Contents
Overview
During the time working on CampyLOCATOR, we carried out many individual sub-projects which, combined, form our biosensing device. Due to time limitations we were unable to get as far as combining them - however, we did showcase working parts of our project on this wiki which could be improved upon with more time. This page contains short descriptions of the work we did demonstrating the functionality of our sub-projects, with links to the pages with longer descriptions if these are of interest.
Mannitol Operon
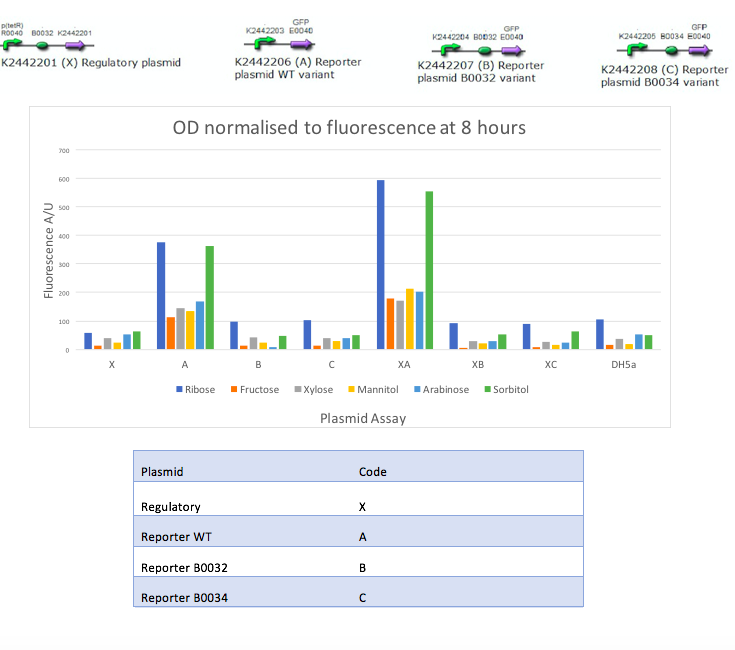
In the mannitol operon sub-project, we aimed to test an inducible promoter system (mtlR-mtlE) taken from the mannitol operon of Pseudomonas fluorescens. We tested the induction of the linked promoter (PmtlE) with various sugars in order to replicate results from Liu et al (2015).[1] We produced the following graph:
The results obtained from our tests do not reflect the findings of Liu et al [2]. We got positive results for the working of the regulatory protein, mtlR and its regulated promoter, PmtlE in E. coli in response to ribose and sorbitol. Whilst Liu et al demonstrated a strong response to sorbitol and mannitol, our constructs showed ribose and sorbitol evoke the largest fluorescence response across all plasmids. A potential reason our results do not reflect those of Liu et al is the use of different organisms. Our findings could show that E. coli exhibits a different response to ribose and mannitol than Pseudomonas fluorescens. E. coli may not utilize these sugars in induction of this system and therefore downstream genes are not turned on as they are in Pseudomonas.
Further detail on this sub-project can be found on the mannitol operon page of our wiki.
Mutagenesis of the L-Arabinose Operon
Another sub-project we worked on was mutagenesis of the L-arabinose operon as an alternative route to biosense our target sugar, xylulose. In this sub-project we constructed new BioBricks, splitting pBAD and AraC into two seperate BioBricks instead of being combined in the case of BBa_I0500. We showed that these BioBricks were functional in seperate plasmids, and additionally showed successful mutagenesis of the AraC protein in order to alter its characteristics. Future iGEM teams working with the detection of small molecules will be able to work with these tools to create new biosensors.
Further detail on this sub-project can be found on the Arabinose Operon Mutagenesis page of our wiki.