|
|
| (56 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{Glasgow}} | + | {{GlasgowHeader}} |
| − | <p></p>
| + | |
| − | {{Glasgow_NavBar}}
| + | |
| − | <p></p>
| + | |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| − | <p></p>
| + | <div class="photo-block" id="Description"> |
| − | <head>
| + | <div class="text left"> |
| − | <style>
| + | <div class="title"> |
| − | | + | Project Background |
| − | </style>
| + | </div> |
| − | </head>
| + | </div> |
| − | <body>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <div class="column full_size"> | + | |
| − | <h1> Project Description </h1>
| + | |
| − | <p> Our project idea is to develop a biosensor to detect the presence of the bacteria <i>Campylobacter</i>. This sensor will utilise the rare sugar xylulose, which is found in the polysaccharide capsule of campylobacter and is released when the bacteria is run through an acidic solution. By exploiting the mannitol operon that is present in the bacteria <i>Pseudomonas fluorescens</i> and expressing this in our chassis organism, <i>Escherichia Coli</i>, we will produce a biosensor that will express the reporter molecule Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) when xylulose interacts with the repressor molecule of the mannitol operon. Additional sub-projects will include; investigating the quorum sensing mechanisms in <i>campylobacter</i> to increase the specificity of our sensor, developing hardware to produce a functioning biosensor and investigating the legal and ethical issues associated with our project.</p> | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <div class="column half_size" > | + | |
| − | <p>The mannitol operon contains a promoter, Pe, which is regulated by xylulose, sorbitol and mannitol. The operon typically regulates the expression of genes required for mannitol consumption. By hijacking this xylulose regulated promoter we hope to develop a construct capable of activating GFP in the presence of xylulose. A schematic of the construct is shown in the diagram opposite. To provide increased specificity to our biosensor, we are aiming to detect autoinducer-2, a quorum sensing molecule released by <i>campylobacter</i>. We aim to insert the LsrA promotor followed by YFP into a plasmid which turns on when autoinducer-2 is present. For our proof of concept, we need to work with xylulose. However, xylulose is rare and, as such, is expensive. Therefore, we will synthesise xylulose by utilising a metabolic step in the bacterial pentose pathway. The enzyme Xylose Isomerase can be purified from E. coli, and used to convert the inexpensive sugar xylose in to xylulose.</p>
| + | |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | <div class="wiki-block"> |
| | + | <div id="article"> |
| | + | |
| | + | </html> |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="column half_size" >
| + | ==Context== |
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2017/5/56/Glasgow_iGEM_2017_MannitolOperon.png"> | + | <i>Campylobacter jejuni</i> is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, corkscrew-shaped bacteria which has been implicated as being one of the most common causes of human gastroenteritis worldwide. WHO estimates that 1 in 10 people around the world fall ill with a <i>Campylobacter</i> infection annually.<ref name= "WHO">http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs255/en/</ref> Infection with this bacteria in the UK was recently estimated to cost health services £50 million (in 2008-2009 prices), with a cost of £85 per case.<ref>Tam CC, O’Brien SJ (2016) Economic Cost of Campylobacter, Norovirus and Rotavirus Disease in the United Kingdom. PLoS ONE11(2): e0138526. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138526</ref> |
| − | </div> | + | |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="column full_size" > | + | Infection with <i>Campylobacter</i> causes common symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain, fever, headache, nausea and vomiting. <ref name= "WHO"/> |
