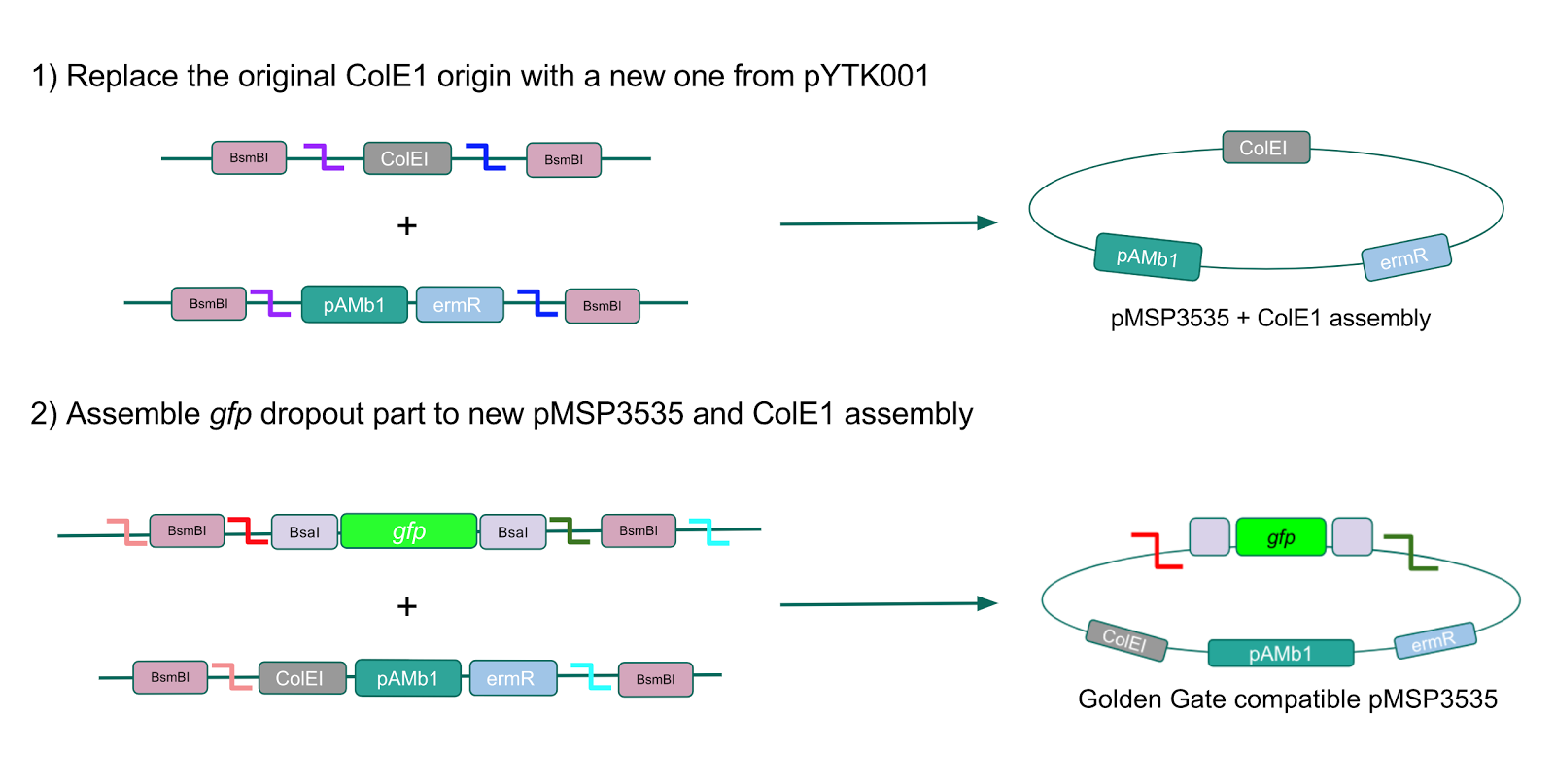
The process of making the pMSP3535 vector Golden Gate compatible involved two steps: 1) assembling the pMSP3535 backbone (pAMb1 origin and erythromycin resistance gene) with a new ColE1 origin; 2) assembling a gfp dropout part to the assembly of the pMSP3535 backbone and the new ColE1 origin (Fig. 10).
