| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<p style="font-family: verdana"> The goal of our model is to simulate the expected behavior of our transformed <i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i> after consumption. | <p style="font-family: verdana"> The goal of our model is to simulate the expected behavior of our transformed <i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i> after consumption. | ||
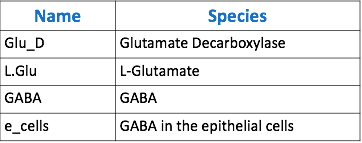
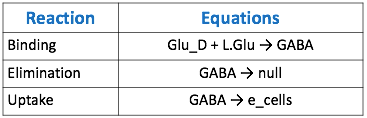
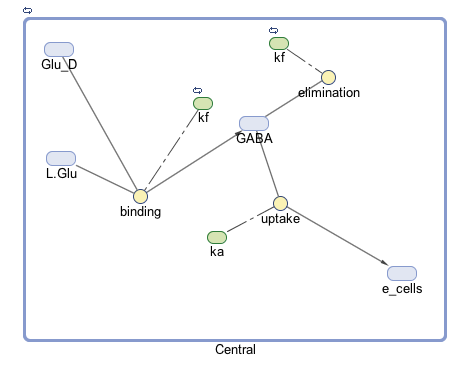
| − | We focused on modeling the binding reaction of glutamate decarboxylase and L-glutamate. We looked specifically at how our <i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i> would encode the <i>gadB</i> gene to produce higher levels of glutamate decarboxylase and increase the uptake of GABA by the ENS. In our model, we aimed to compare the rates of GABA uptake by the ENS at differing concentrations dependent on an increased production of glutamate decarboxylase from <i>gadB</i> overexpression. Our model assumes a first-order dosing type and an enzymatic elimination type. Table 1 displays the chemical species involved in the reactions detailed in Table 2. Specifically, the binding reaction (which takes place in the intracellular environment of our probiotic) involves the conversion of L-glutamate into GABA via glutamate decarboxylase. This binding reaction has a special binding constant, which we accounted for in our model. The second chemical reaction we accounted for was the elimination of GABA to the extracellular environment through the membrane transport system of our probiotic. | + | We focused on modeling the binding reaction of glutamate decarboxylase and L-glutamate. We looked specifically at how our <i>Lactobacillus plantarum</i> would encode the <i>gadB</i> gene to produce higher levels of glutamate decarboxylase and increase the uptake of GABA by the ENS. In our model, we aimed to compare the rates of GABA uptake by the ENS at differing concentrations dependent on an increased production of glutamate decarboxylase from <i>gadB</i> overexpression. Our model assumes a first-order dosing type and an enzymatic elimination type. <b>Table 1</b> displays the chemical species involved in the reactions detailed in <b>Table 2.</b> Specifically, the binding reaction (which takes place in the intracellular environment of our probiotic) involves the conversion of L-glutamate into GABA via glutamate decarboxylase. This binding reaction has a special binding constant, which we accounted for in our model. The second chemical reaction we accounted for was the elimination of GABA to the extracellular environment through the membrane transport system of our probiotic. This elimination reaction also involved a binding constant that was accounted for in the model. The third chemical reaction we took into consideration was the uptake of extracellular GABA by epithelial cells in the gut. The corresponding acid dissociation constant (Ka) was accounted for in the model. All of the different enzymatic reactions and the corresponding reaction constants in our model can be seen in schematically in <b>Figure 1.</b> </p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | All of the different enzymatic reactions and the corresponding reaction constants | + | |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 32: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | [[File:Tabbble.png|thumb|center|800px|<b> | + | [[File:Tabbble.png|thumb|center|800px|<b>Table 1.</b> Table of species corresponding to the above model.]] |
<html> | <html> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | [[File:Tabble2.png|thumb|center|800px|<b> | + | [[File:Tabble2.png|thumb|center|800px|<b>Table 2.</b> Table of reaction equations corresponding to the above model.]] |
<html> | <html> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | [[File:T--Austin UTexas--Gmodel2017.png|thumb|center|800px|<b>Figure | + | [[File:T--Austin UTexas--Gmodel2017.png|thumb|center|800px|<b>Figure 1.</b> Diagram of our model including the chemical species involved (blue), type of reaction (yellow), and parameters (green).]] |
<html> | <html> | ||
Revision as of 03:51, 2 November 2017
Why Model?