| − | <p>For the engineering part of the project, we are aiming to build a functional biosensor that will be able to prove our construct. We will use technologies such as microfluidics and ultrafiltration to produce a sensor that will use our modified E.coli to give a visual indication of the presence of campylobacter. In terms of human practices, we will be adopting a double approach; one that focuses on the legal and political issues concerning EU legislation, which will affect our ability to manufacture a biosensor outside a properly licensed laboratory; and one on ethical issues concerning the impact that food safety has on human health. This second approach will mainly aim to raise awareness among the public on preventative measures in order to avoid campylobacter poisoning.</p> | + | <i>C. jejuni</i> grows optimally between 37 and 42°C and is most commonly found on undercooked poultry, though it has been reported in other undercooked meat and meat products, raw milk, and in untreated drinking water <ref name= "WHO"/>. The high prevalence of <i>C. jejuni</i> makes it an interesting target for synthetic biology-based solutions. |
| − | </div> | + | |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="column full_size">
| + | ===Treatment and Prevention=== |
| − | <p></p>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | <p>Tell us about your project, describe what moves you and why this is something important for your team.</p> | + | Treatment for Campylobacteriosis (<i>Campylobacter</i>-caused diarrhoeal disease) is generally only given in the most severe cases or when patients are vulnerable, and usually consists of giving more fluids and glucose-electrolyte solutions to ensure dehydration does not occur. <ref name="eMedicineTreatment"> https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213720-treatment </ref> Erythromycin therapy can also be given but little clinical benefit is seen if the treatment is begun after four days of symptom onset. <ref>https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/176400-overview</ref> However, the use of antibiotics can be recommended in the case of patients who are immunocompromised, pregnant, or with very severe symptoms.<ref name="eMedicineTreatment"/> |
| | | | |
| | + | Prevention of this infection is very easy, with several strategies from the farm to the consumer recommended by WHO: <ref name ="WHO"/> |
| | + | *Enhanced biosecurity to avoid transmission of <i>Campylobacter</i> from the environment to the flock of birds – only in closed housing conditions |
| | + | *Good hygienic slaughtering practices carried out |
| | + | *Prevention methods in domestic kitchens are similar to those specified for other foodborne bacterial infections – ensure meat is cooked through and that milk has been pasteurized before consumption |
| | | | |
| − | <h5>What should this page contain?</h5>
| + | ==Current Detection Methods== |
| − | <ul>
| + | |
| − | <li> A clear and concise description of your project.</li>
| + | |
| − | <li>A detailed explanation of why your team chose to work on this particular project.</li>
| + | |
| − | <li>References and sources to document your research.</li>
| + | |
| − | <li>Use illustrations and other visual resources to explain your project.</li>
| + | |
| − | </ul>
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | ====Culture-based screening==== |
| | | | |
| − | </div>
| |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="column full_size" > | + | Traditional methods for detection of <i>Campylobacter</i> include culturing a swabbed sample on selective media and incubating for 48 hours at 42°C under microaerobic conditions. |
| | | | |
| − | <h5>Advice on writing your Project Description</h5> | + | [[File:GlasgowCJejuniCulture.jpeg|thumb|center|500px|<b>Figure 1:</b> Campylobacter jejuni colonies isolated on blood-free, charcoal based selective medium (CSM)<ref>https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Campylobacter_jejuni.jpg</ref>]] |
| | | | |
| − | <p>
| + | After isolating the bacteria in this way, identification through looking at the morphology and overall characteristics of the bacteria is carried out. Culture-based methods are relatively cheap to carry out and require less training than others techniques, but are incredibly time and labour intensive and therefore, in recent years, a move has been made towards use of rapid detection testing. <ref>http://www.rapidmicrobiology.com/test-method/campylobacter-detection-and-identification-methods/</ref> |
| − | We encourage you to put up a lot of information and content on your wiki, but we also encourage you to include summaries as much as possible. If you think of the sections in your project description as the sections in a publication, you should try to be consist, accurate and unambiguous in your achievements.
| + | |
| − | </p> | + | |
| | | | |
| − | <p>
| + | ==== Rapid detection==== |
| − | Judges like to read your wiki and know exactly what you have achieved. This is how you should think about these sections; from the point of view of the judge evaluating you at the end of the year.
