| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <p class="text12j">The initial focus for this collection was submitting all 38 TX-TL protein genes, codon optimized, hexahistidine tagged, and under the control of a T7 promoter system for controlled expression. We have submitted and characterized 9 of these parts to the registry in pSB1C3, characterized | + | <p class="text12j">The initial focus for this collection was submitting all 38 TX-TL protein genes, codon optimized, hexahistidine tagged, and under the control of a T7 promoter system for controlled expression. We have submitted and characterized 9 of these parts to the registry in pSB1C3, characterized expression of 17 parts, and are working toward completing the remaining parts following the competition.</p> |
<p class="text12j">The tRNA component of the N<i>ex</i>t <i>vivo</i> system was another of our focuses for this years project. | <p class="text12j">The tRNA component of the N<i>ex</i>t <i>vivo</i> system was another of our focuses for this years project. | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 31 October 2017


The Next vivo system is made up of >50 unique parts encoding both protein and RNA components. The main focus of our team this year was to submit all 38 TX-TL protein components to the registry as a collection of parts that anyone could use to produce their own Next vivo system.
Several of these TX-TL components were already in the registry but were under different expression control, lacked purification tags, and/or were not codon optimized for expression in E. coli. As such we sought to improve these parts for future use.
What is in the Part Collection?
Our part collection will contain all the major biomolecules required for a cell-free transcription-translation system providing them in an easy to express and purify way that anyone can easily produce for their experimental purposes. These biomolecules include:
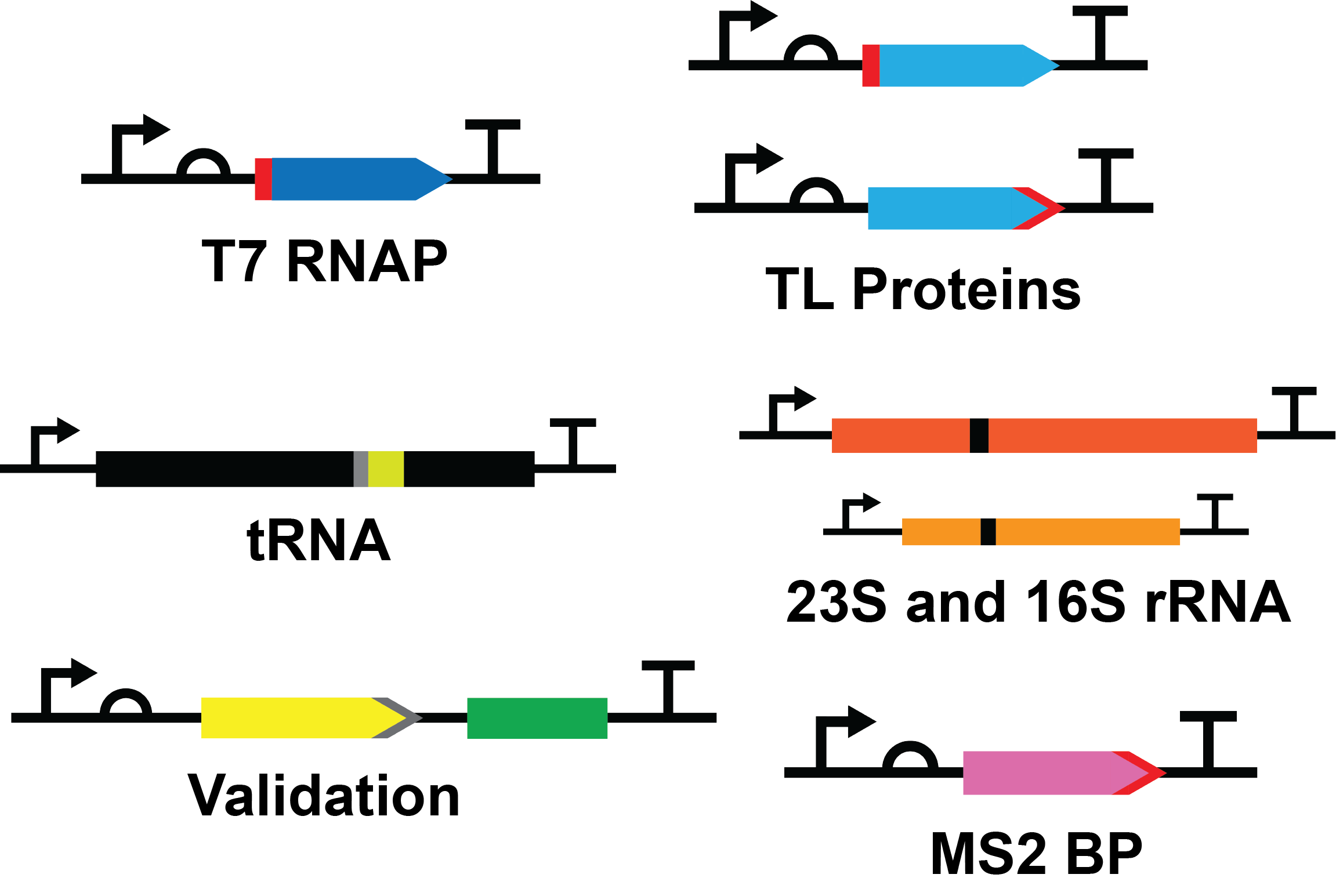
- 38 Transcription and Translation (TX-TL) protein genes codon optimized for E. coli expression
- 20 Next vivo MS2-tagged tRNA isolation genes
- 2 MS2-tagged ribosomal rRNA genes for isolation of functional ribosomes from the cell lysate
The initial focus for this collection was submitting all 38 TX-TL protein genes, codon optimized, hexahistidine tagged, and under the control of a T7 promoter system for controlled expression. We have submitted and characterized 9 of these parts to the registry in pSB1C3, characterized expression of 17 parts, and are working toward completing the remaining parts following the competition.