Scientific models are mathematical renditions of real-world systems. In synthetic biology, models are often used to define the kinetics of biochemical systems to aid in the visualization of information, and can be used to predict the behavior or outcome of biological systems.
Our Model
The goal of our model is to simulate the expected behavior of our transformed Lactobacillus plantarum after consumption. We focused on modeling the binding reaction of glutamate decarboxylase and L-glutamate. We looked specifically at how our Lactobacillus plantarum would encode the gadB gene to produce higher levels of glutamate decarboxylase and increase the uptake of GABA by the ENS. In our model, we aimed to compare the rates of GABA uptake by the ENS at differing concentrations dependent on an increased production of glutamate decarboxylase from gadB overexpression. Our model assumes a first-order dosing type and an enzymatic elimination type. Table 1 displays the chemical species involved in the reactions detailed in Table 2. Specifically, the binding reaction (which takes place in the intracellular environment of our probiotic) involves the conversion of L-glutamate into GABA via glutamate decarboxylase. This binding reaction has a special binding constant, which we accounted for in our model. The second chemical reaction we accounted for was the elimination of GABA to the extracellular environment through the membrane transport system of our probiotic. This elimination reaction also involved a binding constant that was accounted for in the model. The third chemical reaction we took into consideration was the uptake of extracellular GABA by epithelial cells in the gut. The corresponding acid dissociation constant (Ka) was accounted for in the model. All of the different enzymatic reactions and the corresponding reaction constants in our model can be seen in schematically in Figure 1.
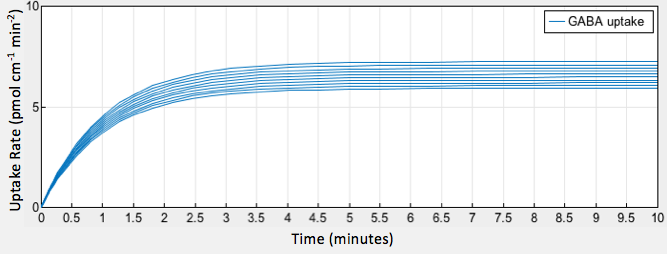
We turned to literature to acquire a better understanding of GABA uptake in the gut and to find parameters for the uptake reaction in our model. GABA produced in the gut is proposed to accumulate in glial cells throughout the ENS (1). Enteric ganglia exist in the submucosal and myenteric plexuses beneath epithelial cells lining the intestinal wall (2). GABA uptake by epithelial Caco-2 cells at pH 6.0 was recorded as 6.6 pmol.cm-2 min-1(44% uptake) (3).
Results
The simulation of our model provided a graphical output showing the increase in GABA uptake by epithelial cells as a result of increased glutamate decarboxylase activity in gut bacteria.
We compared the results of our modeling with results from literature examining other factors contributing to GABA production by Lactobacillus strains. According to a 2015 article published in Microbial Biotechnology, GABA production was shown to increase as glutamic acid concentration increased up to 520 mM in conjunction with optimal pH, 525 mM in conjunction with optimal temperature (4). The significance of the glutamate decarboxylase concentration as a factor for GABA production led us to look into a constitutive promoter that could overexpress the gadB gene.
References
- Jessen, KR. GABA and the enteric nervous system. A neurotransmitter function? Mol Cell Biochem. 38: 69-76 (1981).
- Yu Y-B, Li Y-Q. Enteric glial cells and their role in the intestinal epithelial barrier. World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG. 2014;20(32):11273-11280.
- Thwaites DT, Basterfield L, McCleave PMJ, Carter SM, Simmons NL. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transport across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cell monolayers. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2000;129(3):457-464.
- Tajabadi N, Baradaran A, Ebrahimpour A, Rahim RA, Bakar FA, et al. Overexpression and optimization of glutamic decarboxylase in Lactobacillus plantarum Taj-Apis362 for high gamma-aminobutyric acid production. Microb Biotechnol .2015.