| + | More recently, techniques such as enzyme immunoassay and lateral flow systems have been utilised to test for Campylobacter, as they require only between one and two hours until a result is given. |
| − | </p> | + | <ref>Giltner CL, Saeki S, Bobenchik AM, Humphries RM. Rapid Detection of Campylobacter Antigen by Enzyme Immunoassay Leads to Increased Positivity Rates. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2013;51(2):618-620. doi:10.1128/JCM.02565-12.</ref> However, use of these methods required much more highly trained employees to carry them out, and so therefore detection of Campylobacter in an industrial or agricultural setting would most likely have to be outsourced to a company specialising in these services. |
| | + | A particular study doing a comparison into three rapid detection systems showed a high number of false negative results, which can be considered an additional drawback when looking at detection of C. jejuni in order to reduce the incidence of disease outbreaks. |
| | + | <ref>Granato PA, Chen L, Holiday I, et al. Comparison of Premier CAMPY Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA), ProSpecT Campylobacter EIA, and ImmunoCard STAT! CAMPY Tests with Culture for Laboratory Diagnosis of Campylobacter Enteric Infections . Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2010;48(11):4022-4027. doi:10.1128/JCM.00486-10.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | </div> | + | ==Our device - <i>Campy</i>LOCATOR== |
| | | | |
| | + | In an attempt to reduce incidences of food poisoning by <i>Campylobacter jejuni</i>, and to improve upon current methods of detection, we decided to create a biosensor that was able to detect the presence of <i>Campylobacter jejuni</i> quickly and accurately. To do this we aimed to create a two part biosensor that will detect two sensory inputs. The first, xylulose, is a rare sugar most commonly associated with the pentose-phosphate pathway, where formation of xylulose-5-phosphate is an important intermediate step. Interestingly, xylulose was found incorporated into the polysaccharide capsule of Campylobacter jejuni strain RM1221 <ref>Gilbert, M., Mandrell, R., Parker, C., Li, J., and Vinogradov, E. (2017). Structural Analysis of the Capsular Polysaccharide from Campylobacter jejuni RM1221</ref>. The presence of xylulose is not common in bacterial polysaccharide capsules, and additionally the glyosidic bonds which incorporate xylulose were found to be extremely acid-labile. A large focus of the project was aimed at xylulose. The other molecule we identified as a marker for Campylobacter was autoinducer-2 (AI-2). AI-2 is a secreted quorum sensing molecule. AI-2 is a significantly less specific biomarker, as many varied gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial species sense their population density and surrounding bacterial environment using this molecule <ref>Miller, M. and Bassler, B. (2001). Quorum Sensing in Bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 55(1), pp.165-199.</ref> On the other hand, this ubiquity meant that AI-2 gene regulation was well characterised, with prior iGEM teams having worked on the natural E. coli AI-2 quorum sensing regulatory system. |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="column half_size" > | + | For the detection of xylulose two possible avenues were explored: utilising the [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/mtlR mannitol regulatory system] from <i>Pseudomonas fluorescens</i>, which is known to detect xylulose but may have some off-target effects; and [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/araC mutagenesis of the arabinose regulatory system] from <i>Escherichia coli</i>, with an aim to change its target sugar to xylulose. The detectors for both xylulose and [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/QuorumSensing autoinducer-2] will form the two components of an [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/ANDGate AND gate] that will ensure only a signal is seen when both xylulose and autoinducer-2 are present. |
| | | | |
| − | <h5>References</h5>
| + | Regarding the application of our biosensor we went through [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/Applied_Design several design iterations] to create [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/Hardware a device] that would house the biosensor to make the application simple and easy. In addition to this we also looked at [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/XyluloseBiosynthesis producing xylulose in a cheap and efficient way] as the cost of xylulose held us back with regards to thorough testing of the biosensor elements. All of the above were done with thought of the implications with regards to [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/HP/Gold_Integrated human practices] and how a genetically engineered biosensor would be received by [https://2017.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/Outreach the public.] |