The tRNA component of the Next vivo system was another of our focuses for this years project. Currently no simple protocol exists for efficient and specific isolation of tRNA from the cell. We are happy to announce that we were able to develop a system that allows for the purification of specific, fully modified tRNA from cell lysate. The first tRNA in our part collection is that of tRNAPhe. With the success of our purification strategy we plan to synthesize the remaining tRNA in our expression construct for submission into this collection.
Part Design Overview

Each TX-TL gene in our collection was designed with several features in mind:
- Optimized for expression in E. coli
- N- or C-terminal hexahistidine affinity tag
- Constructs contain the T7 promoter (BBa_I719005), medium RBS (BBa_B0034), and double terminator (BBa_B0015)
Future Use for iGEM
Our hopes are that going forward, teams will be able to use our Next vivo system in the design of their projects. Whether they require a cell-free system to run constructs or just want to test constructs outside of their host organism, Next vivo can be that tool! Designing the system to be purified easily and open-source was key design feature to make this technology available to anyone who wants a cell-free system.
We envision Next vivo continually improving through the addition of new modules and features that can expand the functionalities of the system. These range from accepting non-standard amino acids, to thermostable homologs of each TX-TL protein, to proteins that aid in folding of difficult proteins.
Our Parts in the Registry
| BioBrick | Protein | Full Construct |
|---|---|---|
| BBa_K2443000 | AlaRS | pT7-mRBS-AlaRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443001 | ArgRS | pT7-mRBS-ArgRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443002 | AsnRS | pT7-mRBS-AsnRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443003 | AspRS | pT7-mRBS-AspRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443004 | CysRS | pT7-mRBS-CysRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443005 | GlnRS | pT7-mRBS-GlnRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443006 | GluRS | pT7-mRBS-GluRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443007 | GlyRS alpha subunit | pT7-mRBS-GlyRSAlpha-dT |
| BBa_K2443008 | GlyRS beta subunit | pT7-mRBS-GlyRSBeta-dT |
| BBa_K2443009 | HisRS | pT7-mRBS-HisRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443010 | IleRS | pT7-mRBS-IleRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443011 | LeuRS | pT7-mRBS-LeuRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443012 | LysRS | pT7-mRBS-LysRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443013 | MetRS | pT7-mRBS-MetRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443014 | PheRS alpha subunit | pT7-mRBS-PheRSAlpha-dT |
| BBa_K2443015 | PheRS beta subunit | pT7-mRBS-PheRSBeta-dT |
| BBa_K2443016 | ProRS | pT7-mRBS-ProRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443017 | SerRS | pT7-mRBS-SerRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443018 | ThrRS | pT7-mRBS-ThrRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443019 | TrpRS | pT7-mRBS-TrpRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443020 | TyrRS | pT7-mRBS-TyrRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443021 | ValRS | pT7-mRBS-ValRS-dT |
| BBa_K2443022 | MTF | pT7-mRBS-MTF-dT |
| BBa_K2443023 | IF1 | pT7-mRBS-IF1-dT |
| BBa_K2443024 | IF2 | pT7-mRBS-IF2-dT |
| BBa_K2443025 | IF3 | pT7-mRBS-IF3-dT |
| BBa_K2443026 | EF-G | pT7-mRBS-EFG-dT |
| BBa_K2443027 | EF-Tu | pT7-mRBS-EFTu-dT |
| BBa_K2443028 | EF-Ts | pT7-mRBS-EFTs-dT |
| BBa_K2443029 | RF1 | pT7-mRBS-RF1-dT |
| BBa_K2443030 | RF2 | pT7-mRBS-RF2-dT |
| BBa_K2443031 | RF3 | pT7-mRBS-RF3-dT |
| BBa_K2443032 | RRF | pT7-mRBS-RRF-dT |
| BBa_K2443033 | MK | pT7-mRBS-MK-dT |
| BBa_K2443034 | CK | pT7-mRBS-CK-dT |
| BBa_K2443035 | NDK | pT7-mRBS-NDK-dT |
| BBa_K2443036 | PPiase | pT7-mRBS-PPiase-dT |
| BBa_K2443037 | T7 RNA Polymerase | pT7-mRBS-T7 RNA Polymerase-dT |
| BBa_K2443038 | tRNAPhe | pT7-tRNAPhe-2xMS2 Hairpin-dT |
| BBa_K2443039 | EYFP-Spinach TX-TL Measurement Construct | pT7-mRBS-EYFP-Spinach-dT |