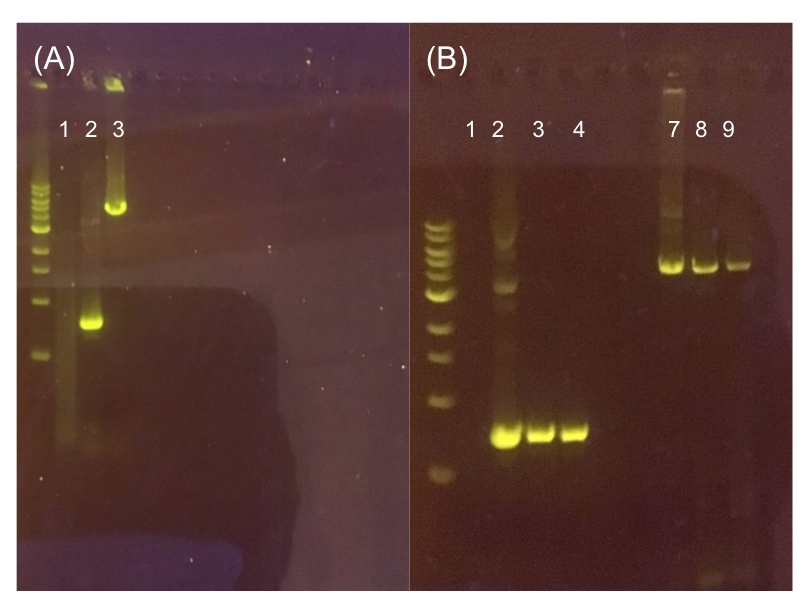
Since the original pMSP3535 vector contained two illegal BsaI sites within the ColE1 origin, we sought to replace this ColE1 origin with a BsaI-free one isolated from pYTK001. This assembly process involved linearizing and adding BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs to the pMSP3535 backbone and the pYTK001 ColE1 origin via PCR. After the pMSP3535 backbone and ColE1 origin were successfully amplified by PCR (Fig. 11a), they were joined together using BsmBI assembly. Diagnostic PCR was performed on pMSP3535 + ColE1 minipreps from E. coli transformants to screen for positive samples containing both the pMSP3535 backbone and the ColE1 inserts (Fig. 11b). After confirming the presence of the pMSP3535 vector and ColE1 origin, we partially sequence-confirmed the two miniprep samples.
To this pMSP3535 + ColE1 assembly, we wanted to add a gfp dropout part containing internal BsaI sites that will generate overhangs compatible with those in the P8/P32 promoter and M13 terminator part plasmids. Additionally, the incorporation of this gfp dropout part will also allow us to visually screen for positive and negative transformants based on their fluorescence. BsmBI sites and compatible overhangs were added to the gfp dropout part by PCR amplifying it from pYTK047. We have been attempting to linearize and add BsmBI sites and overhangs to the positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 assemblies via PCR, with no success. However, results from diagnostic digests suggested that our assemblies may have contained extra, undesired DNA such as IS elements (Fig. 12). Thus, as of right now, we are screening for more positive pMSP3535 + ColE1 transformants. Once we have trouble-shooted this problem, the pMSP3535 + ColE1 and the gfp dropout PCR products will be joined through BsmBI assembly to form the final Golden Gate compatible pMSP3535 vector.
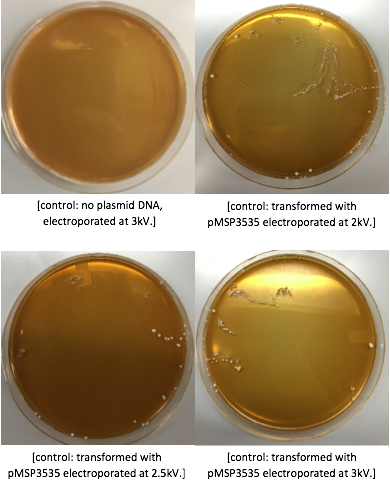
Assessing erythromycin susceptibility of E. coli
Because we are creating our Golden Gate compatible pMSP3535 shuttle vector in E. coli, we wanted to determine the natural susceptibility of E. coli to erythromycin as the minimum concentration to use has not been established clearly in the literature. Thus, we performed an erythromycin minimum inhibitory concentration test in liquid LB media (Fig. 13). After one-day incubation, we observed that E. coli was resistant up to around 150 µg/mL of erythromycin. From this experiment, we have determined that the optimal erythromycin concentration for selecting against E. coli in liquid culture is around 200-250 µg/mL.