| − | <p>iGEM teams are encouraged to record references you use during the course of your research. They should be posted somewhere on your wiki so that judges and other visitors can see how you thought about your project and what works inspired you.</p>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | </div>
| + | ==References== |
| − | | + | <small><references/></small> |
| − | | + | <html></div> |
| − | <div class="column half_size" >
| + | </div></html> |
| − | <h5>Inspiration</h5>
| + | {{GlasgowFooter}} |
| − | <p>See how other teams have described and presented their projects: </p>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <ul>
| + | |
| − | <li><a href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College/Description">2016 Imperial College</a></li>
| + | |
| − | <li><a href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Wageningen_UR/Description">2016 Wageningen UR</a></li>
| + | |
| − | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Project_Overview"> 2014 UC Davis</a></li> | + | |
| − | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:SYSU-Software/Overview">2014 SYSU Software</a></li> | + | |
| − | </ul>
| + | |
| − | </div> | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | </html> | + | |
Context
Campylobacter jejuni is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, corkscrew-shaped bacteria which has been implicated as being one of the most common causes of human gastroenteritis worldwide. WHO estimates that 1 in 10 people around the world fall ill with a Campylobacter infection annually.[1] Infection with this bacteria in the UK was recently estimated to cost health services £50 million (in 2008-2009 prices), with a cost of £85 per case.[2]
Infection with Campylobacter causes common symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain, fever, headache, nausea and vomiting. [1]
C. jejuni grows optimally between 37 and 42°C and is most commonly found on undercooked poultry, though it has been reported in other undercooked meat and meat products, raw milk, and in untreated drinking water [1]. The high prevalence of C. jejuni makes it an interesting target for synthetic biology-based solutions.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment for Campylobacteriosis (Campylobacter-caused diarrhoeal disease) is generally only given in the most severe cases or when patients are vulnerable, and usually consists of giving more fluids and glucose-electrolyte solutions to ensure dehydration does not occur. [3] Erythromycin therapy can also be given but little clinical benefit is seen if the treatment is begun after four days of symptom onset. [4] However, the use of antibiotics can be recommended in the case of patients who are immunocompromised, pregnant, or with very severe symptoms.[3]
Prevention of this infection is very easy, with several strategies from the farm to the consumer recommended by WHO: [1]
- Enhanced biosecurity to avoid transmission of Campylobacter from the environment to the flock of birds – only in closed housing conditions
- Good hygienic slaughtering practices carried out
- Prevention methods in domestic kitchens are similar to those specified for other foodborne bacterial infections – ensure meat is cooked through and that milk has been pasteurized before consumption
Current Detection Methods
Culture-based screening
Traditional methods for detection of Campylobacter include culturing a swabbed sample on selective media and incubating for 48 hours at 42°C under microaerobic conditions.
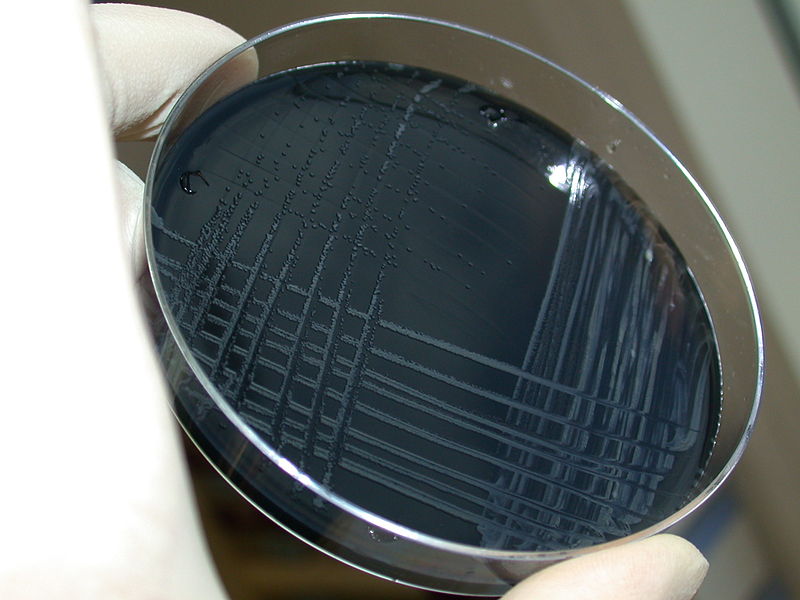
Figure 1: Campylobacter jejuni colonies isolated on blood-free, charcoal based selective medium (CSM)
[5] After isolating the bacteria in this way, identification through looking at the morphology and overall characteristics of the bacteria is carried out. Culture-based methods are relatively cheap to carry out and require less training than others techniques, but are incredibly time and labour intensive and therefore, in recent years, a move has been made towards use of rapid detection testing. [6]
Rapid detection
More recently, techniques such as enzyme immunoassay and lateral flow systems have been utilised to test for Campylobacter, as they require only between one and two hours until a result is given.
[7] However, use of these methods required much more highly trained employees to carry them out, and so therefore detection of Campylobacter in an industrial or agricultural setting would most likely have to be outsourced to a company specialising in these services.
A particular study doing a comparison into three rapid detection systems showed a high number of false negative results, which can be considered an additional drawback when looking at detection of C. jejuni in order to reduce the incidence of disease outbreaks.
[8]
Our device - CampyLOCATOR
In an attempt to reduce incidences of food poisoning by Campylobacter jejuni, and to improve upon current methods of detection, we decided to create a biosensor that was able to detect the presence of Campylobacter jejuni quickly and accurately. To do this we aimed to create a two part biosensor that will detect two sensory inputs. The first, xylulose, is a rare sugar most commonly associated with the pentose-phosphate pathway, where formation of xylulose-5-phosphate is an important intermediate step. Interestingly, xylulose was found incorporated into the polysaccharide capsule of Campylobacter jejuni strain RM1221 [9]. The presence of xylulose is not common in bacterial polysaccharide capsules, and additionally the glyosidic bonds which incorporate xylulose were found to be extremely acid-labile. A large focus of the project was aimed at xylulose. The other molecule we identified as a marker for Campylobacter was autoinducer-2 (AI-2). AI-2 is a secreted quorum sensing molecule. AI-2 is a significantly less specific biomarker, as many varied gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial species sense their population density and surrounding bacterial environment using this molecule [10] On the other hand, this ubiquity meant that AI-2 gene regulation was well characterised, with prior iGEM teams having worked on the natural E. coli AI-2 quorum sensing regulatory system.
For the detection of xylulose two possible avenues were explored: utilising the mannitol regulatory system from Pseudomonas fluorescens, which is known to detect xylulose but may have some off-target effects; and mutagenesis of the arabinose regulatory system from Escherichia coli, with an aim to change its target sugar to xylulose. The detectors for both xylulose and autoinducer-2 will form the two components of an AND gate that will ensure only a signal is seen when both xylulose and autoinducer-2 are present.
Regarding the application of our biosensor we went through several design iterations to create a device that would house the biosensor to make the application simple and easy. In addition to this we also looked at producing xylulose in a cheap and efficient way as the cost of xylulose held us back with regards to thorough testing of the biosensor elements. All of the above were done with thought of the implications with regards to human practices and how a genetically engineered biosensor would be received by the public.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs255/en/
- ↑ Tam CC, O’Brien SJ (2016) Economic Cost of Campylobacter, Norovirus and Rotavirus Disease in the United Kingdom. PLoS ONE11(2): e0138526. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138526
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213720-treatment
- ↑ https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/176400-overview
- ↑ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Campylobacter_jejuni.jpg
- ↑ http://www.rapidmicrobiology.com/test-method/campylobacter-detection-and-identification-methods/
- ↑ Giltner CL, Saeki S, Bobenchik AM, Humphries RM. Rapid Detection of Campylobacter Antigen by Enzyme Immunoassay Leads to Increased Positivity Rates. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2013;51(2):618-620. doi:10.1128/JCM.02565-12.
- ↑ Granato PA, Chen L, Holiday I, et al. Comparison of Premier CAMPY Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA), ProSpecT Campylobacter EIA, and ImmunoCard STAT! CAMPY Tests with Culture for Laboratory Diagnosis of Campylobacter Enteric Infections . Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2010;48(11):4022-4027. doi:10.1128/JCM.00486-10.
- ↑ Gilbert, M., Mandrell, R., Parker, C., Li, J., and Vinogradov, E. (2017). Structural Analysis of the Capsular Polysaccharide from Campylobacter jejuni RM1221
- ↑ Miller, M. and Bassler, B. (2001). Quorum Sensing in Bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 55(1), pp.165-199.



